Basic organic chemistry of important macromolecules (Lecture 11-12)
... 2) serve in the several cellular structures that choose, and then link into the correct order the amino acids of a protein chain (RNA). The structures of nucleotides and polynucleotides (a) Nucleotides, the monomers of nucleic acids, are themselves composed of three ...
... 2) serve in the several cellular structures that choose, and then link into the correct order the amino acids of a protein chain (RNA). The structures of nucleotides and polynucleotides (a) Nucleotides, the monomers of nucleic acids, are themselves composed of three ...
Definitions
... •Lipids are nonpolar molecules that include ___________________________________. •Many contain carbon chains called __________________ •Fats and oils contain fatty acids bonded to glycerol. •Lipids have several different functions. •_____________________________________________________ •____________ ...
... •Lipids are nonpolar molecules that include ___________________________________. •Many contain carbon chains called __________________ •Fats and oils contain fatty acids bonded to glycerol. •Lipids have several different functions. •_____________________________________________________ •____________ ...
STUDY GUIDE –Intro to Cell Biology
... Which part of a phospholipid molecule is polar and hydrophilic? HEAD Which parts of a phospholipid molecule are non-polar and hydrophobic? TAILS The attraction between the hydrogen atom in one molecule and the negatively charged part of a nearby molecule is an example of a HYDROGEN BOND. Reaction th ...
... Which part of a phospholipid molecule is polar and hydrophilic? HEAD Which parts of a phospholipid molecule are non-polar and hydrophobic? TAILS The attraction between the hydrogen atom in one molecule and the negatively charged part of a nearby molecule is an example of a HYDROGEN BOND. Reaction th ...
MACROMOLECULE WEBQUEST Name: Site 1 The Lipids Site
... Site 7 Biochemistry Jeopardy Site Location:http://www.quia.com/cb/86263.html Test your knowledge of the macromolecules -- compete against yourself in Biochemistry ...
... Site 7 Biochemistry Jeopardy Site Location:http://www.quia.com/cb/86263.html Test your knowledge of the macromolecules -- compete against yourself in Biochemistry ...
3rd Quarter Exam Review with Answers NEW
... Glucose; to store as starch, build cellulose to make cell walls, make other sugars 7. Why do plants appear green? Chlorophyll is the most abundant pigment and it reflects green light 8. What factors will affect the rate of photosynthesis? Carbon dioxide, temperature, intensity of light Cellular Resp ...
... Glucose; to store as starch, build cellulose to make cell walls, make other sugars 7. Why do plants appear green? Chlorophyll is the most abundant pigment and it reflects green light 8. What factors will affect the rate of photosynthesis? Carbon dioxide, temperature, intensity of light Cellular Resp ...
ALL: What is diffusion? What are the consequences to molecules in
... ribosome How do the large & small subunits get together with the mRNA? How does it know where to start? How does it 'define' a codon? How does it know when to stop? How does it determine which amino acid to add? termination factor How does it know when to tell the ribosome to quit? How does it avoid ...
... ribosome How do the large & small subunits get together with the mRNA? How does it know where to start? How does it 'define' a codon? How does it know when to stop? How does it determine which amino acid to add? termination factor How does it know when to tell the ribosome to quit? How does it avoid ...
Document
... macromolecules to run smoothly: The 4 Macromolecules are Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic acids Proteins ...
... macromolecules to run smoothly: The 4 Macromolecules are Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic acids Proteins ...
Chapter 2 Section 3: The Chemistry of Life
... Mulder found that they all contained carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. Proud of the discovery, he named his four-element formula, protein, from a Greek word meaning "of first importance." That is how much he thought of his formula! But it stuck as the name for the strange substances. ...
... Mulder found that they all contained carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. Proud of the discovery, he named his four-element formula, protein, from a Greek word meaning "of first importance." That is how much he thought of his formula! But it stuck as the name for the strange substances. ...
MCB Lecture 2 – Amino Acids and Proteins
... polypeptide chain can take multiple secondary arrangements. Changing domains has been the cause of evolutionary differences in species. Example: actin fold where ATP binds. Quaternary Structure – Multiple protein subunits bound together to form a 3dimensional shape. Hydropathy Plot – A plot that det ...
