Classifying Matter and the Periodic Table
... Dalton’s atomic theory of matter • each element is composed of extremely small particles called atoms • all atoms of a given element are identical, but they differ from those of other any other element ...
... Dalton’s atomic theory of matter • each element is composed of extremely small particles called atoms • all atoms of a given element are identical, but they differ from those of other any other element ...
Unit 2 Overview
... periodic table possesses. In part two, we will relate the number of neutrons to the formation of isotopes which are linked to radioactive behavior allowing us to study many applications of radioactivity in everyday life. In part three, we will seek to understand how the electron is inextricably link ...
... periodic table possesses. In part two, we will relate the number of neutrons to the formation of isotopes which are linked to radioactive behavior allowing us to study many applications of radioactivity in everyday life. In part three, we will seek to understand how the electron is inextricably link ...
Chapter 1 Learning Objective Summary
... and understand fission and fusion Chemical reactions involve the gain, loss, or sharing of the outer electrons, whereas nuclear reactions involve changes to the composition of the nucleus. This means that alchemy is possible (though not economical!), because transmutation of one element into another ...
... and understand fission and fusion Chemical reactions involve the gain, loss, or sharing of the outer electrons, whereas nuclear reactions involve changes to the composition of the nucleus. This means that alchemy is possible (though not economical!), because transmutation of one element into another ...
Pre-Knowledge: Chemistry and Physics Vocabulary Atomic Number
... The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of an atom. Nucleus The small “core” of the atom, where most of its mass and all of its positive charge is concentrated. Except for ordinary hydrogen (which has only a proton), atomic nuclei consist of protons and neutrons. For this reason ...
... The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of an atom. Nucleus The small “core” of the atom, where most of its mass and all of its positive charge is concentrated. Except for ordinary hydrogen (which has only a proton), atomic nuclei consist of protons and neutrons. For this reason ...
Chapter 4.1
... 1. Protons – positive particles in the nucleus -charge is +1 -# protons = atomic # 2. Electrons – negative particles on orbits around the nucleus -charge is -1 -# electons = # protons= atomic # 3. Neutrons – neutral particles in the nucleus -charge is 0 -#neutrons= mass-atomic # ...
... 1. Protons – positive particles in the nucleus -charge is +1 -# protons = atomic # 2. Electrons – negative particles on orbits around the nucleus -charge is -1 -# electons = # protons= atomic # 3. Neutrons – neutral particles in the nucleus -charge is 0 -#neutrons= mass-atomic # ...
Gr 10 Review sheet chemistry
... Ex. For calcium nitrate 2Ca(NO3)2 The coefficient (2) applies to all elements: Therefore, 2 Ca atoms total 2 N atoms 2 O atoms The subscript 3 only follows O so we have 2 x 3 O = 6 O The subscript 2 is outside brackets, so it applies to N and O Therefore, 2 x 6 O = 12 oxygen atoms total 2 x 2 N = 4 ...
... Ex. For calcium nitrate 2Ca(NO3)2 The coefficient (2) applies to all elements: Therefore, 2 Ca atoms total 2 N atoms 2 O atoms The subscript 3 only follows O so we have 2 x 3 O = 6 O The subscript 2 is outside brackets, so it applies to N and O Therefore, 2 x 6 O = 12 oxygen atoms total 2 x 2 N = 4 ...
the atomic theory
... 3. Ernest Rutherford 4. James Chadwick 5. Neils Bohr 6. nucleus 7. proton 8. neutron 9. electron 10. shell 11. atomic number 12. atomic mass 13. Bohr Model 14. subatomic particle 15. isotope 16. empty bus seat rule B/ THE HISTORY OF THE ATOM: - John Dalton ...
... 3. Ernest Rutherford 4. James Chadwick 5. Neils Bohr 6. nucleus 7. proton 8. neutron 9. electron 10. shell 11. atomic number 12. atomic mass 13. Bohr Model 14. subatomic particle 15. isotope 16. empty bus seat rule B/ THE HISTORY OF THE ATOM: - John Dalton ...
