* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemistry Exam Review
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Coordination complex wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Livermorium wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Particle-size distribution wikipedia , lookup
Bond valence method wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Geiger–Marsden experiment wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Alkaline earth metal wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
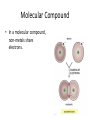
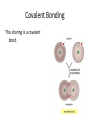
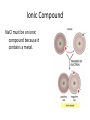
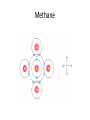
SNC1D: CHEMISTRY Atoms, Elements and Compounds Exam Review Mixture • a substance made of different pure substances Heterogenous • not uniform Homogenous • uniform (in composition and properties) Ex. a solution Pure Substance • a substance made of only one kind of particle Element • a pure substance made of only one kind of atom Compound • a pure substance made of more than one type of atom that have been chemically bonded together Particle Theory of Matter 1. All matter is made of tiny particles. 2. Different pure substances are made up of different types of particles. 3. Particles are always in constant random motion. 4. The particles in a substance attract each other. 5. The particles of a substance move faster when heated. Physical change • a change in which no new substances are produced Ex: ice melting Chemical Change • a change in which new substances are produced Ex: iron rusting Physical Property • description of the nature of a substance Ex: gold is a relatively soft metal Chemical Property • description of how a substance reacts with other substances Ex: iron rusts Element Symbols • • • • Ca Cl Mg Na calcium chlorine magnesium sodium Element Names • • • • Oxygen Iron Argon Tungsten O Fe Ar W Chemical families IA alkali metals IIA alkaline earth metals VIIA halogens VIIIA noble gases Metals • • • • Shiny Malleable Good conductors Found on the left side of the Periodic Table (most reactive: Alkali Metals) Non-Metals • • • • Dull Brittle Poor conductors Found on the right side of the Periodic Table (most reactive: Halogen; least: Noble Gases) Atomic Number • the number of protons in the nucleus Atomic Mass • the number of protons + neutrons in the nucleus Isotope • an atom with a different number of neutrons and therefore a different mass Experiments • Thomson’s cathode ray experiments: atoms contain electrons • Rutherford’s gold foil scattering experiments: atoms contain small, dense, positively-charged nuclei • Bohr’s flame tests: electrons are only found in certain orbits (energy levels) Atomic Numbers Bohr Diagram Magnesium: Rows and Columns • Elements in the 3rd period (row) all have 3 orbits around the nucleus. • Elements in the 1st column all have 1 electron in their outer (valence) orbit. Word Equations sulphur + oxygen → reactants sulphur dioxide product Word Equations sodium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce sodium chloride and water Word Equations Silver chloride and calcium nitrate are produced when calcium chloride reacts with silver nitrate. Valence Shell • An atom wants 8 electrons in its outer (valence) shell to be stable. Valence Shell How many electrons do elements in the following families gain or lose to become stable? i) IA ii) IIA iii) VIIA iv) VIIIA lose 1 lose 2 gain 1 neither lose nor gain Ionic Compound • In an ionic compound, a positive metal ion is electrically attracted to a negative non-metal ion. Molecular Compound • In a molecular compound, non-metals share electrons. Covalent Bonding This sharing is a covalent bond. Ionic Compound NaCl must be an ionic compound because it contains a metal. Methane