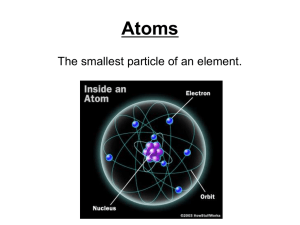
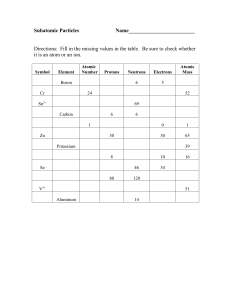
Ch. 2 note packet
... 3. Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements combine. In a given compound, the relative numbers of atoms of each kind are definite and constant. In general, these relative numbers can be expressed as integers or simple fractions. IN GENERAL Elements consist of tiny particles called __ ...
... 3. Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements combine. In a given compound, the relative numbers of atoms of each kind are definite and constant. In general, these relative numbers can be expressed as integers or simple fractions. IN GENERAL Elements consist of tiny particles called __ ...
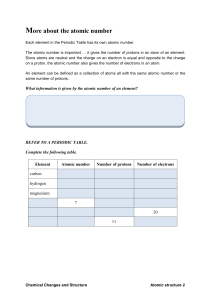
14 more about the atomic number
... Each element in the Periodic Table has its own atomic number. The atomic number is important it gives the number of protons in an atom of an element. Since atoms are neutral and the charge on an electron is equal and opposite to the charge on a proton, the atomic number also gives the number of elec ...
... Each element in the Periodic Table has its own atomic number. The atomic number is important it gives the number of protons in an atom of an element. Since atoms are neutral and the charge on an electron is equal and opposite to the charge on a proton, the atomic number also gives the number of elec ...
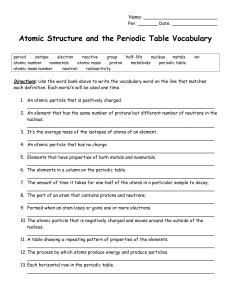
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Vocabulary
... nucleus. __________________________________________________________________ 3. It’s the average mass of the isotopes of atoms of an element. __________________________________________________________________ 4. An atomic particle that has no charge. __________________________________________________ ...
... nucleus. __________________________________________________________________ 3. It’s the average mass of the isotopes of atoms of an element. __________________________________________________________________ 4. An atomic particle that has no charge. __________________________________________________ ...
Chemistry Review: Antoine Lavoisier (1743
... Isotopes: atoms of the same element that differs in mass. Ex there are 3 isotopes of hydrogen, with mass numbers of 1, 2 and 3. These atoms have different masses because they have different numbers of neutrons. However, since they have the same number of protons, they are the same element. Most el ...
... Isotopes: atoms of the same element that differs in mass. Ex there are 3 isotopes of hydrogen, with mass numbers of 1, 2 and 3. These atoms have different masses because they have different numbers of neutrons. However, since they have the same number of protons, they are the same element. Most el ...
Exam 1 Review Questions
... Argon, xenon, krypton, and neon were discovered by Humphry Davy using electrolysis to separate them from their compounds. Arsenic is in the carbon family. Astatine is likely to have very similar properties to radon. Atomic number decreases as you go down a column of the Periodic Table. Atoms are so ...
... Argon, xenon, krypton, and neon were discovered by Humphry Davy using electrolysis to separate them from their compounds. Arsenic is in the carbon family. Astatine is likely to have very similar properties to radon. Atomic number decreases as you go down a column of the Periodic Table. Atoms are so ...
NOTES: 2.1 - Intro to Chemistry
... Isotopes: atoms of an element that have different # of neutrons ● in nature, elements occur as mixtures of isotopes ● some are radioactive: unstable isotope where nucleus decays emitting subatomic particles and/or energy as radioactivity causing one element to transform into another element ...
... Isotopes: atoms of an element that have different # of neutrons ● in nature, elements occur as mixtures of isotopes ● some are radioactive: unstable isotope where nucleus decays emitting subatomic particles and/or energy as radioactivity causing one element to transform into another element ...
History of the Atom and Periodic Table
... Electrons are negatively charged and orbit the nucleus. He later discovered a subatomic, positively charged particle in the nucleus called the proton. ...
... Electrons are negatively charged and orbit the nucleus. He later discovered a subatomic, positively charged particle in the nucleus called the proton. ...
Thursday, October 31, 2013 D-day
... – Only group which has all three states of matter at STP. (what is STP?) – Most reactive nonmetals. – These elements are all brightly colored. ...
... – Only group which has all three states of matter at STP. (what is STP?) – Most reactive nonmetals. – These elements are all brightly colored. ...
Ch. 4: Atoms and the Periodic Table – Study Guide
... Ch. 4: Atoms and the Periodic Table – Study Guide The first person who suggested that matter was made up of atoms was the Greek philosopher Democritus. The word atom comes from the Greek word that means “unable to be divided.” Dalton’s atomic theory stated that every element was made of atoms that c ...
