BOTANY DEPARTMENT - university of nairobi staff profiles
... Define homeostatis, differentiate between Homoeotherms and Poikilotherms Distinguish different modes autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition Understand anaerobic and aerobic metabolism and its importance A good understanding of biological reductive and oxidative reactions. Evaluate the function of A ...
... Define homeostatis, differentiate between Homoeotherms and Poikilotherms Distinguish different modes autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition Understand anaerobic and aerobic metabolism and its importance A good understanding of biological reductive and oxidative reactions. Evaluate the function of A ...
Teacher`s Copy Biochem test prep
... They are complex molecules made from smaller molecules. They are used to assemble larger inorganic materials. They are simple molecules used as energy sources. ...
... They are complex molecules made from smaller molecules. They are used to assemble larger inorganic materials. They are simple molecules used as energy sources. ...
Chapter 6, Section 3
... Organic: contains carbon ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
... Organic: contains carbon ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... determines the characteristics of an organism and directs its cell activities • Building block of RNA (____________________) which stores and transfers information from DNA in order to make proteins • Made of ____________________ • Made up of 3 main components ...
... determines the characteristics of an organism and directs its cell activities • Building block of RNA (____________________) which stores and transfers information from DNA in order to make proteins • Made of ____________________ • Made up of 3 main components ...
Nutrients
... and Electron transport chain ii. Glucose actively transported in GI tract then insulin-mediated facilitated diffusion in body cells ...
... and Electron transport chain ii. Glucose actively transported in GI tract then insulin-mediated facilitated diffusion in body cells ...
Macromolecules Notes Macromolecules Notes
... Proteins are also called Polypeptides The monomer is called an amino acid •20 different kinds of amino acids 5 functions of proteins: • Transport (e.g., hemoglobin) • Provides immunity (e.g., immune system) • Regulate the body (e.g., hormones, enzymes, metabolism) • Muscle tissue (e.g., movement) • ...
... Proteins are also called Polypeptides The monomer is called an amino acid •20 different kinds of amino acids 5 functions of proteins: • Transport (e.g., hemoglobin) • Provides immunity (e.g., immune system) • Regulate the body (e.g., hormones, enzymes, metabolism) • Muscle tissue (e.g., movement) • ...
The Chemistry of Life
... a. All enzymes are catalysts, but not all catalysts are enzymes b. Most are proteins c. Speed up reaction or reduce activation energy required ...
... a. All enzymes are catalysts, but not all catalysts are enzymes b. Most are proteins c. Speed up reaction or reduce activation energy required ...
AP Respiration Test Review
... 3. What is the term for the metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules? 4. What is the term for the metabolic pathways that use store energy to build macromoleulces? 5. What is the primary role of the ADP-ATP cycle? 6. What is the difference between reduction an ...
... 3. What is the term for the metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules? 4. What is the term for the metabolic pathways that use store energy to build macromoleulces? 5. What is the primary role of the ADP-ATP cycle? 6. What is the difference between reduction an ...
ReviewExamIII
... How does fermentation allow glycolysis to start up again even in the absence of oxygen? Where in aerobic cellular respiration is the most carbon dioxide released (What set of reactions and where in the cell? What are the products of fermentation for human muscle cells, yeast, and bacteria? Where do ...
... How does fermentation allow glycolysis to start up again even in the absence of oxygen? Where in aerobic cellular respiration is the most carbon dioxide released (What set of reactions and where in the cell? What are the products of fermentation for human muscle cells, yeast, and bacteria? Where do ...
Cell Metabolism
... • Describe the difference between anabolic and catabolic processes, and explain how metabolic pathways can be reversible and irreversible steps as well as alternative processes. • The key role played by specific enzymes in regulating rates of reactions. ...
... • Describe the difference between anabolic and catabolic processes, and explain how metabolic pathways can be reversible and irreversible steps as well as alternative processes. • The key role played by specific enzymes in regulating rates of reactions. ...
