Gene Expression and Gene Regulation
... • Ribosomes are the sites on which protein synthesis occurs ...
... • Ribosomes are the sites on which protein synthesis occurs ...
III B.Sc. (CHEMISTRY) MODEL CURRICULUM FOR
... gama amino acids. Natural and essential amino acids – definition and examples, classification of alpha amino acids into acidic, basic and neutral amino acids with examples. Methods of synthesis: General methods of synthesis of alpha amino acids (specific examples – Glycine, Alanine, valine and leuce ...
... gama amino acids. Natural and essential amino acids – definition and examples, classification of alpha amino acids into acidic, basic and neutral amino acids with examples. Methods of synthesis: General methods of synthesis of alpha amino acids (specific examples – Glycine, Alanine, valine and leuce ...
Document
... Three Molecules of Life DNA: four nucleotide bases (GC,AT) (2 bits) genetic code in 3 base ‘codons’ information storage and propagation, genetic regulation ...
... Three Molecules of Life DNA: four nucleotide bases (GC,AT) (2 bits) genetic code in 3 base ‘codons’ information storage and propagation, genetic regulation ...
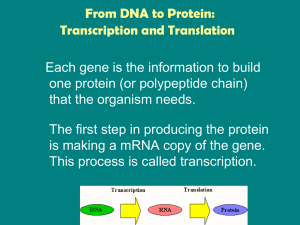
From DNA to Protein: Transcription and Translation
... mRNA • While DNA is a double helix, mRNA is a single strand of nucleotides. • mRNA nucleotides have the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose • mRNA has the nitrogen base uracil instead of thymine. ...
... mRNA • While DNA is a double helix, mRNA is a single strand of nucleotides. • mRNA nucleotides have the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose • mRNA has the nitrogen base uracil instead of thymine. ...
Matching review Connect with lines
... Matching review Connect with lines Water Carbon dioxide Oxygen PGAL NADP NAD+ FAD Glucose ...
... Matching review Connect with lines Water Carbon dioxide Oxygen PGAL NADP NAD+ FAD Glucose ...
CHAPTER 5 THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF LARGE
... 26. List the major components of a nucleotide, and describe how these monomers are linked to form a nucleic acid. Name the type of bond that holds two nucleotides together. 27. Distinguish between: a. pyrimidine and purine b. nucleotide and nucleoside c. ribose and deoxyribose d. 5’ end and 3’ end o ...
... 26. List the major components of a nucleotide, and describe how these monomers are linked to form a nucleic acid. Name the type of bond that holds two nucleotides together. 27. Distinguish between: a. pyrimidine and purine b. nucleotide and nucleoside c. ribose and deoxyribose d. 5’ end and 3’ end o ...
Biochemistry - El Camino College
... 3. DNA is a double-stranded _________ (like a twisted ladder) held together by hydrogen bonds and is composed of: a. ______________ sugar and ____________ groups form the side rails of the “ladder” b. Nitrogenous _______ held together by __________ bonds form the ladder steps. These bases include: 1 ...
... 3. DNA is a double-stranded _________ (like a twisted ladder) held together by hydrogen bonds and is composed of: a. ______________ sugar and ____________ groups form the side rails of the “ladder” b. Nitrogenous _______ held together by __________ bonds form the ladder steps. These bases include: 1 ...
Chemistry Test Study Guide
... 22. _____________ and ______________ are the two types of nucleic acids. 23. Name the function of nucleic acids. _________________________________________ 24. Describe/Draw the structure of DNA. ( What does it look like?) ____________________________ Energy and Enzymes 25. ______________________ are ...
... 22. _____________ and ______________ are the two types of nucleic acids. 23. Name the function of nucleic acids. _________________________________________ 24. Describe/Draw the structure of DNA. ( What does it look like?) ____________________________ Energy and Enzymes 25. ______________________ are ...
Macromolecules, Chemical Reactions & Enzymes
... 3) label the water molecule with O, H, +, and – 4) Match the pH scale with the following word: Neutral, Strong Acid, Strong Base, Weak Acid, Weak Base ...
... 3) label the water molecule with O, H, +, and – 4) Match the pH scale with the following word: Neutral, Strong Acid, Strong Base, Weak Acid, Weak Base ...
Molecular Orbital Interactions in the Anticodon of Transfer RNA
... to RNA and then protein synthesis. ...
... to RNA and then protein synthesis. ...
