Biomolecules Test Review
... _______________________ Contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen _______________________ Two types are monosaccharides and disaccharides. _______________________ Used by the body for quick energy. _______________________ Contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus. ___________ ...
... _______________________ Contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen _______________________ Two types are monosaccharides and disaccharides. _______________________ Used by the body for quick energy. _______________________ Contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus. ___________ ...
Organic Compounds The Big Four
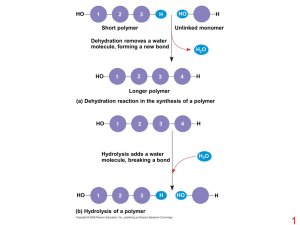
... • Contain hydrogen, oxygen and several other atoms. • They are called macromolecules (means giant molecules) and are made from thousands of smaller molecules. • The smaller units are called monomers and they join together to form polymers. ...
... • Contain hydrogen, oxygen and several other atoms. • They are called macromolecules (means giant molecules) and are made from thousands of smaller molecules. • The smaller units are called monomers and they join together to form polymers. ...
Amino acids 1
... Water is very happy in bulk water because there it has on average 3.6 H-bonds and about six degrees of freedom. So, whenever we discuss protein structure, folding, and stability, it is all the entropy of water, and that is called the hydrophobic effect. ...
... Water is very happy in bulk water because there it has on average 3.6 H-bonds and about six degrees of freedom. So, whenever we discuss protein structure, folding, and stability, it is all the entropy of water, and that is called the hydrophobic effect. ...
amino acids
... Why is shape important? The shape of an enzyme is very important because it has a direct effect on how it catalyzes a reaction. Why do enzymes have different shapes? An enzyme’s shape is determined by the sequence of amino acids in its structure, and the bonds which form between the atoms of those ...
... Why is shape important? The shape of an enzyme is very important because it has a direct effect on how it catalyzes a reaction. Why do enzymes have different shapes? An enzyme’s shape is determined by the sequence of amino acids in its structure, and the bonds which form between the atoms of those ...
The Chemistry of Cells
... – Heat will flow only from hot to cold – Entropy of a closed system always increases – The second law, in its most general form, states that the world acts spontaneously to minimize potentials – All reactions proceed in an “energetically favorable” direction until they reach equilibrium • Intrinsic ...
... – Heat will flow only from hot to cold – Entropy of a closed system always increases – The second law, in its most general form, states that the world acts spontaneously to minimize potentials – All reactions proceed in an “energetically favorable” direction until they reach equilibrium • Intrinsic ...
Chapter 10 - Power Point Presentation
... Often portions of the original gene are not used in the final product These ‘extra’ unused portions are called introns they must be removed before making the protein. The portions that remain and ARE used are called exons So, eukaryotes undergo RNA splicing This is one way a gene can have some varia ...
... Often portions of the original gene are not used in the final product These ‘extra’ unused portions are called introns they must be removed before making the protein. The portions that remain and ARE used are called exons So, eukaryotes undergo RNA splicing This is one way a gene can have some varia ...
Document
... Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates made of long chains of monosaccharides. glycogen--storage form of glucose in animals. stored in the liver. starch--storage form of glucose in plants cellulose--makes up the cell wall of plants, gives plant cells their ...
... Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates made of long chains of monosaccharides. glycogen--storage form of glucose in animals. stored in the liver. starch--storage form of glucose in plants cellulose--makes up the cell wall of plants, gives plant cells their ...
3D-structure of bacterial ribosomes, the machines that make
... most proteins don’t During production many proteins can only obtain correct folding if assisted by other proteins (chaperones) during production in living cells If large quantities of a specific chaperone-dependent protein is produced in a cell, it may become misfolded. This represents a very seriou ...
... most proteins don’t During production many proteins can only obtain correct folding if assisted by other proteins (chaperones) during production in living cells If large quantities of a specific chaperone-dependent protein is produced in a cell, it may become misfolded. This represents a very seriou ...