2 Biochemistry
... • pH scale- 1 (acid), 7 (water), 14 (base or alkaline) • Acids- digestion HCl in stomach, Acetic Acid, & Carbonic Acid are produced in the body • Bases- Bicarbonate ion (HCO3-) is abundant in the blood, Ammonia (NH3) common waste product of protein breakdown ...
... • pH scale- 1 (acid), 7 (water), 14 (base or alkaline) • Acids- digestion HCl in stomach, Acetic Acid, & Carbonic Acid are produced in the body • Bases- Bicarbonate ion (HCO3-) is abundant in the blood, Ammonia (NH3) common waste product of protein breakdown ...
Annexure `CD-01` L T P/S SW/FW TOTAL CREDIT UNITS 3 0 0 0 3
... Mechanism of enzyme action – Lock and Key model and induced fit models. Coenzymes – cofactors – prosthetic groups of enzymes (TPP, NAD, NADP, FAD, ATP).Their importance in enzyme action. Mechanism of inhibition (competitive, non- and uncompetitive and allosteric) Immobilization of enzymes. Enzyme sp ...
... Mechanism of enzyme action – Lock and Key model and induced fit models. Coenzymes – cofactors – prosthetic groups of enzymes (TPP, NAD, NADP, FAD, ATP).Their importance in enzyme action. Mechanism of inhibition (competitive, non- and uncompetitive and allosteric) Immobilization of enzymes. Enzyme sp ...
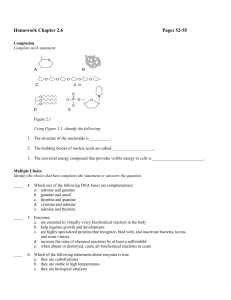
Homework Chapter 2.6 Pages 52-55 Completion Complete each
... ____ 11. Which of the following statements about ATP is false: a. it drives the transport of certain solutes (e.g., amino acids) across cell membranes b. it activates contractile proteins in muscle cells so that cells can shorten and perform mechanical work c. it provides the energy needed to drive ...
... ____ 11. Which of the following statements about ATP is false: a. it drives the transport of certain solutes (e.g., amino acids) across cell membranes b. it activates contractile proteins in muscle cells so that cells can shorten and perform mechanical work c. it provides the energy needed to drive ...
Unit 1 Lesson 3 - Belle Vernon Area School District
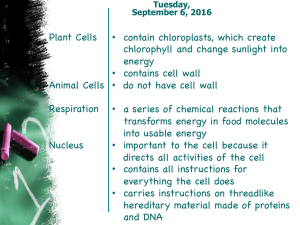
... Cell membrane – determine what enters and leaves the cell Cytoplasm - gel like material that surrounds organelles / contains nutrients Cytoskeleton – protein filament that gives shape/ support to cell Nucleus – contains genetic material (DNA) DNA – stores information for making proteins Nuclear Memb ...
... Cell membrane – determine what enters and leaves the cell Cytoplasm - gel like material that surrounds organelles / contains nutrients Cytoskeleton – protein filament that gives shape/ support to cell Nucleus – contains genetic material (DNA) DNA – stores information for making proteins Nuclear Memb ...
Modern Biology: Chapter 3
... – Small, simple molecules – Amino acid, fatty acid, nucleotide, monosaccharide ...
... – Small, simple molecules – Amino acid, fatty acid, nucleotide, monosaccharide ...
Modern Biology: Chapter 3
... – Small, simple molecules – Amino acid, fatty acid, nucleotide, monosaccharide ...
... – Small, simple molecules – Amino acid, fatty acid, nucleotide, monosaccharide ...
Biological Molecules - Princeton High School
... Enzyme bonds to substrate and the enzyme shape changed slightly The chemical bonds in the substrate are weakened Lowers the activation energy ...
... Enzyme bonds to substrate and the enzyme shape changed slightly The chemical bonds in the substrate are weakened Lowers the activation energy ...
Organic Compounds
... the structure. These are clusters of atoms that behave in a particular manner regardless of how the rest of the molecule looks. ...
... the structure. These are clusters of atoms that behave in a particular manner regardless of how the rest of the molecule looks. ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.