Chapter 2: The Chemical Level of Organization
... – damages cells and tissues, alters proteins – interferes with normal functions ...
... – damages cells and tissues, alters proteins – interferes with normal functions ...
Biotechnology Unit 3: DNA to Proteins Essential Cell Biology
... 2. An α-helix is caused by a single polypeptide chain __________________ around itself to form a __________________ a. A hydrogen bond forms between every __________________ amino acid whit the C=O of one bonding to the N-H of the other b. The __________________ makes a complete turn every 3.6 amino ...
... 2. An α-helix is caused by a single polypeptide chain __________________ around itself to form a __________________ a. A hydrogen bond forms between every __________________ amino acid whit the C=O of one bonding to the N-H of the other b. The __________________ makes a complete turn every 3.6 amino ...
MC 2
... and the two hydrogen atoms with slight positive charges. The charge distribution is significant enough that a collection of water molecules is held together by strong hydrogen bonds, which are intermolecular forces between the hydrogen atom of one molecule and the oxygen atom of another molecule. Th ...
... and the two hydrogen atoms with slight positive charges. The charge distribution is significant enough that a collection of water molecules is held together by strong hydrogen bonds, which are intermolecular forces between the hydrogen atom of one molecule and the oxygen atom of another molecule. Th ...
Regulation on Cellular respiration
... • These links permit the respiration of excess fats and proteins in the diet. • No special mechanism of cellular respiration is needed by those animals that depend largely on ingested fats (e.g., many birds) or proteins (e.g., carnivores) for their energy supply. • Many of the points that connect ...
... • These links permit the respiration of excess fats and proteins in the diet. • No special mechanism of cellular respiration is needed by those animals that depend largely on ingested fats (e.g., many birds) or proteins (e.g., carnivores) for their energy supply. • Many of the points that connect ...
Biological Molecules
... Lipids are a group of compounds that include fats, oils and waxes. They all contain the elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Importantly, they do not mix with water. There are 2 main types – Triglycerides and Phospholipids. ...
... Lipids are a group of compounds that include fats, oils and waxes. They all contain the elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Importantly, they do not mix with water. There are 2 main types – Triglycerides and Phospholipids. ...
What are enzymes and how do they work
... 6. Label the 5' and 3' sides of the anticodons. 7. a. How many nucleotides are there in a codon? __________ in an anticodon? __________ b. Which molecule contains codons? ___________ Which contains anticodons? __________ c. What type of bond holds the tRNA in the ribosome? ________________ d. How ma ...
... 6. Label the 5' and 3' sides of the anticodons. 7. a. How many nucleotides are there in a codon? __________ in an anticodon? __________ b. Which molecule contains codons? ___________ Which contains anticodons? __________ c. What type of bond holds the tRNA in the ribosome? ________________ d. How ma ...
Molecular Structure & Function of Genetic Material
... • Amino acids. How many are there? • 20 total. Of these 11 are naturally occuring, the other 9 must be consumed through food, those are known as “essential amino acids” (in kids 10 are essential, 1 loses this status once we produce it) • How do we get these essential amino acids? ...
... • Amino acids. How many are there? • 20 total. Of these 11 are naturally occuring, the other 9 must be consumed through food, those are known as “essential amino acids” (in kids 10 are essential, 1 loses this status once we produce it) • How do we get these essential amino acids? ...
7.1 DNA Structure
... DNA Structure • How are the two strands of nucleotides connected? • Two strands arrange themselves so that the Nbases are in the center • N-bases complementary bond with each other using hydrogen bonds ▫ Cytosine – Guanine (C-G) ▫ Adenine – Thymine (A-T) ...
... DNA Structure • How are the two strands of nucleotides connected? • Two strands arrange themselves so that the Nbases are in the center • N-bases complementary bond with each other using hydrogen bonds ▫ Cytosine – Guanine (C-G) ▫ Adenine – Thymine (A-T) ...
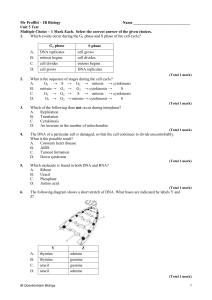
Mr Proffitt – IB Biology Name Unit 3 Test Multiple Choice – 1 Mark
... anaphase produces an intracellular phosphorylation gradient”. Nature. Vol 453.] ...
... anaphase produces an intracellular phosphorylation gradient”. Nature. Vol 453.] ...
