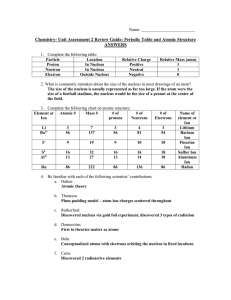
Chem Unit 2 Review Guide ANSWERS
... 17.) How are chemical reactions different than nuclear reactions? How does the Law of Conservation of Mass apply to each type of reaction? Chemical reactions only involve the atoms’ valence electrons. In a nuclear reaction, the nucleus is actually altered. The Law of Conservation of Mass holds true ...
... 17.) How are chemical reactions different than nuclear reactions? How does the Law of Conservation of Mass apply to each type of reaction? Chemical reactions only involve the atoms’ valence electrons. In a nuclear reaction, the nucleus is actually altered. The Law of Conservation of Mass holds true ...
Biochemistry I (CHE 418 / 5418)
... – Excited state when electrons is pushed into an orbit farther from the nucleus. • When electrons move from an excited state (higher energy level) to the ground state (lower energy level), the energy produced is given off often as light. • Worked well to explain the emision spectrum of hydrogen, but ...
... – Excited state when electrons is pushed into an orbit farther from the nucleus. • When electrons move from an excited state (higher energy level) to the ground state (lower energy level), the energy produced is given off often as light. • Worked well to explain the emision spectrum of hydrogen, but ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... – Other isotopes are radioactive, having unstable atoms that spontaneously break apart (decay) to form other atoms – When radioactive atoms decay, energy is released ...
... – Other isotopes are radioactive, having unstable atoms that spontaneously break apart (decay) to form other atoms – When radioactive atoms decay, energy is released ...
Atomic Structure
... •All atoms of an element are considered an isotope, only some are more common than others. •Atomic mass is the ______________________ of all isotopes of the element. •Even though isotopes have different amounts of neutrons they are still chemically alike since they have the same number of protons an ...
... •All atoms of an element are considered an isotope, only some are more common than others. •Atomic mass is the ______________________ of all isotopes of the element. •Even though isotopes have different amounts of neutrons they are still chemically alike since they have the same number of protons an ...
History of Atomic Models Greek Model 450 B.C. Dalton`s Atomic
... • Based on experiments involving firing tiny streams of positively charged particles (bullets) through gold foil. • Dense nucleus (center) surrounded by scattered electrons (negative charge). • Proposed a positively charged center called a nucleus. ...
... • Based on experiments involving firing tiny streams of positively charged particles (bullets) through gold foil. • Dense nucleus (center) surrounded by scattered electrons (negative charge). • Proposed a positively charged center called a nucleus. ...
CHAPTER 1 Practice Exercises 1.1 x = 12.3 g Cd 1.3 2.24845 ×12 u
... There is no space in the periodic table for another element of mass 73 u. Germanium has an atomic mass of 72.6 u and an atomic number of 32. Next to it on the periodic table is arsenic which has an atomic number of 33. In order for there to be a new element with an atomic mass of 73, it would be exp ...
... There is no space in the periodic table for another element of mass 73 u. Germanium has an atomic mass of 72.6 u and an atomic number of 32. Next to it on the periodic table is arsenic which has an atomic number of 33. In order for there to be a new element with an atomic mass of 73, it would be exp ...
Lesson 13 - Highline Public Schools
... weighted average of the masses of the isotopes in a sample of the element. The most common isotope of an element, frequently has a mass that is close to the average atomic mass given in the periodic table. ...
... weighted average of the masses of the isotopes in a sample of the element. The most common isotope of an element, frequently has a mass that is close to the average atomic mass given in the periodic table. ...
and View
... b. Isotopes—atoms of same element that have different numbers of neutrons. Ex: carbon-12, carbon-13, carbon-14 c. Mass number—number of neutrons plus protons in an atom. i. Neutron number is found by--Mass number - Atomic number _______________ Number of neutrons ...
... b. Isotopes—atoms of same element that have different numbers of neutrons. Ex: carbon-12, carbon-13, carbon-14 c. Mass number—number of neutrons plus protons in an atom. i. Neutron number is found by--Mass number - Atomic number _______________ Number of neutrons ...
CHAPTER 3: The Building Blocks of Matter
... I. Early Atomic Theory□Democritus (400 B.C.)- suggested that the world was made of two things: -empty space and -tiny, indivisible particles called ‘____________’. □Dalton (early 1800s)- using the experimental observations of others, including Lavoisier and Proust, he proposed□Dalton’s Atomic Theory ...
... I. Early Atomic Theory□Democritus (400 B.C.)- suggested that the world was made of two things: -empty space and -tiny, indivisible particles called ‘____________’. □Dalton (early 1800s)- using the experimental observations of others, including Lavoisier and Proust, he proposed□Dalton’s Atomic Theory ...
Development of the Atomic Theory
... silver the same? What part of Dalton’s theory supports your answer? Are new elements formed in a chemical reaction? ...