... Ch. 4: Atoms and the Periodic Table – Study Guide The first person who suggested that matter was made up of atoms was the Greek philosopher Democritus. The word atom comes from the Greek word that means “unable to be divided.” Dalton’s atomic theory stated that every element was made of atoms that c ...
IPC Atoms and Periodic Table
... of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element • Reported as atomic mass on the periodic ...
... of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element • Reported as atomic mass on the periodic ...
Chap 7: Around the Room Review
... 1. The central part of an atom is called the _____ 2. A proton has a _____ charge. 3. The atomic number tells us __________. 4. Nitrogen’s atomic number is 7. An isotope of nitrogen containing 7 neutrons would be nitrogen_____. 5. How does the size of a negative ion compare to the size of the atom t ...
... 1. The central part of an atom is called the _____ 2. A proton has a _____ charge. 3. The atomic number tells us __________. 4. Nitrogen’s atomic number is 7. An isotope of nitrogen containing 7 neutrons would be nitrogen_____. 5. How does the size of a negative ion compare to the size of the atom t ...
Test 2 Review Test 2 Review (15-16)_2
... (17) ____________ Which column from above contains VERY non-reactive elements? (18) ____________ How many of these elements are gases at 0 degrees Celsius? (19) ____________ How many of these elements are metalloids? (20) ____________ How many of these elements are NON-metals and solids? (21) ______ ...
... (17) ____________ Which column from above contains VERY non-reactive elements? (18) ____________ How many of these elements are gases at 0 degrees Celsius? (19) ____________ How many of these elements are metalloids? (20) ____________ How many of these elements are NON-metals and solids? (21) ______ ...
Learning Standards vocab chemical basis and molecules of life 09
... two hydrogen atoms). Explain the meaning of a chemical formula for a molecule (e.g., CH4 or H2O).*a Demonstrate how carbon atoms form four covalent bonds to make large molecules. Identify the functions of these molecules (e.g., plant and animal tissue, polymers, sources of food and nutrition, fo ...
... two hydrogen atoms). Explain the meaning of a chemical formula for a molecule (e.g., CH4 or H2O).*a Demonstrate how carbon atoms form four covalent bonds to make large molecules. Identify the functions of these molecules (e.g., plant and animal tissue, polymers, sources of food and nutrition, fo ...
C2- Topic 1: Atomic structure and the periodic table. Assessable
... Explain how Mendeleev: - arranged the elements, known at that time, in a periodic table by using properties of these elements and their compounds - used his table to predict the existence and properties of some elements not then discovered ...
... Explain how Mendeleev: - arranged the elements, known at that time, in a periodic table by using properties of these elements and their compounds - used his table to predict the existence and properties of some elements not then discovered ...
C2 Topic 1 Can Do Sheet
... 1.1 Explain how Mendeleev: a arranged the elements, known at that time, in a periodic table by using properties of these elements and their compounds b used his table to predict the existence and properties of some elements not then discovered 1.2 Classify elements as metals or non-metals according ...
... 1.1 Explain how Mendeleev: a arranged the elements, known at that time, in a periodic table by using properties of these elements and their compounds b used his table to predict the existence and properties of some elements not then discovered 1.2 Classify elements as metals or non-metals according ...
Notes
... -the number of protons in an atom of an element •all atoms of an element have the same atomic # •written as a subscript next to the element’s symbol •in a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons (balanced charges). ...
... -the number of protons in an atom of an element •all atoms of an element have the same atomic # •written as a subscript next to the element’s symbol •in a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons (balanced charges). ...
Fall Final Exam Review Questions
... 41. What are properties of metals and where are they generally located on a periodic table? 42. What are properties of nonmetals and where are they generally located? 43. What are properties of metalloids and where are they generally located? 44. Make sure you know the major groups/chemical families ...
... 41. What are properties of metals and where are they generally located on a periodic table? 42. What are properties of nonmetals and where are they generally located? 43. What are properties of metalloids and where are they generally located? 44. Make sure you know the major groups/chemical families ...
Periodic Table Vocabulary Periodic Table – a chart that organizes
... Inert – elements and/or compounds that when put together are unable to react chemically. The Law of Conservation of Matter – a scientific law that states that during a chemical reaction, matter cannot be created or destroyed but can be changed into a different form. Period law- The chemical properti ...
... Inert – elements and/or compounds that when put together are unable to react chemically. The Law of Conservation of Matter – a scientific law that states that during a chemical reaction, matter cannot be created or destroyed but can be changed into a different form. Period law- The chemical properti ...
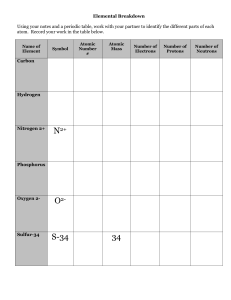
atomic number - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... The periodic table is a chart containing information about the atoms that make up all matter. An element is a substance made up of only one type of atom. The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. The number of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom is equal ...
... The periodic table is a chart containing information about the atoms that make up all matter. An element is a substance made up of only one type of atom. The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. The number of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom is equal ...