Atomic Structure PPT Notes Sheet
... 32. A _______________ is a substance that is made up of different elements. The atoms of the elements are joined together by _________________. Bonds are chemical connections between atoms. 33. There are two basic types of bonds: ____________________ and ______________________. The reason that bonds ...
... 32. A _______________ is a substance that is made up of different elements. The atoms of the elements are joined together by _________________. Bonds are chemical connections between atoms. 33. There are two basic types of bonds: ____________________ and ______________________. The reason that bonds ...
Comprehensive Science 3 Module 4 Practice Test
... Different elements are made up of different atoms Atoms of different elements combine to make different compounds 5. The elements listed at the far right side of the periodic table are _______. Metalloids Nonmetals Metals Transitional Metals ...
... Different elements are made up of different atoms Atoms of different elements combine to make different compounds 5. The elements listed at the far right side of the periodic table are _______. Metalloids Nonmetals Metals Transitional Metals ...
CP Chemistry First Semester Final Exam 1
... ____ 1. Reactants ____ 2. Metals ____ 3. Ionic bond ____ 4. Atomic number ____ 5. Isoelectronic ____ 6. Quantum ____ 7. JJ Thomson ____ 8. Anion ____ 9. Cation ____ 10. Mendeleev ____ 11. Atomic mass ____ 12. Covalent bond ...
... ____ 1. Reactants ____ 2. Metals ____ 3. Ionic bond ____ 4. Atomic number ____ 5. Isoelectronic ____ 6. Quantum ____ 7. JJ Thomson ____ 8. Anion ____ 9. Cation ____ 10. Mendeleev ____ 11. Atomic mass ____ 12. Covalent bond ...
Elements - Heartland
... 1/12 of the mass of a Carbon atom with 6 protons and 6 neutrons. A neutron has no charge, but does have a mass of about 1 amu. An electron has a –1 charge and a mass so small that we usually say that it weighs 0 amu. ...
... 1/12 of the mass of a Carbon atom with 6 protons and 6 neutrons. A neutron has no charge, but does have a mass of about 1 amu. An electron has a –1 charge and a mass so small that we usually say that it weighs 0 amu. ...
First Semester Honors Chemistry Exam Review (2011
... 41. What is the element with electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2 ? 1s2 2s2 2p2 ? 42. The atomic number of silicon is… 43. What is the electron configuration for nitrogen, atomic number 7? 44. Mendeleev noticed that properties of elements usually repeated at regular intervals when the elements ...
... 41. What is the element with electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2 ? 1s2 2s2 2p2 ? 42. The atomic number of silicon is… 43. What is the electron configuration for nitrogen, atomic number 7? 44. Mendeleev noticed that properties of elements usually repeated at regular intervals when the elements ...
What is Matter? Anything that can be smelled, tasted, touched… Has
... First organized using the known properties from other chemists like Stanislao Cannizzaro, Dmitri Mendeleev created the table of elements in 1869 of elements Organized horizontally Indicates # of electron levels of elements Organized vertically Indicates # of electrons in outer cloud (# of P+) (Often ...
... First organized using the known properties from other chemists like Stanislao Cannizzaro, Dmitri Mendeleev created the table of elements in 1869 of elements Organized horizontally Indicates # of electron levels of elements Organized vertically Indicates # of electrons in outer cloud (# of P+) (Often ...
17 review for test - Blair Community Schools
... What is the atomic mass? What determines that identity of an atom? What happens to metallic properties as one goes across the table? ...
... What is the atomic mass? What determines that identity of an atom? What happens to metallic properties as one goes across the table? ...
Atomic theory
... different properties, including mass and chemical reactivity. 4. Atoms are not changed by chemical reactions, but merely rearranged into different compounds. ...
... different properties, including mass and chemical reactivity. 4. Atoms are not changed by chemical reactions, but merely rearranged into different compounds. ...
Atoms: The building blocks of matter
... ○ The law of conservation of mass. ○ The law of definite proportions. ○ The law of multiple proportions. ...
... ○ The law of conservation of mass. ○ The law of definite proportions. ○ The law of multiple proportions. ...
ATOMIC THEORY
... 3. Law of Multiple Proportions- if two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses is always a ratio of small whole numbers. (John Dalton 1804) C. Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. In 1810, Dalton published the ideas of the atomic theory, explaining that a ...
... 3. Law of Multiple Proportions- if two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses is always a ratio of small whole numbers. (John Dalton 1804) C. Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. In 1810, Dalton published the ideas of the atomic theory, explaining that a ...
Atoms and Atomic Structure
... one element differ from those of another. • Compounds form when atoms of elements combine in certain proportions • During chemical reactions, atoms are rearranged, not changed or destroyed. ...
... one element differ from those of another. • Compounds form when atoms of elements combine in certain proportions • During chemical reactions, atoms are rearranged, not changed or destroyed. ...
Chapter 18 Atoms and Elements
... 1. Mass number- the total number of _______________ (in the nucleus). * Atoms of the same element ________ have different number of ___________, which means the mass can vary. 2. Atomic Mass- the average of ________________ of an element. ...
