* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download + 2 HCL(aq) CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Livermorium wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Oxidation state wikipedia , lookup
Bond valence method wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Alkaline earth metal wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Bonds, Formulas, Naming Compounds, and Chemical Reactions Study Guide
KEY
Vocabulary
Cation: An ion with a positive charge
Anion: An ion with a negative charge
Covalent Bond: A bond between two non-metals where a pair of electrons are shared.
Ionic Bond: A bond between a non-metal and a metal where electrons are lost or gained.
Subscript: A number that represents how many atoms of an element are in a compound.
Compound: A substance made of the combined atoms of two or more elements.
Chemical Formula: States what elements a compound contains and the exact number of
atoms of these elements.
Oxidation Number: positive or negative number on the periodic table that indicates how
many electrons an element has gained, lost or shared when bonding with another element.
Polyatomic Atom: A compound with two or more elements.
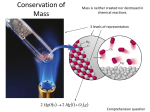
Law of Conservation of Mass: states that matter can never be created or destroyed. The
reactants and products must be equal in mass.
What are the parts of a Chemical Equation?
Coefficient
Produces/Yields
CaCO3(s) + 2 HCL(aq)
Reactants
Solid
Subscript
CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
Products
Aqueous
Liquid
Gas
What are the steps to name an ionic compound?
Metal Part:
Say the Entire Element Name
Nonmetal Part:
Say the Element Name Changing the Ending to: IDE
***NO PREFIXES***
What are the names and oxidation numbers for the following found in polyatomic compounds?
NO2
NO3
OH
PO4
CO3
SO4
List the steps to name a covalent compound.
First Nonmetal Part:
Add a Prefix (none if there is only 1 atom {Unless it’s Oxygen}), Say the Entire Element
Name
Second Nonmetal Part:
Add a Prefix, Say the Element Name Changing the Ending to IDE
List the prefixes used to identify the number of atoms of an element in a chemical formula when it is covalent (Non-metal –
Non-metal).
One
Six
Two
Seven
Three
Eight
Four
Nine
Five
Ten
Prefixes
Number of atoms
Prefix
1
mono- (use only for oxygen)
2
di-
3
tri-
4
tetra-
5
penta-
6
hexa-
7
hepta-
8
octa-
9
nona-
10
deca-
Practice Writing Formulas and Naming Compounds (both Ionic and Covalent):
Formula or
Formula or
Compound Name
Type of Bond
Compound Name
1. Magnesium Sulfide
Ionic
2. K2O
Ionic
Potassium oxide
3. CO
Covalent
Carbon monoxide
4. Dinitrogen Monoxide
Covalent
N2O
5. MnBr2
Ionic
Manganese bromide
6. Calcium Hydroxide
Ionic
Ca(OH)2
7. NaNO3
Ionic
Sodium Nitrate
8. MgCl2
Ionic
Magnesium chloride
MgS
Directions: Use a periodic table, complete the table below:
Element
Total # of
Protons
Total # of
Electrons
# of Valence
Electrons
Oxidation Number
(Do not forget the
required sign +/-)
Cesium
55
55
1
+1
Beryllium
4
4
2
+2
Calcium
20
20
2
+2
Iodine
53
53
7
-1
List and explain the 4 types of Chemical Reactions.
1. Synthesis -
A+B
AB
2. Decomposition –
AB
A+B
3. Single Displacement -
A + BC
AB + C
4. Double Displacement-
AB + CD
AC + BD
Describe evidence that would tell you a chemical reaction has occurred.
Color Change
Bubbling
Foaming
Odor
How do the following affect the Rate of a Chemical Reaction?
Surface Area – the more surface area the higher the rate of the
reaction
Concentration – the more concentrated the compound, the
higher the reaction rate
Catalyst – speeds up the reaction
Temperature – speed it up or slow it down
Inhibitor – slows down the reaction