Mader/Biology, 11/e – Chapter Outline
... b. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is a nucleotide used to supply energy for synthetic reactions and other energy-requiring metabolic activities in the cell. A. Structure of DNA and RNA 1. Nucleotides are a molecular complex of three types of molecules: a phosphate (phosphoric acid), a pentose sugar, a ...
... b. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is a nucleotide used to supply energy for synthetic reactions and other energy-requiring metabolic activities in the cell. A. Structure of DNA and RNA 1. Nucleotides are a molecular complex of three types of molecules: a phosphate (phosphoric acid), a pentose sugar, a ...
Review for Chapter 12, 13, 15 16, 17 Exam
... Chapter 16: DNA/The Molecular Basis of Inheritance What functional group are DNA made of, how are they put together and what kind of bonds join the different parts? What are the roles of DNA Polymerase III, DNA Polymerase I, Ligase, Helicase, RNA primer, and telomerase in DNA replication? What dete ...
... Chapter 16: DNA/The Molecular Basis of Inheritance What functional group are DNA made of, how are they put together and what kind of bonds join the different parts? What are the roles of DNA Polymerase III, DNA Polymerase I, Ligase, Helicase, RNA primer, and telomerase in DNA replication? What dete ...
Carbon Sodium Boron Iodine Nitrogen Magnesium Cobalt
... Nucleic acids (RNA/DNA) Phospholipids (membranes) Bones ...
... Nucleic acids (RNA/DNA) Phospholipids (membranes) Bones ...
Amino Acids Objectives
... pancreas. This insulin stimulates uptake of branched chain amino acids by muscle, where they are used as oxidizable substrates. Their metabolism releases even more NH4+. This elevated NH4+ concentration in the brain stimulates glutamine synthesis, which in turn promotes tryptophan transport, which i ...
... pancreas. This insulin stimulates uptake of branched chain amino acids by muscle, where they are used as oxidizable substrates. Their metabolism releases even more NH4+. This elevated NH4+ concentration in the brain stimulates glutamine synthesis, which in turn promotes tryptophan transport, which i ...
Packet
... a. Lipids are nonpolar-hydrophobic-__________________________ b. Some examples are: __________, _____________, and ___________ c. Build a triglyceride (common lipid)- 3-carbon backbone attached to 3 fatty acids. d. The building block/monomers of all lipids are _________________. But to build a trigl ...
... a. Lipids are nonpolar-hydrophobic-__________________________ b. Some examples are: __________, _____________, and ___________ c. Build a triglyceride (common lipid)- 3-carbon backbone attached to 3 fatty acids. d. The building block/monomers of all lipids are _________________. But to build a trigl ...
AP Biology, Chapter 5, 9th ed. The Structure and Function of Large
... that is conserved through evolution: adenine pairs with thymine or uracil (A-T or A-U) and cytosine pairs with guanine (C-G). i. Purines (G and A) have a double ring structure. ii. Pyrimidines (C, T and U) have a single ring structure. DNA and Proteins as Tape Measures of Evolution 30. Explain how t ...
... that is conserved through evolution: adenine pairs with thymine or uracil (A-T or A-U) and cytosine pairs with guanine (C-G). i. Purines (G and A) have a double ring structure. ii. Pyrimidines (C, T and U) have a single ring structure. DNA and Proteins as Tape Measures of Evolution 30. Explain how t ...
Macs Notes
... that BREAK DOWN molecules.) Water is used during the process. Why? b/c now you have to break up one or more of the covalent links. This leaves unhappy atoms with electrons that need to be shared. So... ...water breaks up into –H and –OH and attaches to make each side happy. In the body these r ...
... that BREAK DOWN molecules.) Water is used during the process. Why? b/c now you have to break up one or more of the covalent links. This leaves unhappy atoms with electrons that need to be shared. So... ...water breaks up into –H and –OH and attaches to make each side happy. In the body these r ...
sickle cell anemia explained by protein shape, northeast 2012
... This unit would be taught early in an Introductory Biology course as part of a broader discussion about biological macromolecules. Students would have already been introduced to major themes in biology, such as the chemistry of life (including atomic structure and types of chemical bonds). They will ...
... This unit would be taught early in an Introductory Biology course as part of a broader discussion about biological macromolecules. Students would have already been introduced to major themes in biology, such as the chemistry of life (including atomic structure and types of chemical bonds). They will ...
Amino acids have many roles in living organisms
... Proteins are essential components of all organisms and carry out a diversity of functions ...
... Proteins are essential components of all organisms and carry out a diversity of functions ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.