CHAPTER6_MEET_THE_ELEMENTS
... Atomic number – is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. This number is ABOVE the element’s symbol. An element’s position in the periodic table is determined by it’s atomic number. The atomic number (number of protons) makes each element unique from the others. Vertical columns are calle ...
... Atomic number – is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. This number is ABOVE the element’s symbol. An element’s position in the periodic table is determined by it’s atomic number. The atomic number (number of protons) makes each element unique from the others. Vertical columns are calle ...
CHAPTER 3 sec 1 - Leon County Schools
... Can you still see it? NO? Of course not, it’s been reduced to the size of an ...
... Can you still see it? NO? Of course not, it’s been reduced to the size of an ...
Unit Description - Honors Chemistry
... Use the Aufbau Principle, the Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund’s Rule to write the electron configurations and orbital diagrams of the elements (5.3) Relate valence electrons to Lewis (electron dot) structures (5.3) Describe the ground-state arrangement of electrons in atoms of any element u ...
... Use the Aufbau Principle, the Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund’s Rule to write the electron configurations and orbital diagrams of the elements (5.3) Relate valence electrons to Lewis (electron dot) structures (5.3) Describe the ground-state arrangement of electrons in atoms of any element u ...
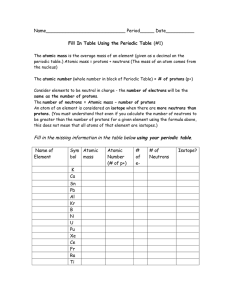
Periodic Table Fill in Table 1
... The atomic mass is the average mass of an element (given as a decimal on the periodic table.) Atomic mass = protons + neutrons (The mass of an atom comes from the nucleus) The atomic number (whole number in block of Periodic Table) = # of protons (p+) Consider elements to be neutral in charge - the ...
... The atomic mass is the average mass of an element (given as a decimal on the periodic table.) Atomic mass = protons + neutrons (The mass of an atom comes from the nucleus) The atomic number (whole number in block of Periodic Table) = # of protons (p+) Consider elements to be neutral in charge - the ...
key - Greenslime.info
... Which of the following elements is most reactive: carbon, sodium, magnesium, boron? Most reactive is sodium, followed by magnesium, boron and then carbon. Why? Sodium only has one valence electron to lose in order to react. Magnesium has two valance electrons, boron has three, and carbon has four. T ...
... Which of the following elements is most reactive: carbon, sodium, magnesium, boron? Most reactive is sodium, followed by magnesium, boron and then carbon. Why? Sodium only has one valence electron to lose in order to react. Magnesium has two valance electrons, boron has three, and carbon has four. T ...
Semester 1 Exam Review Part 1
... are positively (+)charged Neutrons are neutral (0) Electrons are negatively (-)charged ...
... are positively (+)charged Neutrons are neutral (0) Electrons are negatively (-)charged ...
Name Period _____ Chemistry Review
... ____ 13. A change that produces one or more new substances is called a physical change. _________________________ ____ 14. A(n) pure substance is made of only one kind of matter and has definite properties. _________________________ ____ 15. A substance that undergoes a chemical change is still the ...
... ____ 13. A change that produces one or more new substances is called a physical change. _________________________ ____ 14. A(n) pure substance is made of only one kind of matter and has definite properties. _________________________ ____ 15. A substance that undergoes a chemical change is still the ...
CH 115 Fall 2014Exam I Review Brief overview of topics/concepts to
... What does it mean for something to be quantized? Four quantum numbers – Range Abbreviation What do they each determine What makes a set of quantum numbers invalid Know shapes of the s and p orbitals Electron configurations – Pauli exclusion principle Hund’s rule Aufbau principle Co ...
... What does it mean for something to be quantized? Four quantum numbers – Range Abbreviation What do they each determine What makes a set of quantum numbers invalid Know shapes of the s and p orbitals Electron configurations – Pauli exclusion principle Hund’s rule Aufbau principle Co ...
(null): 096.AtomReview
... a. Each specific color tells us about the structure of specific electrons inside the atom b. Zinc spectrum s different from ANY other element (compare to sulfur and helium on same slide) E. Atomic structure basics (see AtomOverview.ppt) – what we’ve learned by seeing without seeing … 1. PROTONS: a. ...
