* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NOTES: 2.1 - Intro to Chemistry
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Bond valence method wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Livermorium wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear transmutation wikipedia , lookup
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
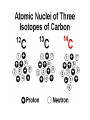
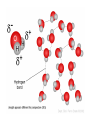
NOTES: 2.1 The Nature of Matter (Chemistry Review) Molecular Level (DNA) Atomic Level (Phosphorus) VOCABULARY ● Atom ● Isotope ● Compound ● Covalent Bond ● Ionic Bond ● Molecule ● Mixture ● Solution ● Acid ● Base Life is made up of MATTER! ● MATTER can be defined as anything that has mass and takes up space…this includes individual atoms!! ● just as buildings are made from bricks, steel, glass, and wood, LIVING THINGS are made from CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS. The Chemistry of Life… ● when you breathe, eat, or drink, your body uses the substances in air, food, and water to carry out chemical reactions that keep you alive… ● just as an architect first must understand the building materials, a BIOLOGIST must first understand the compounds that make up living things! ATOM: smallest unit of matter that retains the physical and chemical properties of its element ● three subatomic particles: Particle Charge Location Mass PROTON + nucleus 1.009 amu NEUTRON 0 nucleus - electron cloud ELECTRON 1.007 amu 0.0005 amu ATOMIC NUMBER: # of protons in an atom of an element ● all atoms of an element have the same atomic # ● written as a subscript next to the element’s symbol ● in a neutral atom, # protons = # electrons MASS NUMBER: # of protons + # of neutrons ● written as a superscript next to element’s symbol ● # of neutrons can vary in an element, but proton # is constant Isotopes: atoms of an element that have different # of neutrons ● in nature, elements occur as mixtures of isotopes ● some are radioactive: unstable isotope where nucleus decays emitting subatomic particles and/or energy as radioactivity causing one element to transform into another element Half-life: the time it takes for 50% of radioactive atoms in a sample to decay ● Some ways radioactive isotopes are useful to scientists: • Ages rocks or fossils • Treats cancer • Kills bacteria in food • Used as a “tracer” in human body or as a way to label something in the body Nitrogen vs. No Nitrogen ELEMENT: a pure substance that consists entirely of one type of atom; a substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical reactions Enlarged thyroid gland caused by iodine deficiency. COMPOUND: pure substance composed of 2 or more elements combined in a fixed ratio • examples: NaCl, H2O, CO2, C6H12O6 • cmpds. have unique properties beyond those of the combined elements Chemical Compounds ● a MOLECULE is the smallest unit of most compounds! ● EXAMPLE: 1 molecule of water, H2O, is the smallest unit of water possible; it consists of 2 hydrogen atoms & 1 oxygen atom bonded together. Energy Levels of Electrons ● Electrons are the only subatomic particle involved in chemical reactions because they occupy energy levels surrounding the nucleus *IONIC BOND: bond formed by the attraction of a positive ion to a negative ion -anion: negatively charged ion; has gained 1 or more electrons -cation: positively charged ion; has lost 1 or more electrons *COVALENT BOND: strong chemical bond between atoms formed by sharing a pair of valence electrons Chemical Reactions • In a chemical reaction, bonds between atoms are formed or broken, causing substances to combine and recombine as different molecules; • All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism are referred to as that organism’s METABOLISM. Chemical Equations: • REACTANTS: the substance(s) at the beginning of a reaction; shown on the left side of the equation; • PRODUCTS: the substance(s) at the end of a reaction; shown on the right side of the equation. • Example: 2H2 + O2 2H2O