The simplest enzyme revisited: The chicken and
... connect dots to reactions that they catalyze. This is then a metagraph that organizes the array of substances, the concentration distribution, and the array of cycles in the network. The distributions and flows with the overlay will be vastly different from the uncatalyzed network. The distribution i ...
... connect dots to reactions that they catalyze. This is then a metagraph that organizes the array of substances, the concentration distribution, and the array of cycles in the network. The distributions and flows with the overlay will be vastly different from the uncatalyzed network. The distribution i ...
The Nature of Matter
... Made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms (C, H, O) Hydrogen and carbon will be in a 2:1 ratio Used by cells as the main source of energy. Plants and some animals use carbohydrates in structures. Examples: Starches and sugars, such as glucose (C6H12O6) and cellulose (in plant cell wall ...
... Made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms (C, H, O) Hydrogen and carbon will be in a 2:1 ratio Used by cells as the main source of energy. Plants and some animals use carbohydrates in structures. Examples: Starches and sugars, such as glucose (C6H12O6) and cellulose (in plant cell wall ...
Slide 1 - KU CTE
... This general class of lipids, shown below, is characterized by four fused rings ...
... This general class of lipids, shown below, is characterized by four fused rings ...
Chapter 3: Section 3 – Carbon Compounds
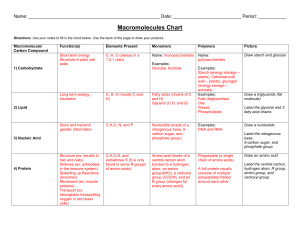
... complex molecules called __________________ ____________ _______________. 2. Large, complex biomolecules or organic molecules are built from smaller, simpler molecules called ___________________. 3. These simple molecules or monomers are like Lego blocks, which can be used to build a variety of diff ...
... complex molecules called __________________ ____________ _______________. 2. Large, complex biomolecules or organic molecules are built from smaller, simpler molecules called ___________________. 3. These simple molecules or monomers are like Lego blocks, which can be used to build a variety of diff ...
Notes Ch. 2.3 2013 - Red Hook Central Schools
... o Two or more saccharides joined: polysaccharides Uses of Carbohydrates: Main source of energy in all living things o Sometimes animals take in more carbohydrate energy than they need. o In humans and other animals, unused (extra) glucose molecules are stored in the liver as glycogen. Complex c ...
... o Two or more saccharides joined: polysaccharides Uses of Carbohydrates: Main source of energy in all living things o Sometimes animals take in more carbohydrate energy than they need. o In humans and other animals, unused (extra) glucose molecules are stored in the liver as glycogen. Complex c ...
Enzymes/Macromolecules/Bonding
... Double sugar needs to be broken apart Only one enzyme can function for this reaction Shape of an Enzyme can determine its functions ...
... Double sugar needs to be broken apart Only one enzyme can function for this reaction Shape of an Enzyme can determine its functions ...
Test #4: Biomolecule Foldable
... subunits called nucleotides has which of these functions in the cell? F ...
... subunits called nucleotides has which of these functions in the cell? F ...
Standard 3
... form. Made of sugar, phosphate and nitrogen-containing bases. Two types DNA and RNA. ...
... form. Made of sugar, phosphate and nitrogen-containing bases. Two types DNA and RNA. ...
File - Mrs. Durako`s Classroom
... 1. The carbon atoms in large, complex biomolecules are bonded to other atoms with ____________________ bonds. 2. The four major classes of organic compounds are _____________________, ______________________, ______________________, and nucleic acids. 3. The building blocks of carbohydrates are _____ ...
... 1. The carbon atoms in large, complex biomolecules are bonded to other atoms with ____________________ bonds. 2. The four major classes of organic compounds are _____________________, ______________________, ______________________, and nucleic acids. 3. The building blocks of carbohydrates are _____ ...
Lecture 6 POWERPOINT here
... An average cell has both general reactions which it needs to perform to sustain life, as well as specialized ones that make that cell type unique, i.e. pancreatic cell. The general reactions are called housekeeping reactions These can be many in number and their interactions are pretty comple ...
... An average cell has both general reactions which it needs to perform to sustain life, as well as specialized ones that make that cell type unique, i.e. pancreatic cell. The general reactions are called housekeeping reactions These can be many in number and their interactions are pretty comple ...
Biochemistry Test Review KEY
... 20. Which macromolecule is composed of glycerol and fatty acids and functions as a hormone? Lipids 21. Know the functions of the following molecules Lipid store energy and provide barriers Nucleotide store and communicate genetic information Enzyme speed up the rate of chemical reactions Car ...
... 20. Which macromolecule is composed of glycerol and fatty acids and functions as a hormone? Lipids 21. Know the functions of the following molecules Lipid store energy and provide barriers Nucleotide store and communicate genetic information Enzyme speed up the rate of chemical reactions Car ...