... silver the same? What part of Dalton’s theory supports your answer? Are new elements formed in a chemical reaction? ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table Study Guide
... 15) Draw a Bohr model and electron dot mode for the following elements using the descriptions ...
... 15) Draw a Bohr model and electron dot mode for the following elements using the descriptions ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table Notes
... Atoms of the same __________________ with ___________________ numbers Company,ofInc. ____________________________. ...
... Atoms of the same __________________ with ___________________ numbers Company,ofInc. ____________________________. ...
Notes - Organization of Matter
... • Compounds are pure substances that are composed of two or more atoms that are chemically combined • Compounds can only be changed into simpler substances called elements by chemical changes ...
... • Compounds are pure substances that are composed of two or more atoms that are chemically combined • Compounds can only be changed into simpler substances called elements by chemical changes ...
Chapter 3
... 1. All matter is made of indivisible and indestructible atoms. 2. All atoms of the same element are identical in their physical and chemical properties. ...
... 1. All matter is made of indivisible and indestructible atoms. 2. All atoms of the same element are identical in their physical and chemical properties. ...
PowerPoint - Models of the Atom - A Historical Perspective
... • Electrons orbit the nucleus in “shells” 1. An electron can travel indefinitely within an energy level without losing energy 2. The greater the distance between the nucleus and the energy level, the greater the energy level 3. An electron cannot exist between energy levels, but can move to a higher ...
... • Electrons orbit the nucleus in “shells” 1. An electron can travel indefinitely within an energy level without losing energy 2. The greater the distance between the nucleus and the energy level, the greater the energy level 3. An electron cannot exist between energy levels, but can move to a higher ...
Atomic Mass
... Atomic masses can be different for atoms of the same element if they have different numbers of neutrons Atoms with different masses are called Isotopes or Nuclides ...
... Atomic masses can be different for atoms of the same element if they have different numbers of neutrons Atoms with different masses are called Isotopes or Nuclides ...
Chemistry Test Review - Greenslime Home Page
... a. Atom – the smallest part of an element that still acts like that element; can’t be broken down; basic part of matter b. Element – a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances containing only 1 type of atom c. Compound – two or more different elements chemically combined d. Molec ...
... a. Atom – the smallest part of an element that still acts like that element; can’t be broken down; basic part of matter b. Element – a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances containing only 1 type of atom c. Compound – two or more different elements chemically combined d. Molec ...
CHEM 1305 - HCC Learning Web
... C) Neuton D) Proton -------5. How many neutrons are in the nucleus of an atom of silver-107? A) 47 B) 60 C) 107 D) 154 ------6. What is the name of the family of elements in Group IIA/ 2? A) Alkali metals B) Alkaline earth metals C) Halogens D) Noble gases -------7. Which fifth period representative ...
... C) Neuton D) Proton -------5. How many neutrons are in the nucleus of an atom of silver-107? A) 47 B) 60 C) 107 D) 154 ------6. What is the name of the family of elements in Group IIA/ 2? A) Alkali metals B) Alkaline earth metals C) Halogens D) Noble gases -------7. Which fifth period representative ...
State Changes Scavenger Hunt
... Go to the “ChemTime Clock” area to find the answers to these questions. 1. All materials, whether solid, liquid or gas, are made of _______________. Atoms are the smallest _______ of ___________. Scientists have found over _______ different kinds of atoms. The many different materials we encounter a ...
... Go to the “ChemTime Clock” area to find the answers to these questions. 1. All materials, whether solid, liquid or gas, are made of _______________. Atoms are the smallest _______ of ___________. Scientists have found over _______ different kinds of atoms. The many different materials we encounter a ...
Chemistry I Honors – Semester Exam Review – Fall 2000
... Matter – Ch. 1 6. Classify the following substances as solid, liquid, gas, or plasma based on their properties. a. flexible volume, high KE, particles can disperse freely. b. flexible volume, very high KE, particles are charged. c. fixed volume, very low KE, orderly particles. d. fixed volume, low K ...
... Matter – Ch. 1 6. Classify the following substances as solid, liquid, gas, or plasma based on their properties. a. flexible volume, high KE, particles can disperse freely. b. flexible volume, very high KE, particles are charged. c. fixed volume, very low KE, orderly particles. d. fixed volume, low K ...
Week 1 Grade 7 Thursday
... Isotopes have different numbers of neutrons, H normally has 0 neutrons ...
... Isotopes have different numbers of neutrons, H normally has 0 neutrons ...
Final Exam Review
... E. shiny 31. In general, how are metalloids different from metals and nonmetals? 51. In which pair of elements are the chemical properties of the elements most similar? Explain your reasoning. A. sodium and chlorine B. nitrogen and phosphorous C. boron and oxygen 88. The volume of a liquid in a grad ...
... E. shiny 31. In general, how are metalloids different from metals and nonmetals? 51. In which pair of elements are the chemical properties of the elements most similar? Explain your reasoning. A. sodium and chlorine B. nitrogen and phosphorous C. boron and oxygen 88. The volume of a liquid in a grad ...























