Food Biotechnology Dr. Tarek Elbashiti 7. Metabolic Engineering of
... • Ikeda and Katsumata engineered a tryptophanproducing mutant of C. glutamicum to produce L-tyrosine or L-phenylalanine in abundance (26 and 28 g/L, respectively) by overexpressing the branch-point enzymes (chorismate mutase and prephenate dehydratase), catalyzing the conversion of the common interm ...
... • Ikeda and Katsumata engineered a tryptophanproducing mutant of C. glutamicum to produce L-tyrosine or L-phenylalanine in abundance (26 and 28 g/L, respectively) by overexpressing the branch-point enzymes (chorismate mutase and prephenate dehydratase), catalyzing the conversion of the common interm ...
Test 1 Notecards
... Response to Stimulus, Genetic Material, Homeostasis, cells, growth and development pH: acids = 0-6, neutral = 7, base = 8-14; buffer helps to maintain homeostasis Organic compounds: contain carbon; include lipids, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and proteins. Lipids: made of glycerol and fatty acids; ...
... Response to Stimulus, Genetic Material, Homeostasis, cells, growth and development pH: acids = 0-6, neutral = 7, base = 8-14; buffer helps to maintain homeostasis Organic compounds: contain carbon; include lipids, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and proteins. Lipids: made of glycerol and fatty acids; ...
A1 B1 C1 D1 A2 B2 C2 D2 A1 B1 C1 A2 B2 C2
... Using the amino acid sequence created by the previous activity, students will create a protein with Duplo or Lego blocks. Teacher notes: Duplo blocks work best for this activity, but Legos will also work. The model that results from this activity is very simplistic, but shows the three-dimensional s ...
... Using the amino acid sequence created by the previous activity, students will create a protein with Duplo or Lego blocks. Teacher notes: Duplo blocks work best for this activity, but Legos will also work. The model that results from this activity is very simplistic, but shows the three-dimensional s ...
PASS MOCK EXAM
... A) Nonsense mutation; will. B) Missense mutation; will not. C) Nonsense mutation; will. D) Missense mutation; will not. E) Silent mutation; will not. ...
... A) Nonsense mutation; will. B) Missense mutation; will not. C) Nonsense mutation; will. D) Missense mutation; will not. E) Silent mutation; will not. ...
Poster 2: Primary Structure - IMSA Digital Commons
... angles; the measurements of these angles will vary between -180 degrees and 180 degrees depending on the R group. (1) However, it will never go to a conformation that is geometrically impossible in the secondary structure. (1) Picture: (3) The peptide bonds are resonance bonds, which are stronger th ...
... angles; the measurements of these angles will vary between -180 degrees and 180 degrees depending on the R group. (1) However, it will never go to a conformation that is geometrically impossible in the secondary structure. (1) Picture: (3) The peptide bonds are resonance bonds, which are stronger th ...
AP BIOLOGY Unit 1 – Chemistry and Molecules of Life
... Describe what occurs during a dehydration synthesis reaction? Describe what occurs during a hydrolysis reaction? What are the two types of nucleic acids? What are the monomers of nucleic acids? What are the three components of a nucleic acid monomer? What are the functions of nucleic acids? How do w ...
... Describe what occurs during a dehydration synthesis reaction? Describe what occurs during a hydrolysis reaction? What are the two types of nucleic acids? What are the monomers of nucleic acids? What are the three components of a nucleic acid monomer? What are the functions of nucleic acids? How do w ...
Lecture 6
... • The pH where this occurs is called the pI • We can calculate the pI of an amino acid using the following equation: ...
... • The pH where this occurs is called the pI • We can calculate the pI of an amino acid using the following equation: ...
Chemistry of Life: The Four Macromolecules
... C. Nucleic acids are polymers assembled from individual monomers known as nucleotides. ...
... C. Nucleic acids are polymers assembled from individual monomers known as nucleotides. ...