BIO C211 - BITS Pilani
... 4. Nucleic acids, Genomic structure & function, systhesis B. Enzymes 4 Ch. 1. Classification 2. Enzyme kinetics 3. Enzyme inhibitors and regulators 4. Allosteric enzymes 5. Multienzyme systems 6. Isoenzymes C. Vitamins and coenzymes 3 Ch. 1. Classification of vitamins 2. Structures and functions of ...
... 4. Nucleic acids, Genomic structure & function, systhesis B. Enzymes 4 Ch. 1. Classification 2. Enzyme kinetics 3. Enzyme inhibitors and regulators 4. Allosteric enzymes 5. Multienzyme systems 6. Isoenzymes C. Vitamins and coenzymes 3 Ch. 1. Classification of vitamins 2. Structures and functions of ...
Course Specifications General Information
... 1 - The objective of this course is to know the metabolic pathways of different food stuffs 2 - To know different biochemical reactions taking place in our bodies catalysed by enzymes and how metabolic disorder of some pathways lead to diseases ...
... 1 - The objective of this course is to know the metabolic pathways of different food stuffs 2 - To know different biochemical reactions taking place in our bodies catalysed by enzymes and how metabolic disorder of some pathways lead to diseases ...
Name - MsOttoliniBiology
... Structure (ex: keratin in hair and nails) Defense (ex: antibodies in the immune system) Speeding up Reactions (enzymes) Movement (ex: muscle proteins) Transport (ex: hemoglobin transporting oxygen in red blood cells) ...
... Structure (ex: keratin in hair and nails) Defense (ex: antibodies in the immune system) Speeding up Reactions (enzymes) Movement (ex: muscle proteins) Transport (ex: hemoglobin transporting oxygen in red blood cells) ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Ch. 6 Cellular Respiration
... Cells use many kinds of organic molecules as fuel for cellular respiration ...
... Cells use many kinds of organic molecules as fuel for cellular respiration ...
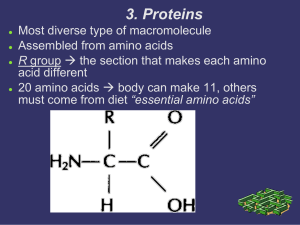
3. Proteins
... Key components of reactions that give energy, and make, or break down compounds Only needed in small amounts ...
... Key components of reactions that give energy, and make, or break down compounds Only needed in small amounts ...
Biomolecules - Fall River Public Schools
... ENZYMES are Proteins! Enzymes are important proteins that speed up the chemical reactions in your body • Because they help these reactions happen, they are called catalysts Ex. The enzyme amylase helps break down carbohydrates into sugar when you chew ...
... ENZYMES are Proteins! Enzymes are important proteins that speed up the chemical reactions in your body • Because they help these reactions happen, they are called catalysts Ex. The enzyme amylase helps break down carbohydrates into sugar when you chew ...
Catabolic Pathways and Glycolysis
... Stages of Cellular Respiration • Glycolysis • Citric Acid Cycle • Oxidative Phosphorylation ...
... Stages of Cellular Respiration • Glycolysis • Citric Acid Cycle • Oxidative Phosphorylation ...
SMicroChapter5
... 1. Every cell acquires nutrients 2. Metabolism requires energy from light or from catabolism of nutrients 3. Energy is stored in adenosine triphosphate (ATP) 4. Cells catabolize nutrients to form precursor metabolites 5. Precursor metabolites, energy from ATP, and enzymes used in anabolic reactions ...
... 1. Every cell acquires nutrients 2. Metabolism requires energy from light or from catabolism of nutrients 3. Energy is stored in adenosine triphosphate (ATP) 4. Cells catabolize nutrients to form precursor metabolites 5. Precursor metabolites, energy from ATP, and enzymes used in anabolic reactions ...
Carbon compounds class web14
... • Can form up to 4 bonds. • It can form single, double or triple bonds with other atoms. • Carbon is central to large, organic molecules • It is the ‘backbone’ of the molecule. ...
... • Can form up to 4 bonds. • It can form single, double or triple bonds with other atoms. • Carbon is central to large, organic molecules • It is the ‘backbone’ of the molecule. ...
Topic Vocabulary Test A
... Organ system - several organs may work together to perform one of the life processes Organelle - specialized structures found in cells that have specific life maintenance functions Organic - Molecules that contain BOTH carbon and hydrogen Receptor molecule - proteins found in the cell membrane that ...
... Organ system - several organs may work together to perform one of the life processes Organelle - specialized structures found in cells that have specific life maintenance functions Organic - Molecules that contain BOTH carbon and hydrogen Receptor molecule - proteins found in the cell membrane that ...
Chemistry of Living Things
... A. Water (H2O) Most common substance in all living things (about 60% of body mass) ...
... A. Water (H2O) Most common substance in all living things (about 60% of body mass) ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.