Cell Biology Workshop I
... 5. Many proteins contain strong binding sites for calcium ions. a. What is the expected charge state for calcium ions in aqueous solution? +2 b. Design a hypothetical protein binding site for calcium ions, using appropriate amino acids. (Remember, what is the general pattern in the primary structure ...
... 5. Many proteins contain strong binding sites for calcium ions. a. What is the expected charge state for calcium ions in aqueous solution? +2 b. Design a hypothetical protein binding site for calcium ions, using appropriate amino acids. (Remember, what is the general pattern in the primary structure ...
biol-1406_ch3notes.ppt
... • Each carbon can form up to ______ bonds (single(2 electrons), double, or triple) and rings • Carbon makes bonds mostly with ________ ________________ in living systems • Biomolecules are large and contain _______ _____________ attached to the carbon backbone. • Functional groups in organic molecul ...
... • Each carbon can form up to ______ bonds (single(2 electrons), double, or triple) and rings • Carbon makes bonds mostly with ________ ________________ in living systems • Biomolecules are large and contain _______ _____________ attached to the carbon backbone. • Functional groups in organic molecul ...
biol-1406_ch3notes.pdf
... 3.1. Why Is Carbon So Important in Biological Molecules? • Each carbon can form up to ______ bonds (single(2 electrons), double, or triple) and rings • Carbon makes bonds mostly with ________ ________________ in living systems • Biomolecules are large and contain _______ _____________ attached to th ...
... 3.1. Why Is Carbon So Important in Biological Molecules? • Each carbon can form up to ______ bonds (single(2 electrons), double, or triple) and rings • Carbon makes bonds mostly with ________ ________________ in living systems • Biomolecules are large and contain _______ _____________ attached to th ...
Secondary Metabolites and Building Blocks
... May be more prevalent or unique to certain genus, species, and similar compounds occur within genuses and families Often have vital functions in the source • attractants for propagation of species • defense against predators • signaling May have useful nutritional benefits to humans/other organisms ...
... May be more prevalent or unique to certain genus, species, and similar compounds occur within genuses and families Often have vital functions in the source • attractants for propagation of species • defense against predators • signaling May have useful nutritional benefits to humans/other organisms ...
Protein mteabolism
... well-being and happiness. Approximately 90% of the human body's total serotonin is located in the intestine, where it is used to regulate intestinal movements. The remainder is synthesized in neurons of the CNS, where it has various functions. These include the regulation of mood, appetite, and slee ...
... well-being and happiness. Approximately 90% of the human body's total serotonin is located in the intestine, where it is used to regulate intestinal movements. The remainder is synthesized in neurons of the CNS, where it has various functions. These include the regulation of mood, appetite, and slee ...
MACROMOLECULE WEBQUEST
... What is the ratio of Carbon to Hydrogen to Oxygen? ________ Carbohydrates comprise what percentage of our body cells? ________ List 4 monosaccharide ...
... What is the ratio of Carbon to Hydrogen to Oxygen? ________ Carbohydrates comprise what percentage of our body cells? ________ List 4 monosaccharide ...
Remember: Condensation makes bonds: Hydrolysis breaks bonds.
... a. State what happens to the structure of monosaccharides when they are placed in water. b. Draw the simplified (ring) structures of glucose and ribose. Number the carbon atoms correctly. Condensation of monosaccharides is a polymerization reaction. It can continue to create a longer chain of saccha ...
... a. State what happens to the structure of monosaccharides when they are placed in water. b. Draw the simplified (ring) structures of glucose and ribose. Number the carbon atoms correctly. Condensation of monosaccharides is a polymerization reaction. It can continue to create a longer chain of saccha ...
河北交通职业技术学院教案 Lesion 5 Alcoholic Beverages (1) 课题引
... transport systems exist in yeast. Proline permease is repressed by other amino acids 至少其他 11 种特定氨基酸转运系统存在于酵母中。 脯氨酸透性酶被其他氨基酸和氨抑制了活性。 ...
... transport systems exist in yeast. Proline permease is repressed by other amino acids 至少其他 11 种特定氨基酸转运系统存在于酵母中。 脯氨酸透性酶被其他氨基酸和氨抑制了活性。 ...