RESEARCH NOTES
... o many-fold increase (e.g.. phenyloloninc increases from l-2 pMJg +o 100 PM/g). However, with the exception of orginine, os soon os sucrose is odded to the incubation medium or the exogenous omiiio acid is removed, the pool concentration drops. By careful selection of the amino acids (i.e., members ...
... o many-fold increase (e.g.. phenyloloninc increases from l-2 pMJg +o 100 PM/g). However, with the exception of orginine, os soon os sucrose is odded to the incubation medium or the exogenous omiiio acid is removed, the pool concentration drops. By careful selection of the amino acids (i.e., members ...
Basics of Molecular Biology
... range from fewer than 20 to more than 5000 amino acids in length, although an average protein is about 350 amino acids in length. Each protein that an organism can produce is encoded in a piece of the DNA called a “gene” (see Section 1.6). To give an idea of the variety of proteins one organism can ...
... range from fewer than 20 to more than 5000 amino acids in length, although an average protein is about 350 amino acids in length. Each protein that an organism can produce is encoded in a piece of the DNA called a “gene” (see Section 1.6). To give an idea of the variety of proteins one organism can ...
Unit One “Science Introduction & Cellular Function”
... parts • An OH and H group are added to opposite sides of a subunit , therefore causing the polymer to be broken into its monomer parts ...
... parts • An OH and H group are added to opposite sides of a subunit , therefore causing the polymer to be broken into its monomer parts ...
DOC
... The following fragment of a DNA strand was used in RNA transcription to produce a peptide chain. Show both the mRNA chain and the resulting peptide chain using the chart attached at the end of this test. ( 3pts.) ...
... The following fragment of a DNA strand was used in RNA transcription to produce a peptide chain. Show both the mRNA chain and the resulting peptide chain using the chart attached at the end of this test. ( 3pts.) ...
Macromolecules
... be categorized by chemical properties • Hydrophobic – hate water • hydrophilic - love water • Ionic ...
... be categorized by chemical properties • Hydrophobic – hate water • hydrophilic - love water • Ionic ...
amino acid
... Because of their uniform structure, any amino acid can bond These atoms create a _water_______ molecule, which is a product of the reaction. to any other amino acid using a covalent bond called a peptide bond. THINK ABOUT IT: What process will link together two individual amino acids? _dehydration s ...
... Because of their uniform structure, any amino acid can bond These atoms create a _water_______ molecule, which is a product of the reaction. to any other amino acid using a covalent bond called a peptide bond. THINK ABOUT IT: What process will link together two individual amino acids? _dehydration s ...
Organic Molecules Worksheet: Review
... meaning they all contain carbon. They are formed from just a few elements which join together to form small molecules which join together, or bond, to form large molecules. The third characteristic of all organic molecules is that each is kind of organic molecule is built from a single type of build ...
... meaning they all contain carbon. They are formed from just a few elements which join together to form small molecules which join together, or bond, to form large molecules. The third characteristic of all organic molecules is that each is kind of organic molecule is built from a single type of build ...
here
... A physical quantity, entropy-S, is often employed to quantify the degree of disordering for a thermodynamic system. Let be the number of allowed states of N particles in the system. S can be then given by S k B ln where kB is the Boltzmann constant. If a polypeptide consists of 4 amino acids, ...
... A physical quantity, entropy-S, is often employed to quantify the degree of disordering for a thermodynamic system. Let be the number of allowed states of N particles in the system. S can be then given by S k B ln where kB is the Boltzmann constant. If a polypeptide consists of 4 amino acids, ...
Биологическая химия
... NH2- group has a basic character, it can bind hydrogen proton and become positively charged. In AA molecule proton from the carboxyl group may be transferred to amino group – forming the so called zwitter-ion. In solutions the amino acids are in the form of zwitter-ions. ...
... NH2- group has a basic character, it can bind hydrogen proton and become positively charged. In AA molecule proton from the carboxyl group may be transferred to amino group – forming the so called zwitter-ion. In solutions the amino acids are in the form of zwitter-ions. ...
Paper - IndiaStudyChannel.com
... (A) stimulates the activity of acetyl CoA carboxylase (B) is important for fatty acid oxidation (C) inhibits the formation of triacylglycerol (D) none of these 29. In the major pathway by which liver produces ketone bodies, the immediate precursor of acetoacetate is : (A) acetoacetyl CoA (B) -hydro ...
... (A) stimulates the activity of acetyl CoA carboxylase (B) is important for fatty acid oxidation (C) inhibits the formation of triacylglycerol (D) none of these 29. In the major pathway by which liver produces ketone bodies, the immediate precursor of acetoacetate is : (A) acetoacetyl CoA (B) -hydro ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.