Lecture Resource ()
... In each of these transformations, one of the bonds to the a-carbon of the amino acid substrate is broken in the first step of the reaction ...
... In each of these transformations, one of the bonds to the a-carbon of the amino acid substrate is broken in the first step of the reaction ...
Cellular Chemical Reactions
... called a chemical reaction, bonds between atoms are broken and new bonds to make different molecules. ...
... called a chemical reaction, bonds between atoms are broken and new bonds to make different molecules. ...
... A fat that is solid at room temperature, found in animal fats such as lard and butter. All of its carbon to carbon bonds are single. Too much of this can increase the chance of cardiovascular disease 11. What are unsaturated fats? A fat that contains fewer numbers of hydrogen (less stored energy) a ...
Chemical Principles
... synthesis rx. Glycosidic bond between two adjacent monosaccharides. Glucose + fructose ----- sucrose Glucose + Galactose ----- Lactose Isomers: have same chemical but different structural formula. ...
... synthesis rx. Glycosidic bond between two adjacent monosaccharides. Glucose + fructose ----- sucrose Glucose + Galactose ----- Lactose Isomers: have same chemical but different structural formula. ...
BIO 101 Exam 2 Practice Quiz Name
... 2. _____ differ in the number of neutrons they contain, but all have the same chemical properties. a. Isotopes b. Organic Molecules c. Amino Acids d. Macromolecules 3. The atomic number for Neon is a. 13 b. 22 ...
... 2. _____ differ in the number of neutrons they contain, but all have the same chemical properties. a. Isotopes b. Organic Molecules c. Amino Acids d. Macromolecules 3. The atomic number for Neon is a. 13 b. 22 ...
Macro-molecule study guide / worksheet
... 3. There are two basic kinds of nucleic acids. Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) which contains the sugar ribose and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) which contains the sugar deoxyribose. 4. DNA - 2 strands of nucleotides; RNA - 1 strand of nucleotides Enzymes - with few exceptions, they are proteins Catalyst - sub ...
... 3. There are two basic kinds of nucleic acids. Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) which contains the sugar ribose and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) which contains the sugar deoxyribose. 4. DNA - 2 strands of nucleotides; RNA - 1 strand of nucleotides Enzymes - with few exceptions, they are proteins Catalyst - sub ...
Name: Date: Per: ______ Study Guide for AP Biology CHEMISTRY
... 1. Give 2 examples of a Hydrogen Bond (in proteins and nucleic acids) ...
... 1. Give 2 examples of a Hydrogen Bond (in proteins and nucleic acids) ...
2-A Chemical Compounds of Life Organic Compounds
... A. Contain the element carbon, in chains or rings, and hydrogen. B. Built by combining monomers (single molecules) into polymers (many molecules) ...
... A. Contain the element carbon, in chains or rings, and hydrogen. B. Built by combining monomers (single molecules) into polymers (many molecules) ...
Chemistry of Life
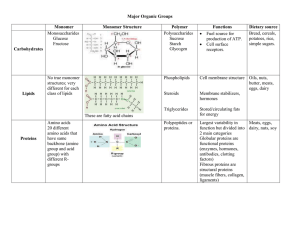
... Macromolecules of Life 4 Macromolecules of life – Carbohydrates – Lipids – Proteins – Nucleic Acids These four macromolecules make up ...
... Macromolecules of Life 4 Macromolecules of life – Carbohydrates – Lipids – Proteins – Nucleic Acids These four macromolecules make up ...
Chapter 3 Review
... • A class of organic compounds made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in a 1:2:1 ratio ...
... • A class of organic compounds made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in a 1:2:1 ratio ...
Molecules of Life Worksheet
... 22. Most lipids are made of ______________ acids. Describe their shape. What functional group is found on the head end of the molecule? 23. Are both ends of a fatty acid polar? Explain. 24. Hydrophilic means water ___________. Which end of a fatty acid is hydrophilic? The non-polar end of a fatty a ...
... 22. Most lipids are made of ______________ acids. Describe their shape. What functional group is found on the head end of the molecule? 23. Are both ends of a fatty acid polar? Explain. 24. Hydrophilic means water ___________. Which end of a fatty acid is hydrophilic? The non-polar end of a fatty a ...
Slide 1
... • Imbedded in the inner mitochondria membrane are a series of electron carriers. These electron carriers pass electrons from NADH and FADH to one another down a red-ox stairway. The net result of this series of step-wise electron exchanges is to pump H+ (protons) out of the matrix into the outer com ...
... • Imbedded in the inner mitochondria membrane are a series of electron carriers. These electron carriers pass electrons from NADH and FADH to one another down a red-ox stairway. The net result of this series of step-wise electron exchanges is to pump H+ (protons) out of the matrix into the outer com ...
Ch 2 - Biochemistry
... usually in ratio of 1:2:1 (glucose is C6H12O6; ribose is C5H10O5) Glucose (blood sugar) is called the universal cellular fuel. 1 g carb= 4 Calories monosaccharide - one unit (simple sugars), single chain or single ring; glucose, fructose, galactose, ribose, deoxyribose disaccharide - double sugars; ...
... usually in ratio of 1:2:1 (glucose is C6H12O6; ribose is C5H10O5) Glucose (blood sugar) is called the universal cellular fuel. 1 g carb= 4 Calories monosaccharide - one unit (simple sugars), single chain or single ring; glucose, fructose, galactose, ribose, deoxyribose disaccharide - double sugars; ...
Unit 3 Biochemistry - The Naked Science Society
... Living things require millions of chemical reactions within the body, just to survive. Metabolism = all the chemical reactions occurring in the body. Organic molecules: ...
... Living things require millions of chemical reactions within the body, just to survive. Metabolism = all the chemical reactions occurring in the body. Organic molecules: ...
→ Why organisms need food: → Elements in Food: → Carbohydrates:
... Elements in Food: o 6 chemical elements: Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Phosphorus Sulfur Nitrogen o Salts of: Sodium Magnesium Chlorine Potassium Calcium o 3 Trace elements: Iron Copper Zinc Biomolecules: Chemicals that are made inside a living thing. o The 4 main types foun ...
... Elements in Food: o 6 chemical elements: Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Phosphorus Sulfur Nitrogen o Salts of: Sodium Magnesium Chlorine Potassium Calcium o 3 Trace elements: Iron Copper Zinc Biomolecules: Chemicals that are made inside a living thing. o The 4 main types foun ...
Modern Biology: Chapter 3
... – Small, simple molecules – Amino acid, fatty acid, nucleotide, monosaccharide ...
... – Small, simple molecules – Amino acid, fatty acid, nucleotide, monosaccharide ...
PP Ch_ 2-3 Modified - Maria Regina High School
... Enzymes are substrate specific (One enzyme for a particular reaction will not work with substrates from another particular reaction) Because of the specific fit, the ES Complex is called a LOCK AND KEY COMPLEX ...
... Enzymes are substrate specific (One enzyme for a particular reaction will not work with substrates from another particular reaction) Because of the specific fit, the ES Complex is called a LOCK AND KEY COMPLEX ...
Biochemistry Study Guide – Exam 1
... Endergonic and exergonic reactions Relationship between free energy and the equilibrium constant Role of ATP (phosphate group transfer potential) Physical connection of ATP hydrolysis to endergonic reaction Coupled reactions: exergonic reactions can pull or push endergonic reactions in a metabolic ...
... Endergonic and exergonic reactions Relationship between free energy and the equilibrium constant Role of ATP (phosphate group transfer potential) Physical connection of ATP hydrolysis to endergonic reaction Coupled reactions: exergonic reactions can pull or push endergonic reactions in a metabolic ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.