Chemistry Notes
... stating that when two elements can combine to form more than one compound the amounts of one of them that combines with a fixed amount of the other will exhibit a simple multiple relation ...
... stating that when two elements can combine to form more than one compound the amounts of one of them that combines with a fixed amount of the other will exhibit a simple multiple relation ...
Chapter 3 – Atomic Structure - Mercer Island School District
... • Each element is composed of tiny atoms • Atoms of an element are identical but differ from those of other elements. • Atoms are neither created nor destroyed. • A given compound always has the same relative numbers and kinds of atoms. ...
... • Each element is composed of tiny atoms • Atoms of an element are identical but differ from those of other elements. • Atoms are neither created nor destroyed. • A given compound always has the same relative numbers and kinds of atoms. ...
effective nuclear charge
... def. the energy change that occurs when an e- is added to a gaseous atom or ion measure of attraction of atom for the added e energy is released when e- added the more negative the EA, the greater the attraction of the atom for an e ex: Cl(g) + e- Cl-(g) ΔE= -349kJ/mol ...
... def. the energy change that occurs when an e- is added to a gaseous atom or ion measure of attraction of atom for the added e energy is released when e- added the more negative the EA, the greater the attraction of the atom for an e ex: Cl(g) + e- Cl-(g) ΔE= -349kJ/mol ...
Integrated Science 3
... 18. As your eyes move across the periodic table from left to right in the second period the atomic radii gets ____________. Explain this pattern. What happens to ionization energy across a period? 19. What is true about the element immediately below the element that has an atomic number 17 in the pe ...
... 18. As your eyes move across the periodic table from left to right in the second period the atomic radii gets ____________. Explain this pattern. What happens to ionization energy across a period? 19. What is true about the element immediately below the element that has an atomic number 17 in the pe ...
periodic table
... periodic table before your reading. What is something you thought was cool/unique about it? What is periodic? What is periodic about the table? ...
... periodic table before your reading. What is something you thought was cool/unique about it? What is periodic? What is periodic about the table? ...
Intro to Atoms - Freehold Borough Schools
... Matter: anything that has mass and takes up space. Mass: measurement of how much matter is in an object Element: a substance that cannot be broken down into any other substances by chemical or physical means Compound: a substance of 2 or more elements Mixture: 2 or more substances that are mixed tog ...
... Matter: anything that has mass and takes up space. Mass: measurement of how much matter is in an object Element: a substance that cannot be broken down into any other substances by chemical or physical means Compound: a substance of 2 or more elements Mixture: 2 or more substances that are mixed tog ...
World of
... Always us a CAPITAL letter for the first letter in element. Use lower case if there is a second letter. – Ex: Hydrogen = H – Gold = Au ...
... Always us a CAPITAL letter for the first letter in element. Use lower case if there is a second letter. – Ex: Hydrogen = H – Gold = Au ...
Physical Science Chapter 3 Test
... their properties will emerge in a regular pattern. 12. Because atoms of elements in the same group of the periodic table have the same number of ____________________, they have similar properties. 13. Some elements are highly ____________________ because their outermost energy levels are only partia ...
... their properties will emerge in a regular pattern. 12. Because atoms of elements in the same group of the periodic table have the same number of ____________________, they have similar properties. 13. Some elements are highly ____________________ because their outermost energy levels are only partia ...
Unit 2: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry
... In this unit students will describe how the arrangement of elements in the periodic table and their electron configurations are related. They will describe how the location of an element in the periodic table can be used to predict the properties of that element. Expected learning outcomes: 1. Deter ...
... In this unit students will describe how the arrangement of elements in the periodic table and their electron configurations are related. They will describe how the location of an element in the periodic table can be used to predict the properties of that element. Expected learning outcomes: 1. Deter ...
Keypoints of Basic Atomic Structure
... Atomic Number Atomic Radius Electrons Element Isotope Neutrons Periodic Table Protons Subatomic Particles Concepts 1. Be able to describe how protons, neutrons and electrons are arranged in an atom. 2. Be able to list the charges on the subatomic particles that make up and atom, and giv ...
... Atomic Number Atomic Radius Electrons Element Isotope Neutrons Periodic Table Protons Subatomic Particles Concepts 1. Be able to describe how protons, neutrons and electrons are arranged in an atom. 2. Be able to list the charges on the subatomic particles that make up and atom, and giv ...
Exam III Review
... 5. An Iron atom is 1.72 angstroms (Å) wide. How many iron atoms would you have to stack end to end to stretch the width of this piece of paper, 8.5 inches? (remember: 1 Å = 10-10 m and 1 inch = 2.54 cm) ...
... 5. An Iron atom is 1.72 angstroms (Å) wide. How many iron atoms would you have to stack end to end to stretch the width of this piece of paper, 8.5 inches? (remember: 1 Å = 10-10 m and 1 inch = 2.54 cm) ...
Test Review: Unit 1 - Ms. Hill`s Pre
... normal chemical and physical changes (Dalton didn’t describe/clarify normal circumstances, matter can be created and destroyed in nuclear reactions) b. Law of Definite Proportions: the fact that a chemical compound contain exactly the same elements in exactly the same proportions in exactly the same ...
... normal chemical and physical changes (Dalton didn’t describe/clarify normal circumstances, matter can be created and destroyed in nuclear reactions) b. Law of Definite Proportions: the fact that a chemical compound contain exactly the same elements in exactly the same proportions in exactly the same ...