... 1. Mass number- the total number of _______________ (in the nucleus). * Atoms of the same element ________ have different number of ___________, which means the mass can vary. 2. Atomic Mass- the average of ________________ of an element. ...
Word format
... Example: carbon can exist in 3 forms: _______________________________ The average weight of an atom of any element, taking into account the relative abundances of the different isotopes of that element, is called the _________________. Ions Ions are what we get when the electrons partnered with one ...
... Example: carbon can exist in 3 forms: _______________________________ The average weight of an atom of any element, taking into account the relative abundances of the different isotopes of that element, is called the _________________. Ions Ions are what we get when the electrons partnered with one ...
pdf format
... Example: carbon can exist in 3 forms: _______________________________ The average weight of an atom of any element, taking into account the relative abundances of the different isotopes of that element, is called the _________________. Ions Ions are what we get when the electrons partnered with one ...
... Example: carbon can exist in 3 forms: _______________________________ The average weight of an atom of any element, taking into account the relative abundances of the different isotopes of that element, is called the _________________. Ions Ions are what we get when the electrons partnered with one ...
Quiz: The Atom (Open Notes)
... 10. T or F A neutron carries a positive charge. 11. T or F A proton has a charge that is equal in force but opposite in charge to each electron. 12. T or F Protons and electrons are about equal in mass. 13. T or F The mass of an atom depends on the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. 14. ...
... 10. T or F A neutron carries a positive charge. 11. T or F A proton has a charge that is equal in force but opposite in charge to each electron. 12. T or F Protons and electrons are about equal in mass. 13. T or F The mass of an atom depends on the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. 14. ...
Chapter 2—Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... • In 1911, Rutherford proved the existence of the proton with his nowfamous gold-foil experiment • He shot α-particles at the foil…most passed through, but some were reflected back at the fluorescent ...
... • In 1911, Rutherford proved the existence of the proton with his nowfamous gold-foil experiment • He shot α-particles at the foil…most passed through, but some were reflected back at the fluorescent ...
The atom - WordPress.com
... The average of all the known isotopes of an element give the element its average atomic mass. Elements on the periodic table have decimals in their masses for this reason (and because they are all based on Carbon-12) ...
... The average of all the known isotopes of an element give the element its average atomic mass. Elements on the periodic table have decimals in their masses for this reason (and because they are all based on Carbon-12) ...
Chem 400 Chem 150 REVIEW SHEET Amanda R
... o Counting valence electrons, electron configuration o Atomic radii increases to the left and down o Electron Affinity/Ionization Energy and electronegativity increases going up and to the right Types of Bonds – must know which bond types can form and how o Covalent o Ionic o Molecular o Bond order ...
... o Counting valence electrons, electron configuration o Atomic radii increases to the left and down o Electron Affinity/Ionization Energy and electronegativity increases going up and to the right Types of Bonds – must know which bond types can form and how o Covalent o Ionic o Molecular o Bond order ...
atomic structure - IGCSE STUDY BANK
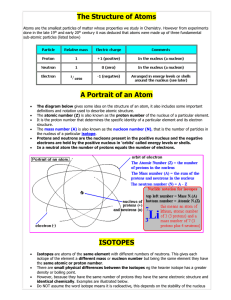
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. This gives each isotope of the element a different mass or nucleon number but being the same element they have the same atomic or proton number. There are small physical differences between the isotopes eg the heavier isotope ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. This gives each isotope of the element a different mass or nucleon number but being the same element they have the same atomic or proton number. There are small physical differences between the isotopes eg the heavier isotope ...
Atomic structure and periodic table
... The noble gas configuration All members of group 0, except helium have 8 outermost electrons. This is a very stable arrangement called a stable octet, and these elements do not take part in chemical reactions Atoms tend to attain noble state/structure by loosing, gaining or sharing of electron ...
... The noble gas configuration All members of group 0, except helium have 8 outermost electrons. This is a very stable arrangement called a stable octet, and these elements do not take part in chemical reactions Atoms tend to attain noble state/structure by loosing, gaining or sharing of electron ...
The History of the Atom Carousel Who-What-When
... ‘airs’ or gasses. In one of his experiments he isolated and ‘discovered’ a new gas – oxygen, in 1772. He visited Antoine Lavoisier in France and explained what he had done. Lavoisier was a noted scientist who used better methodology and measurements in his work. For Priestly’s ‘air’ he ‘invented’ th ...
... ‘airs’ or gasses. In one of his experiments he isolated and ‘discovered’ a new gas – oxygen, in 1772. He visited Antoine Lavoisier in France and explained what he had done. Lavoisier was a noted scientist who used better methodology and measurements in his work. For Priestly’s ‘air’ he ‘invented’ th ...
First 9 weeks Study Guide 8th Grade
... The protons give you an elements identity. The protons give you the atomic number which is like the address for that element on the periodic table. The atomic mass is the sum (the total) of the protons and neutrons. ...
... The protons give you an elements identity. The protons give you the atomic number which is like the address for that element on the periodic table. The atomic mass is the sum (the total) of the protons and neutrons. ...