Sample Exam #1 ( file)
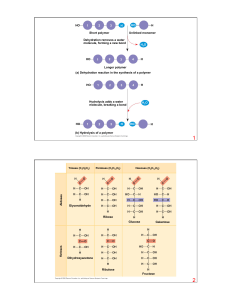
... Condensation reaction involving a glycerol and 2 fatty acid molecules yield_______ and ______. A. 1 Phospholipid / 2 phosphate B. 1 Diacylglycerol / 2 water C. 2 Monoacylglycerol / 2 water D. 2 Monoacylglycerol / 1 water ...
... Condensation reaction involving a glycerol and 2 fatty acid molecules yield_______ and ______. A. 1 Phospholipid / 2 phosphate B. 1 Diacylglycerol / 2 water C. 2 Monoacylglycerol / 2 water D. 2 Monoacylglycerol / 1 water ...
Ch.05The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... mRNA into cytoplasm via nuclear pore ...
... mRNA into cytoplasm via nuclear pore ...
Protein synthesis test review key
... 12. What happens to the mRNA sequence if the DNA sequence changes? What happens to the sequence of amino acids of the DNA sequence changes? What happens to the final protein if the DNA sequence changes? If the DNA sequence changes, then the mRNA sequence will change. The amino acids may or may not c ...
... 12. What happens to the mRNA sequence if the DNA sequence changes? What happens to the sequence of amino acids of the DNA sequence changes? What happens to the final protein if the DNA sequence changes? If the DNA sequence changes, then the mRNA sequence will change. The amino acids may or may not c ...
Lecture 22 Urea Cycle, Gluconeogenesis and Glyoxalate
... 1. Why is it necessary that the first steps of the urea cycle take place in the mitochondria? Answer: FK: This allows the existence of two isoforms of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase (CPS). The mitochondrial isoenzymes CPS I uses free ammonia as nitrogen source, and is (positively) allosterically con ...
... 1. Why is it necessary that the first steps of the urea cycle take place in the mitochondria? Answer: FK: This allows the existence of two isoforms of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase (CPS). The mitochondrial isoenzymes CPS I uses free ammonia as nitrogen source, and is (positively) allosterically con ...
Praxis Review for Science
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). DNA is found in the chromosomes of the nucleus of the cell. It directs all aspects of cell function. It is organized into genes which determine the properties of the organism. ...
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). DNA is found in the chromosomes of the nucleus of the cell. It directs all aspects of cell function. It is organized into genes which determine the properties of the organism. ...
Protein classification
... millimeter _______. Despite the diversity, cells resemble each other to an astonishing degree in their chemistry. For example, the same twenty ____ amino acids ______ are used to make proteins. Similarly, the genetic information of all cells is stored in their ____ DNA __________. Although _______ v ...
... millimeter _______. Despite the diversity, cells resemble each other to an astonishing degree in their chemistry. For example, the same twenty ____ amino acids ______ are used to make proteins. Similarly, the genetic information of all cells is stored in their ____ DNA __________. Although _______ v ...
30_General pathways of amino acids transformation
... variety of amino acids to -ketoglutarate with glutamate formation Glutamate can be deaminated with NH4+ release ...
... variety of amino acids to -ketoglutarate with glutamate formation Glutamate can be deaminated with NH4+ release ...
sg 10
... 24. Distinguish between a point mutation and a frameshift mutation. Which would be more severe? ...
... 24. Distinguish between a point mutation and a frameshift mutation. Which would be more severe? ...
AP Biology
... 24. Distinguish between a point mutation and a frameshift mutation. Which would be more severe? ...
... 24. Distinguish between a point mutation and a frameshift mutation. Which would be more severe? ...
Sept24_26_07 - Salamander Genome Project
... phosphorylation, aminoacyl transfer, peptide bond formation, carbon-carbon bond formation ...
... phosphorylation, aminoacyl transfer, peptide bond formation, carbon-carbon bond formation ...