Macromolecules Vocabulary and Concepts
... Protein Many Uses: structural support, protection, transport, catalysis (enzymes), defense, regulation (hormones), movement. Polymer of amino acids Polypeptide o Peptide Bonds join amino acids. Amino Acids are linked together through a dehydration synthesis reaction. Amino Acids o Central as ...
... Protein Many Uses: structural support, protection, transport, catalysis (enzymes), defense, regulation (hormones), movement. Polymer of amino acids Polypeptide o Peptide Bonds join amino acids. Amino Acids are linked together through a dehydration synthesis reaction. Amino Acids o Central as ...
Sample exam 1
... isomerase acts only when energetically advantageous for the organism – in other words, problem 3 in figure 20-15 is avoided). 9. (3 points) Qualitatively sketch the rate of passive transport uptake of a substance (call it “M”) versus its external (extra-cellular) concentration by: a. diffusion throu ...
... isomerase acts only when energetically advantageous for the organism – in other words, problem 3 in figure 20-15 is avoided). 9. (3 points) Qualitatively sketch the rate of passive transport uptake of a substance (call it “M”) versus its external (extra-cellular) concentration by: a. diffusion throu ...
MoleculesofLifenoanim 3
... monomers with a ribose sugar and the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U); usually single-stranded; functions in protein synthesis and as the genome of some viruses. ...
... monomers with a ribose sugar and the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U); usually single-stranded; functions in protein synthesis and as the genome of some viruses. ...
Non Oxidative deamination
... of vitamin B6 ) . It is also a reversible reaction the equilibrium Constant Is near one , allowing the reaction to function in both amino acid degradation throw removal of α – amino groups ( after consumption of a protein – rich meal ) and biosynthesis through addition of amino groups to the carbon ...
... of vitamin B6 ) . It is also a reversible reaction the equilibrium Constant Is near one , allowing the reaction to function in both amino acid degradation throw removal of α – amino groups ( after consumption of a protein – rich meal ) and biosynthesis through addition of amino groups to the carbon ...
3.13 Amino acids, proteins and DNA
... • The primary structure folds back on itself and held together by hydrogen bonds. • The given shape looks like a ‘pleat’ with the R groups alternating up and down along the ...
... • The primary structure folds back on itself and held together by hydrogen bonds. • The given shape looks like a ‘pleat’ with the R groups alternating up and down along the ...
Protein Synthesis
... Transcription Review Another special codon found in mRNA stops the chain of amino acids and indicates the protein is complete. These codons are called Termination codons. There are only 3 of the codons: UGA; UAA and UAG. We are always going to assume that the coding side of DNA will be the left s ...
... Transcription Review Another special codon found in mRNA stops the chain of amino acids and indicates the protein is complete. These codons are called Termination codons. There are only 3 of the codons: UGA; UAA and UAG. We are always going to assume that the coding side of DNA will be the left s ...
Review on Biochemistry: Protein Chemistry
... -carboxyglutamate: found in prothrombin and certain Ca2+-binding protein. Desmosine (a derivative of four Lys residues): found in the fibrous protein elastin. Selenocysteine: Selenium replaces sulfur in cysteine during amino acid synthesis (derived from serine). Amino acids not as constitue ...
... -carboxyglutamate: found in prothrombin and certain Ca2+-binding protein. Desmosine (a derivative of four Lys residues): found in the fibrous protein elastin. Selenocysteine: Selenium replaces sulfur in cysteine during amino acid synthesis (derived from serine). Amino acids not as constitue ...
Amino acids
... and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Organisms inherit DNA from their parents. While DNA encodes the information that programs all the cell’s activities, it is not directly involved in the day-to-day operations of the cell. Each gene along a DNA molecule directs the synthesis of a specific type of messe ...
... and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Organisms inherit DNA from their parents. While DNA encodes the information that programs all the cell’s activities, it is not directly involved in the day-to-day operations of the cell. Each gene along a DNA molecule directs the synthesis of a specific type of messe ...
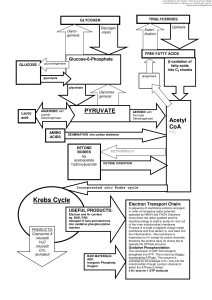
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.