ch2_objectives
... 4. Draw and label a simplified model of an atom. Explain how this model simplifies our understanding of atomic structure. 5. Distinguish between each of the following pairs of terms: a. neutron and proton b. atomic number and mass number c. atomic weight and mass number 6. Explain how the atomic num ...
... 4. Draw and label a simplified model of an atom. Explain how this model simplifies our understanding of atomic structure. 5. Distinguish between each of the following pairs of terms: a. neutron and proton b. atomic number and mass number c. atomic weight and mass number 6. Explain how the atomic num ...
Chapter 8: Chemical Reactions and Physical Changes
... around the nucleus • Mass number: total protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus • Atomic mass: the average mass of a sample of atoms of that element found in nature • Periodic table: chart that arranges elements by atomic number into rows and columns according to similarities in their properties ...
... around the nucleus • Mass number: total protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus • Atomic mass: the average mass of a sample of atoms of that element found in nature • Periodic table: chart that arranges elements by atomic number into rows and columns according to similarities in their properties ...
PP - myndrs.com
... – Gives the order of elements on the periodic table – If an atom gains or loses a proton it not only changes its atomic number, it also becomes a new element. ...
... – Gives the order of elements on the periodic table – If an atom gains or loses a proton it not only changes its atomic number, it also becomes a new element. ...
Structure of an Atom structure_of_atom
... – Gives the order of elements on the periodic table – If an atom gains or loses a proton it not only changes its atomic number, it also becomes a new element. ...
... – Gives the order of elements on the periodic table – If an atom gains or loses a proton it not only changes its atomic number, it also becomes a new element. ...
Periodic Table Test Review
... (TEKS 6.6B) Calculate density to identify an unknown substance. 6. What is density and how is it determined? (TEKS 8.5C) Interpret the arrangement of the Periodic Table, including groups and periods, to explain how properties are used to classify elements. 7. What are the 4 ways elements are arrange ...
... (TEKS 6.6B) Calculate density to identify an unknown substance. 6. What is density and how is it determined? (TEKS 8.5C) Interpret the arrangement of the Periodic Table, including groups and periods, to explain how properties are used to classify elements. 7. What are the 4 ways elements are arrange ...
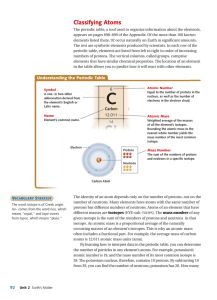
Classifying Atoms
... The periodic table, a tool used to organize information about the elements, appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the perio ...
... The periodic table, a tool used to organize information about the elements, appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the perio ...
Chemistry Exam Review
... Isotope • an atom with a different number of neutrons and therefore a different mass ...
... Isotope • an atom with a different number of neutrons and therefore a different mass ...
I can describe an atom and its components I can relate energy levels
... ○ ex)Chlorine atoms have 17 protons but can have 18 or 20 neutrons. ■ There are chlorine atoms with mass #s of 35 and 37. (17+18=35, 17+20=37) ...
... ○ ex)Chlorine atoms have 17 protons but can have 18 or 20 neutrons. ■ There are chlorine atoms with mass #s of 35 and 37. (17+18=35, 17+20=37) ...
Atomic Structure Power Point
... is a form of an element that has the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. The atomic mass on the periodic table reflects the average mass of all of the known isotopes of an element. Each isotope may have different characteristics. ...
... is a form of an element that has the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. The atomic mass on the periodic table reflects the average mass of all of the known isotopes of an element. Each isotope may have different characteristics. ...
Chemical Bonding
... • The subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. • Protons=Positive charge • Neutrons=Neutral charge • Electrons=Negative charge ...
... • The subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. • Protons=Positive charge • Neutrons=Neutral charge • Electrons=Negative charge ...
Chemistry10AtomicTheory
... Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form chemical compounds; a given compound always has the same relative numbers of types of atoms. Atoms cannot be created, divided into smaller particles, nor destroyed in the chemical process; a chemical reaction simply changes th ...
... Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form chemical compounds; a given compound always has the same relative numbers of types of atoms. Atoms cannot be created, divided into smaller particles, nor destroyed in the chemical process; a chemical reaction simply changes th ...
Unit 2 Notes - School City of Hobart
... Nuclear reactions involve changes in atomic nuclei to generate energy. Nuclear Chemistry is the study of those reactions, with an emphasis on their uses in chemistry and their effects on biological systems 21.1 Radioactivity • Nucleon is simply another name for particles in the nucleus (proton/neutr ...