A, C
... glycerol and 3 fatty acids with the formula C200H348O2). A. Was this a saturated or unsaturated triglyceride? B. Was this an oil or a fat? C. What kind of reaction was this? D. Was water a reactant or a product? E. How many water molecules were ...
... glycerol and 3 fatty acids with the formula C200H348O2). A. Was this a saturated or unsaturated triglyceride? B. Was this an oil or a fat? C. What kind of reaction was this? D. Was water a reactant or a product? E. How many water molecules were ...
Protein Synthesis
... By the end of this unit you will: know what transcription is know what translation is understand how proteins are made. ...
... By the end of this unit you will: know what transcription is know what translation is understand how proteins are made. ...
metabolism of amino acids
... • Due to the defective branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex• Lead to accumulation of leucine in blood- and excreted to urine – smell like maple syrup • Untreated lead to abnormal development of the brain, mental retardation, and death in early ...
... • Due to the defective branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex• Lead to accumulation of leucine in blood- and excreted to urine – smell like maple syrup • Untreated lead to abnormal development of the brain, mental retardation, and death in early ...
File
... We have learned that most cells contain genetic material in their nuclei. This genetic material is normally in the form of chromatin (or chromosomes during the cell division). Normal human body cells contain ___ chromosomes. Obviously, chromosomes are important, but why? Why do all the cells of the ...
... We have learned that most cells contain genetic material in their nuclei. This genetic material is normally in the form of chromatin (or chromosomes during the cell division). Normal human body cells contain ___ chromosomes. Obviously, chromosomes are important, but why? Why do all the cells of the ...
Mentor: James A. MacKay Students: Amanda Williams, Holly Sofka
... Students: Amanda Williams, Holly Sofka Project Description: Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is believed to be an important molecule in the evolution of life and has functionally taken on many important biological roles. Given the many functions of RNA, molecular recognition of RNA represents an attractive go ...
... Students: Amanda Williams, Holly Sofka Project Description: Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is believed to be an important molecule in the evolution of life and has functionally taken on many important biological roles. Given the many functions of RNA, molecular recognition of RNA represents an attractive go ...
model 3 - Instructure
... b. Is the RBS closer to the 5' or 3' end of the mRNA? _____ b. Which are more prevalent in the RBS, pyrimidines or purines? __________________ c. What types of bonds hold the mRNA and small ribosomal subunit together? __________ 7. a. Does the first tRNA bind before or after the ribosome is complete ...
... b. Is the RBS closer to the 5' or 3' end of the mRNA? _____ b. Which are more prevalent in the RBS, pyrimidines or purines? __________________ c. What types of bonds hold the mRNA and small ribosomal subunit together? __________ 7. a. Does the first tRNA bind before or after the ribosome is complete ...
Chemistry of Life Answers 1. Differentiate between an ionic and
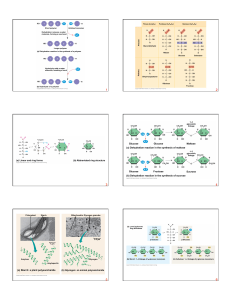
... • Tertiary structure: Supercoiling of a polypeptide chain • Quaternary structure: two or more polypeptide chains bond together to form a functional protein. ...
... • Tertiary structure: Supercoiling of a polypeptide chain • Quaternary structure: two or more polypeptide chains bond together to form a functional protein. ...
a) Water is a good solvent – all molecules in a living things are
... 4.4. Quaternary structure refers to the relationships between the individual polypeptides chains in complex protein. A single molecule of hemoglobin consists of four polypeptide chains: two of them are -chains and two of them are -chains. ...
... 4.4. Quaternary structure refers to the relationships between the individual polypeptides chains in complex protein. A single molecule of hemoglobin consists of four polypeptide chains: two of them are -chains and two of them are -chains. ...
NAME
... FRAMESHIFT MUTATION-This type of mutation may change every amino acid that follows the point of mutation. They can alter a protein so much that it is unable to perform its normal function. ...
... FRAMESHIFT MUTATION-This type of mutation may change every amino acid that follows the point of mutation. They can alter a protein so much that it is unable to perform its normal function. ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.