2.3: Carbon-Based Molecules
... Rate of Chemical Reactions • Biochemical reactions must occur at certain speeds, or rates, in order to be useful. • Rate of a reaction depends on: – Temperature – Concentration of the chemicals – Surface area ...
... Rate of Chemical Reactions • Biochemical reactions must occur at certain speeds, or rates, in order to be useful. • Rate of a reaction depends on: – Temperature – Concentration of the chemicals – Surface area ...
Protein
... Phospholipids have both polar and nonpolar sections. As a result, they are able to dissolve in both type of solvents as well. They are important for living things because they form the borders of all cells (cell membranes) and also participate in forming many cell organelles. ...
... Phospholipids have both polar and nonpolar sections. As a result, they are able to dissolve in both type of solvents as well. They are important for living things because they form the borders of all cells (cell membranes) and also participate in forming many cell organelles. ...
Building Proteins - Marblehead High School
... 1) mRNA leaves the nucleus and travels to the ribosome 2) mRNA attaches to the ribosome at the start codon 3) tRNA attaches the correct amino acid to the growing polypeptide (ex: mRNA reads AUG methionine is added) ...
... 1) mRNA leaves the nucleus and travels to the ribosome 2) mRNA attaches to the ribosome at the start codon 3) tRNA attaches the correct amino acid to the growing polypeptide (ex: mRNA reads AUG methionine is added) ...
Biology Study Guide 10 p
... E. organelles that position tRNA and mRNA to make proteins _____rRNA F. triplet loop of bases on tRNA _____codon G. triplet of bases on mRNA _____anti-codon H. non-coding regions of RNA that are removed _____RNA polymerase I. coding regions of RNA that are expressed and leave nucleus _____ribosomes ...
... E. organelles that position tRNA and mRNA to make proteins _____rRNA F. triplet loop of bases on tRNA _____codon G. triplet of bases on mRNA _____anti-codon H. non-coding regions of RNA that are removed _____RNA polymerase I. coding regions of RNA that are expressed and leave nucleus _____ribosomes ...
Chapter 2 SWBATS Content Standards Cell Biology 1. The
... What are the two main types of chemical bonds? Give an example of each. Why are water molecules polar? What are acidic solutions? What are basic solutions? Give an example of each. What are the functions of each group of organic compounds? What happens to chemical bonds during chemical reactions? Ho ...
... What are the two main types of chemical bonds? Give an example of each. Why are water molecules polar? What are acidic solutions? What are basic solutions? Give an example of each. What are the functions of each group of organic compounds? What happens to chemical bonds during chemical reactions? Ho ...
Jan. 28
... – Rapid initial formation of HCN & aldehydes – This was followed by a decrease of these products as amino acids were slowly formed – Hypothesized that amino acids were being formed via a previously known method, the Strecker synthesis ...
... – Rapid initial formation of HCN & aldehydes – This was followed by a decrease of these products as amino acids were slowly formed – Hypothesized that amino acids were being formed via a previously known method, the Strecker synthesis ...
MACROMOLECULE WEBQUEST
... Site Location: http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP13204 1. Lipids are ___________________molecules that are insoluble in water. 2. What are fatty acid chains? ...
... Site Location: http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP13204 1. Lipids are ___________________molecules that are insoluble in water. 2. What are fatty acid chains? ...
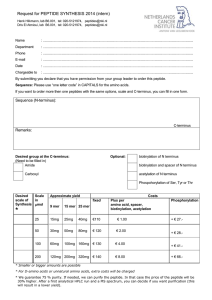
Scale - Netherlands Cancer Institute
... Henk Hilkmann, lab B6.001, tel: 020-5121974, [email protected] Dris El Atmioui, lab B6.001, tel: 020-5121974, [email protected] ...
... Henk Hilkmann, lab B6.001, tel: 020-5121974, [email protected] Dris El Atmioui, lab B6.001, tel: 020-5121974, [email protected] ...
Document
... 1. How is gene expression regulated? 2. How do induction and repression work to regulate microbial metabolism 3. Describe positive and negative control in transcription level of regulation 4. How does lac operon work to regulate lactose metabolism 5. Give an example of attenuation 6. Describe the di ...
... 1. How is gene expression regulated? 2. How do induction and repression work to regulate microbial metabolism 3. Describe positive and negative control in transcription level of regulation 4. How does lac operon work to regulate lactose metabolism 5. Give an example of attenuation 6. Describe the di ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.