... Nuclear reactions involve changes in atomic nuclei to generate energy. Nuclear Chemistry is the study of those reactions, with an emphasis on their uses in chemistry and their effects on biological systems 21.1 Radioactivity • Nucleon is simply another name for particles in the nucleus (proton/neutr ...
here
... 2. Describe how ionization energy and electronegativity change as you move from left to right along the periodic table and from top to bottom. Explain how all three of these plays a role in determining whether an atom “wants” to give away or take electrons. 3. Define what an atom’s atomic radius is. ...
... 2. Describe how ionization energy and electronegativity change as you move from left to right along the periodic table and from top to bottom. Explain how all three of these plays a role in determining whether an atom “wants” to give away or take electrons. 3. Define what an atom’s atomic radius is. ...
Atom The smallest piece of matter that still has the properties of the
... Sub-atomic particle with negative charge; much smaller than protons and neutrons Located at the center of the atom. Consists of protons and neutrons. Electrons surround the nucleus. Electron found in outermost shell of an atom; determines atoms chemical properties The number of protons in an atom. T ...
... Sub-atomic particle with negative charge; much smaller than protons and neutrons Located at the center of the atom. Consists of protons and neutrons. Electrons surround the nucleus. Electron found in outermost shell of an atom; determines atoms chemical properties The number of protons in an atom. T ...
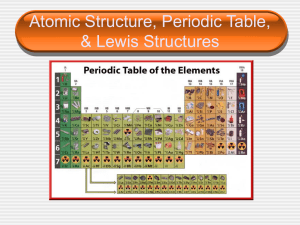
Periodic Table
... Atoms remain unchanged, but the may be rearranged Involve only valence electrons Have small energy changes Reaction rates are influenced by temperature, pressure, concentration, and catalysts ...
... Atoms remain unchanged, but the may be rearranged Involve only valence electrons Have small energy changes Reaction rates are influenced by temperature, pressure, concentration, and catalysts ...
Atoms and Molecules
... • Elements are determined by the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom ...
... • Elements are determined by the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom ...
Vocabulary for Periodic Table
... 3) Nucleus: the central region of an atom where most of the atom’s mass is found in protons and neutrons. 4) Electron: a negatively charged particle located outside an atom’s nucleus. 5) Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. 6) Atomic mass number: the total number of proton ...
... 3) Nucleus: the central region of an atom where most of the atom’s mass is found in protons and neutrons. 4) Electron: a negatively charged particle located outside an atom’s nucleus. 5) Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. 6) Atomic mass number: the total number of proton ...
PP 04 Atoms_ molecules_ ions
... The Law of Constant Composition: Compounds always have the same proportions of the elements within them. The Law of Multiple Proportions: The elements making up a compound will form whole number ratios. Atom: The smallest particle that an element can be broken down into and still maintain the proper ...
... The Law of Constant Composition: Compounds always have the same proportions of the elements within them. The Law of Multiple Proportions: The elements making up a compound will form whole number ratios. Atom: The smallest particle that an element can be broken down into and still maintain the proper ...
PS7aChemistryReviewRevised
... NOW…Keep track of the electrons in the outer energy level! Where on the Periodic Table are the elements with 1 outer ...
... NOW…Keep track of the electrons in the outer energy level! Where on the Periodic Table are the elements with 1 outer ...
chapters 1-4
... A compound is a distinct substance that contains two or more elements combined in a definite proportion by weight. Compounds can be decomposed chemically into simpler substances – that is, into simpler compounds or elements. ...
... A compound is a distinct substance that contains two or more elements combined in a definite proportion by weight. Compounds can be decomposed chemically into simpler substances – that is, into simpler compounds or elements. ...
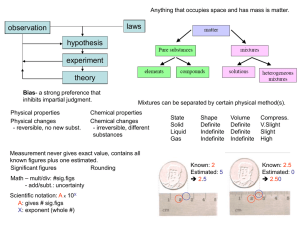
Chapter 18 Notes
... Dimitri Mendeleev (18341907) organized information about all the known elements in a table that visually organized the similarities between them. Mendeleev placed each element on the table in a certain row and column based on its properties. ...
... Dimitri Mendeleev (18341907) organized information about all the known elements in a table that visually organized the similarities between them. Mendeleev placed each element on the table in a certain row and column based on its properties. ...
Atoms and Elements Notes
... number of valence electrons. (Octet Rule) • Number of valence electrons determines how reactive an element is and what type of bonds they form. ...
... number of valence electrons. (Octet Rule) • Number of valence electrons determines how reactive an element is and what type of bonds they form. ...
Metals
... • He did this by studying each element’s melting point, density, color, and atomic mass (average mass of all isotopes of that element) • He predicted the existence of many elements that were discovered later! ...
... • He did this by studying each element’s melting point, density, color, and atomic mass (average mass of all isotopes of that element) • He predicted the existence of many elements that were discovered later! ...