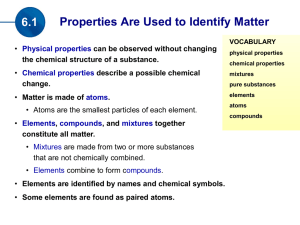
Atoms have a structure that determines their properties.
... • Elements, compounds, and mixtures together constitute all matter. • Mixtures are made from two or more substances that are not chemically combined. • Elements combine to form compounds. • Elements are identified by names and chemical symbols. • Some elements are found as paired atoms. ...
... • Elements, compounds, and mixtures together constitute all matter. • Mixtures are made from two or more substances that are not chemically combined. • Elements combine to form compounds. • Elements are identified by names and chemical symbols. • Some elements are found as paired atoms. ...
Periodic Table Quiz
... 11. Which element is in Period 4, Group 13? a) Na b) Al c) Ga d) K 12. How many electrons does Sulfur contain? a) 15 b) 16 c) 17 d) 18 13. Which elements below are ALL nonmetals? a) K, Ca, Sc b) Be, Br, Kr c) V, Cr, Mn d) Ne, Cl, Br ...
... 11. Which element is in Period 4, Group 13? a) Na b) Al c) Ga d) K 12. How many electrons does Sulfur contain? a) 15 b) 16 c) 17 d) 18 13. Which elements below are ALL nonmetals? a) K, Ca, Sc b) Be, Br, Kr c) V, Cr, Mn d) Ne, Cl, Br ...
Dmitri MendeleevанааA Russian chemist, noticed a repeating
... pattern of chemical properties in the elements that were known at the time. Mendeleev arranged the elements in the order of increasing atomic mass to form something close to the modern day periodic table. The pattern of repeating order is called periodicity. ...
... pattern of chemical properties in the elements that were known at the time. Mendeleev arranged the elements in the order of increasing atomic mass to form something close to the modern day periodic table. The pattern of repeating order is called periodicity. ...
+ 2 HCL(aq) CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
... Subscript: A number that represents how many atoms of an element are in a compound. Compound: A substance made of the combined atoms of two or more elements. Chemical Formula: States what elements a compound contains and the exact number of atoms of these elements. Oxidation Number: positive or nega ...
... Subscript: A number that represents how many atoms of an element are in a compound. Compound: A substance made of the combined atoms of two or more elements. Chemical Formula: States what elements a compound contains and the exact number of atoms of these elements. Oxidation Number: positive or nega ...
Development of atomic theory
... energy and spiral into the nucleus. This difficulty was solved by Niels Bohr (1913), who applied the quantum theory developed by Max Planck and Albert Einstein to the problem of atomic structure. Bohr proposed that electrons could circle a nucleus without radiating energy only in orbits for which th ...
... energy and spiral into the nucleus. This difficulty was solved by Niels Bohr (1913), who applied the quantum theory developed by Max Planck and Albert Einstein to the problem of atomic structure. Bohr proposed that electrons could circle a nucleus without radiating energy only in orbits for which th ...
The_Atoms_Family
... • When the number of neutrons in nuclei vary, you have an isotope • For example, chlorine always has 17 protons, but the number of neutrons could be either 18 or 20. This in turn, changes the atomic mass • The nuclei of some isotopes are unstable and release radiation • During the radioactive decay ...
... • When the number of neutrons in nuclei vary, you have an isotope • For example, chlorine always has 17 protons, but the number of neutrons could be either 18 or 20. This in turn, changes the atomic mass • The nuclei of some isotopes are unstable and release radiation • During the radioactive decay ...
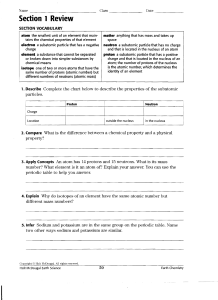
Section 1 Review
... 5. Infer Sodium and potassium are in the same group on the periodic table. Name ...
... 5. Infer Sodium and potassium are in the same group on the periodic table. Name ...
Subject Area Standard Area Organizing Category Course Standard
... 3.2.C.A5: MODELS Recognize discoveries from Dalton (atomic theory), Thomson (the electron), Rutherford (the nucleus), and Bohr (planetary model of atom), and understand how each discovery leads to modern theory. Describe Rutherford’s “gold foil” experiment that led to the discovery of the nuclear at ...
... 3.2.C.A5: MODELS Recognize discoveries from Dalton (atomic theory), Thomson (the electron), Rutherford (the nucleus), and Bohr (planetary model of atom), and understand how each discovery leads to modern theory. Describe Rutherford’s “gold foil” experiment that led to the discovery of the nuclear at ...
Atoms - Science with Mrs. Schulte
... The number of electrons in an atom is equal to the number of protons. ...
... The number of electrons in an atom is equal to the number of protons. ...
Chapter 18
... • Dimitri Mendeleevarranged all the elements known in order of increasing atomic masses and discovered a pattern • Today’s Periodic Table— elements are arranged by increasing atomic number and by changes in physical and chemical properties ...
... • Dimitri Mendeleevarranged all the elements known in order of increasing atomic masses and discovered a pattern • Today’s Periodic Table— elements are arranged by increasing atomic number and by changes in physical and chemical properties ...
Two valence electrons.
... elements by increasing atomic mass, leaving blank spaces where he was sure elements Dmitri yet to be discovered Mendeleev would fit. ...
... elements by increasing atomic mass, leaving blank spaces where he was sure elements Dmitri yet to be discovered Mendeleev would fit. ...