... a. Each specific color tells us about the structure of specific electrons inside the atom b. Zinc spectrum s different from ANY other element (compare to sulfur and helium on same slide) E. Atomic structure basics (see AtomOverview.ppt) – what we’ve learned by seeing without seeing … 1. PROTONS: a. ...
Atom - Sites
... atoms join together chemically. •Combinations of two or more different elements are called compounds. •All compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds. (ex. H2O vs. O2) •Molecules can also join together to form larger molecules. •Many, many repeating small molecules joined together f ...
... atoms join together chemically. •Combinations of two or more different elements are called compounds. •All compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds. (ex. H2O vs. O2) •Molecules can also join together to form larger molecules. •Many, many repeating small molecules joined together f ...
Section 2.1
... • All atoms of a given element are identical to one another in mass and other properties, but atoms of an element are unique to that element only. • Atoms of an element are not changed into atoms of a different element by chemical reactions; they are neither created nor destroyed. • Compounds are fo ...
... • All atoms of a given element are identical to one another in mass and other properties, but atoms of an element are unique to that element only. • Atoms of an element are not changed into atoms of a different element by chemical reactions; they are neither created nor destroyed. • Compounds are fo ...
The Periodic Table - Harlan Independent Schools
... bonds (carbon and silicon) Charge is +4 or -4—contains 4 valence electrons This family includes a non-metal (carbon), metalloids, and metals. The element carbon is called the “basis of life.” There is an entire branch of chemistry devoted to carbon compounds called ...
... bonds (carbon and silicon) Charge is +4 or -4—contains 4 valence electrons This family includes a non-metal (carbon), metalloids, and metals. The element carbon is called the “basis of life.” There is an entire branch of chemistry devoted to carbon compounds called ...
Atomic Structure AKS Correlation Use the modern atomic theory to
... Discovered e-, experiment, predictable shells, indivisible All matter made of plum pudding discovered p+, Bohr model 1st to think atoms model Atoms mostly about matter Matter cannot be empty space, dense and its’ makecreated or center up of atoms destroyed Atoms of same element look the same Chem re ...
... Discovered e-, experiment, predictable shells, indivisible All matter made of plum pudding discovered p+, Bohr model 1st to think atoms model Atoms mostly about matter Matter cannot be empty space, dense and its’ makecreated or center up of atoms destroyed Atoms of same element look the same Chem re ...
Early Chemistry Development of the Atomic Model
... Dalton publishes "A New System of Chemical Philosophy" the first modern atomic model 1- Each element is made up of tiny particles called atoms. 2- The atoms of a given element are identical; the atoms of different elements are different in a fundamental way. 3- Chemical compounds are formed when ele ...
... Dalton publishes "A New System of Chemical Philosophy" the first modern atomic model 1- Each element is made up of tiny particles called atoms. 2- The atoms of a given element are identical; the atoms of different elements are different in a fundamental way. 3- Chemical compounds are formed when ele ...
Atomic Theory - rlhonorschem4
... » 1.All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. » 2. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties.' » 3.Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed. » 4.Atoms of different ...
... » 1.All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. » 2. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties.' » 3.Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed. » 4.Atoms of different ...
Chemistry Presentation: Part One
... Non-Newtonian substances sometimes behave like a solid and sometimes like a liquid ...
... Non-Newtonian substances sometimes behave like a solid and sometimes like a liquid ...
Chapter 4
... Nonmetals: solid, liquid or gas, do not conduct electricity (except graphite) Metalloids (Semimetals): between metals and nonmetals ...
... Nonmetals: solid, liquid or gas, do not conduct electricity (except graphite) Metalloids (Semimetals): between metals and nonmetals ...
answers
... c.) Rutherford – discovered positively charged nucleus d.) Bohr – solar system model of atoms, energy levels at increasing distance from nucleus ...
... c.) Rutherford – discovered positively charged nucleus d.) Bohr – solar system model of atoms, energy levels at increasing distance from nucleus ...