Biomolecules PPT
... hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom are removed from the monomers to form water, and the two monomers are joined together. ...
... hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom are removed from the monomers to form water, and the two monomers are joined together. ...
Document
... • NADH and FADH2 carry electrons to the ETC • ETC series of electron carriers located in cristae of mitochondria • energy from electrons transferred to ________________ • ATP synthase catalyzes the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP • water is formed ...
... • NADH and FADH2 carry electrons to the ETC • ETC series of electron carriers located in cristae of mitochondria • energy from electrons transferred to ________________ • ATP synthase catalyzes the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP • water is formed ...
word
... Plasma membrane structure and components What are the main components of phospholipid bilayer? Diagram the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure What is the role of cholesterol in cell membrane? What are the 3 functions of the cell membrane? What are the major functions of fats and phospholipids ...
... Plasma membrane structure and components What are the main components of phospholipid bilayer? Diagram the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure What is the role of cholesterol in cell membrane? What are the 3 functions of the cell membrane? What are the major functions of fats and phospholipids ...
I-1 I. Introduction BIOCHEMISTRY = METABOLISM At first you may
... that serve as the "raw" materials in the production of new cellular matter. Some of them (e.g. sugars, amino acids, fatty acids) are obtained after rather minimal processing of food while others e.g. pyruvate, acetyl CoA, NADH (usually after conversion to NADPH) and some tricarboxylic acid cycle (se ...
... that serve as the "raw" materials in the production of new cellular matter. Some of them (e.g. sugars, amino acids, fatty acids) are obtained after rather minimal processing of food while others e.g. pyruvate, acetyl CoA, NADH (usually after conversion to NADPH) and some tricarboxylic acid cycle (se ...
Completed Note
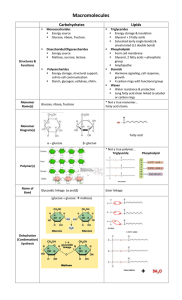
... Long fatty acid chain linked to alcohol or carbon rings * Not a true monomer… Fatty acid chains ...
... Long fatty acid chain linked to alcohol or carbon rings * Not a true monomer… Fatty acid chains ...
Remember: Condensation makes bonds: Hydrolysis breaks bonds.
... IB Biology 3.2 Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins ...
... IB Biology 3.2 Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins ...
First Five 8/26/11
... Ammonia is found in urine as a waste product of breaking down proteins. Carbon dioxide is a waste product that we exhale. ...
... Ammonia is found in urine as a waste product of breaking down proteins. Carbon dioxide is a waste product that we exhale. ...
Chapter 2 Cell Chemistry
... 3. Define acid and base, and explain the concept of pH. 4. Explain the role of dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis in the formation and breakdown of organic molecules. 5. Describe and compare the building blocks, general structures, and biological functions of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and n ...
... 3. Define acid and base, and explain the concept of pH. 4. Explain the role of dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis in the formation and breakdown of organic molecules. 5. Describe and compare the building blocks, general structures, and biological functions of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and n ...
Jim Bidlack - BIO 1114 GENERAL BIOLOGY Lectures 6 and 7
... Glycerol and related compounds - FAT STORAGE, COATING, & MEMBRANES a) Triglycerides (fat) - linoleic and linolenic acid b) Coating (wax, cutin) - ester (RCOOR) of above with 20 - 28 carbons c) ...
... Glycerol and related compounds - FAT STORAGE, COATING, & MEMBRANES a) Triglycerides (fat) - linoleic and linolenic acid b) Coating (wax, cutin) - ester (RCOOR) of above with 20 - 28 carbons c) ...
BIOS 1300 SI WORKSHEET 2 (Chapter 2) SI Leader: Merrin Jeffries
... 18.On average, lipids provide roughly twice as much energy as carbohydrates do, gram for gram, when broken down in the body. T/F ...
... 18.On average, lipids provide roughly twice as much energy as carbohydrates do, gram for gram, when broken down in the body. T/F ...
Chapter 6, Section 3
... Organic: contains carbon ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
... Organic: contains carbon ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
Practice Quiz
... 11. Any compound that possesses carbon is said to be _______________ and is typically associated only with living things. 12. Water molecules that stick to each other are said to demonstrate _____________. 13. Weak acids and weak bases help the body to resist shifts in pH and are therefore called __ ...
... 11. Any compound that possesses carbon is said to be _______________ and is typically associated only with living things. 12. Water molecules that stick to each other are said to demonstrate _____________. 13. Weak acids and weak bases help the body to resist shifts in pH and are therefore called __ ...
Facts about Carbon Compounds (Pages 44-48)
... Nucleic acids are made of smaller units called nucleotides which consist of three parts: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. ...
... Nucleic acids are made of smaller units called nucleotides which consist of three parts: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. ...
Carbon compounds - Sonoma Valley High School
... • It can form single, double or triple bonds with other atoms. • Carbon is central to large, organic molecules • It is the ‘backbone’ of the molecule. Left side: what does ‘backbone’ mean in this context? ...
... • It can form single, double or triple bonds with other atoms. • Carbon is central to large, organic molecules • It is the ‘backbone’ of the molecule. Left side: what does ‘backbone’ mean in this context? ...
Biology I SB1bc Enzymes and Macromolecules Test Study Guide
... Biology I SB1bc Enzymes and Macromolecules Test Study Guide SB1b Explain how enzymes function as catalysts 1. Describe enzymes. “Reusable” proteins that put together or break down substrates to form products 2. Since enzymes are proteins they are made of ……what? Amino acids joined by peptide bonds 3 ...
... Biology I SB1bc Enzymes and Macromolecules Test Study Guide SB1b Explain how enzymes function as catalysts 1. Describe enzymes. “Reusable” proteins that put together or break down substrates to form products 2. Since enzymes are proteins they are made of ……what? Amino acids joined by peptide bonds 3 ...
Essential Elements
... – Insulin (tells cells they can take in sugar) • Jobs – Performs most of the body’s functions – Fight disease, movement ...
... – Insulin (tells cells they can take in sugar) • Jobs – Performs most of the body’s functions – Fight disease, movement ...
Lesson
... * Stages involved with formation of proteins * Primary, secondary, tertiary & quaternary structures ...
... * Stages involved with formation of proteins * Primary, secondary, tertiary & quaternary structures ...
Practice Exam I
... store energy catalyze reactions contain hereditary information make up membranes ...
... store energy catalyze reactions contain hereditary information make up membranes ...
18.1 Macromolecules
... Which answer best describes how carbohydrates and lipids are similar? A. Both contain fats and oils and have an important structural function within the cell. B. Both are polymers that are linked by peptide bonds. C. Both are nucleic acids involved in making ATP. D. Both contain contain carbon, car ...
... Which answer best describes how carbohydrates and lipids are similar? A. Both contain fats and oils and have an important structural function within the cell. B. Both are polymers that are linked by peptide bonds. C. Both are nucleic acids involved in making ATP. D. Both contain contain carbon, car ...
unit plan 1b with vocab
... • Utilize various tools to test the relative strengths of solutions (pH). • Define and discover that the role of enzymes is to speed up chemical reactions that take place in cells. • List the four groups of organic compounds found in living things: carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. ...
... • Utilize various tools to test the relative strengths of solutions (pH). • Define and discover that the role of enzymes is to speed up chemical reactions that take place in cells. • List the four groups of organic compounds found in living things: carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.