* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 18 Atoms and Elements
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
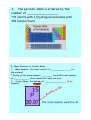
Chapter 18 Atoms and Elements 18.1 Atomic Structure Goals *What are the parts of an atom? *How did the work of numerous scientists lead to the current model of an atom? I. All matter (everything you see, hear, touch, smell and taste) is formed from __________, either by themselves or combined in _______________. A. Size 1. Atoms are tiny!!! A dust speck contains more than___________. B. Parts 1. Atoms contain _____ __________ particles: they are: __________________________ 2. Nucleus- ____________________ ___________________. 3. The _______________ move in space around the nucleus. Their location ___________ be determined at any one time. C. Subatomic particles have charge and mass: Particle Charge Mass (amu) So...how did we find all this out? II. Scientists Involved A. Greek Philosophers- proposed an atomic theory around 400 BC which stated....all matter is made __________________________ ______. B. Democritus- Named the atom from the Greek word _______, meaning "____________". C. 1. John Dalton's Atomic Theory (1808) Elements are made of ___________ 2. Atoms of the same element are ____________. 3. Atoms of __________________________. 4. Atoms are ____________ by chemical reactions. 5. Compounds are formed by joining ___________. 6. Compounds are defined by number, type and proportion of atoms. D. Joseph John Thomson (1904) 1. Discovered the ___________ and determined that they have a ____________charge. 2. He knew that atoms were ___________, so proposed that the atom was a ___________ with negative electrons embedded in it. E. Ernest Rutherford (1911) 1. Conducted the "______________" experiment. 2. Hypothesized that atoms are made _________ ________________________ 3. Introduced the nucleus- ________________. F. Niels Bohr (1885- 1962) 1. Conducted experiments to update Rutherford's model. 2. Stated that ____________ move around the nucleus in ____________ G. James Chadwick (1932) 1. Discovered the _______________ 2. Introduced the __________________ _____________________________. 3. The cloud represents _________ location of an electron. Comparing Atoms Goals: * What is the difference between atomic number, mass number and atomic mass? *How do we create an accurate atom diagram of any element? How is an isotope diagram different? A. Atomic Number 1. The atomic number is the number of _______________________ 2. The atomic number ___________ the type of element you have. Ex. 7 protons= _____________ 15 protons= _____________ ALWAYS!! 3. The periodic table is ordered by the number of ________________. *It starts with 1 (hydrogen) and ends with 118 (ununoctium) B. Mass Number vs. Atomic Mass 1. Mass number- the total number of _______________ (in the nucleus). * Atoms of the same element ________ have different number of ___________, which means the mass can vary. 2. Atomic Mass- the average of ________________ of an element. A i m to c ss a m The mass number would be 31 C. Isotopes 1. Isotope- ________ of the same element that have _________________________. Example: Carbon Carbon-12 Carbon-13 protons= neutons= D. Strong Nucleus Force The nucleus contains positive protons and neutral neutrons, so what holds it together? It is held together by __________ ________________________ ...called the strong ______________. E. Energy Levels 1. Electrons are arranged into _____________ that hold a specific amount of electrons. 2. The energy levels make up the electron cloud. 3. The ___________ out the electrons are, the _______ their energy state. 4. ____________ electronselectrons in the _________ region of the electron cloud- the _________ involved in bonding.