... polypeptide chain can take multiple secondary arrangements. Changing domains has been the cause of evolutionary differences in species. Example: actin fold where ATP binds. Quaternary Structure – Multiple protein subunits bound together to form a 3dimensional shape. Hydropathy Plot – A plot that det ...
RNA and Protein
... What is the function of each? mRNA – messenger RNA carries genetic information from DNA in the nucleus to direct protein synthesis in the cytoplasm. ...
... What is the function of each? mRNA – messenger RNA carries genetic information from DNA in the nucleus to direct protein synthesis in the cytoplasm. ...
Molecuar Structure of DNA Questions
... 5. How many DNA nucleotides are there? List them. Also indicate which are purines, and which are pyrimidines. ...
... 5. How many DNA nucleotides are there? List them. Also indicate which are purines, and which are pyrimidines. ...
CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2
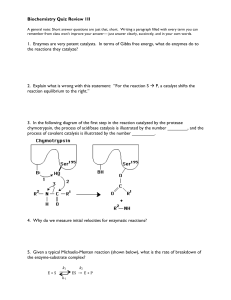
... • Catalyst : inorganic or organic substance which speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction without entering the reaction itself • enzymes: organic catalysts made of protein • most enzyme names end in -ase • enzymes lower the energy needed to start a chemical reaction. (activation energy) • begin to ...
... • Catalyst : inorganic or organic substance which speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction without entering the reaction itself • enzymes: organic catalysts made of protein • most enzyme names end in -ase • enzymes lower the energy needed to start a chemical reaction. (activation energy) • begin to ...
Chem 464 Biochemistry
... 10. (10 points) Histones are proteins found in eukariotic cell nuclei, tightly bound to DNA which has many negatively charged phosphate groups. The pI of histones is very high, about 10.8, What amino acid residues must be present in relatively large numbers in histones? In what way do these residues ...
... 10. (10 points) Histones are proteins found in eukariotic cell nuclei, tightly bound to DNA which has many negatively charged phosphate groups. The pI of histones is very high, about 10.8, What amino acid residues must be present in relatively large numbers in histones? In what way do these residues ...
Princeton H - SchoolNotes
... A. What is organic chemistry? B. Why is carbon such a versatile element? C. What is biochemistry? D. What inorganic compounds are important to living systems? E. What organic compounds are important to living systems? F. What is the most abundant and important compound found inside cells? 1. What ar ...
... A. What is organic chemistry? B. Why is carbon such a versatile element? C. What is biochemistry? D. What inorganic compounds are important to living systems? E. What organic compounds are important to living systems? F. What is the most abundant and important compound found inside cells? 1. What ar ...
Amino acids
... The simplest amino acid is Glycine, which has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. Alanine, Valine, Leucine and Isoleucine have saturated hydrocarbon R groups (i.e. they only have hydrogen and carbon linked by single covalent bonds). Leucine and Isoleucine are isomers of each other. ...
... The simplest amino acid is Glycine, which has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. Alanine, Valine, Leucine and Isoleucine have saturated hydrocarbon R groups (i.e. they only have hydrogen and carbon linked by single covalent bonds). Leucine and Isoleucine are isomers of each other. ...
Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... b) thymine and cytosine c) thymine and adenine d) uracil and guanine e) guanine and cytosine 17. Which of the following describes a difference between DNA and RNA? (Concept ...
... b) thymine and cytosine c) thymine and adenine d) uracil and guanine e) guanine and cytosine 17. Which of the following describes a difference between DNA and RNA? (Concept ...
Biological Molecules
... The shape of an individual protein is determined by the order of amino acids in the primary chain, which affects how the amino acid chain twists and folds into the final shape of the protein. DNA contains the code that instructs the cell machinery to put amino acids together in a particular order to ...
... The shape of an individual protein is determined by the order of amino acids in the primary chain, which affects how the amino acid chain twists and folds into the final shape of the protein. DNA contains the code that instructs the cell machinery to put amino acids together in a particular order to ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.