Proteins
... 4. Contractile Proteins – are involved in movement. Actin and myosin are proteins that enable muscles to contract. 5. Storage Proteins – e.g. albumin / ovalbumin - the protein store that forms the white of eggs. 6. Defensive Proteins – Antibodies, which ...
... 4. Contractile Proteins – are involved in movement. Actin and myosin are proteins that enable muscles to contract. 5. Storage Proteins – e.g. albumin / ovalbumin - the protein store that forms the white of eggs. 6. Defensive Proteins – Antibodies, which ...
Chemistry of Life – Macromolecules and Enzymes
... 1. In living cells, enzymes act as catalysts, which may reduce the amount of activation energy required for a chemical reaction to occur. In the graphs below, pathway x is a solid line representing the uncatalyzed reaction. The dotted line shows the catalyzed reaction. Which graph best illustrates ...
... 1. In living cells, enzymes act as catalysts, which may reduce the amount of activation energy required for a chemical reaction to occur. In the graphs below, pathway x is a solid line representing the uncatalyzed reaction. The dotted line shows the catalyzed reaction. Which graph best illustrates ...
Biochemistry
... Unsaturated fats have one or more double bonds between carbons so they do not have all the possible hydrogens http://www.diffen.com/di fference/Saturated_Fats_ vs_Unsaturated_Fats ...
... Unsaturated fats have one or more double bonds between carbons so they do not have all the possible hydrogens http://www.diffen.com/di fference/Saturated_Fats_ vs_Unsaturated_Fats ...
Ativity 30
... • …are highly specific; they only act only on a small number of substrates (often just one.) • …increase the rate of a chemical reaction. • …are re-used; they are not consumed in the reaction. E + S ES complex E + Product(s) *If there is no working enzyme, the reaction may still occur very slow ...
... • …are highly specific; they only act only on a small number of substrates (often just one.) • …increase the rate of a chemical reaction. • …are re-used; they are not consumed in the reaction. E + S ES complex E + Product(s) *If there is no working enzyme, the reaction may still occur very slow ...
Camp 1 - UCSC Directory of individual web sites
... mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA all participate in translation. Protein synthesis takes place on ribosomes (e.g. rRNA). A ribosome dissociates into larger (60S) and a smaller body (40S). The 5’ end of the mature mRNA is bonded to the 40S ribosome and this unit then joined to the 60S ribosome. • Triplets of bas ...
... mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA all participate in translation. Protein synthesis takes place on ribosomes (e.g. rRNA). A ribosome dissociates into larger (60S) and a smaller body (40S). The 5’ end of the mature mRNA is bonded to the 40S ribosome and this unit then joined to the 60S ribosome. • Triplets of bas ...
classsssssss
... • A comatose laboratory technician is rushed into the emergency room. She dies while you are examining her. Her most dramatic symptom is that her body is literally hot to your touch, indicating an extremely high fever. You learn that her lab has been working on metabolic inhibitors and that there i ...
... • A comatose laboratory technician is rushed into the emergency room. She dies while you are examining her. Her most dramatic symptom is that her body is literally hot to your touch, indicating an extremely high fever. You learn that her lab has been working on metabolic inhibitors and that there i ...
Transcription and Translation computer lab test review
... During transcription, RNA is developed from a strand of DNA. List the base pairs used to make RNA. What is the name of the DNA strand used in transcription? Where does transcription occur? Where does translation occur? Name the RNA codon that is used to start translation. Which three codons will sto ...
... During transcription, RNA is developed from a strand of DNA. List the base pairs used to make RNA. What is the name of the DNA strand used in transcription? Where does transcription occur? Where does translation occur? Name the RNA codon that is used to start translation. Which three codons will sto ...
Big Idea 2 Exam - C2-5
... a. The protein's quaternary structure will be damaged. b. The protein will not change; several amino acids must be altered to have any effect on protein function. c. The protein will always denature and become entirely nonfunctional. d. Depending on the chemical nature of the amino acid the protein ...
... a. The protein's quaternary structure will be damaged. b. The protein will not change; several amino acids must be altered to have any effect on protein function. c. The protein will always denature and become entirely nonfunctional. d. Depending on the chemical nature of the amino acid the protein ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.