File - Mr. Gittermann
... with no charge and is located in the nucleus of the atom • Electrons: Subatomic particle with a negative charge found in a certain region of space around the nucleus called the electron cloud; kept close to the atom due to the attraction between the opposite charges of the electron and proton ...
... with no charge and is located in the nucleus of the atom • Electrons: Subatomic particle with a negative charge found in a certain region of space around the nucleus called the electron cloud; kept close to the atom due to the attraction between the opposite charges of the electron and proton ...
SLE133 – “Chemistry in Our World” Summary Notes Week 1
... Electrons repel one another, protons repel one another, but electrons and protons attract one another. ...
... Electrons repel one another, protons repel one another, but electrons and protons attract one another. ...
Chapter 4 notes outline
... number of neutrons Elements can have several isotopes 4.3 Modern Atomic Theory Bohr’s Model of the Atom Better description of electrons Electrons orbit around nucleus in energy levels like planets 1st Level = holds up to 2 electrons 2nd Level = holds up to 8 electrons Electrons can move to d ...
... number of neutrons Elements can have several isotopes 4.3 Modern Atomic Theory Bohr’s Model of the Atom Better description of electrons Electrons orbit around nucleus in energy levels like planets 1st Level = holds up to 2 electrons 2nd Level = holds up to 8 electrons Electrons can move to d ...
Chapter 9 - Fayetteville State University
... are the alkali metals (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs), the halogens (F, Cl, Br, I). 8) Groups: A sequence of elements of increasing atomic number in the periodic table that share similar chemical properties (Example: group 1A Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs) 9) Metals: are characterized for having extra electrons outside the ...
... are the alkali metals (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs), the halogens (F, Cl, Br, I). 8) Groups: A sequence of elements of increasing atomic number in the periodic table that share similar chemical properties (Example: group 1A Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs) 9) Metals: are characterized for having extra electrons outside the ...
Name Period ______ Unit 4 Study Guide A common isotope of iron
... 1. A common isotope of iron has a mass number of 56. How many neutrons does it have? The atomic number tells you the number of… A particle with zero charge found in the nucleus of an atom is called a(n): Atoms of the same element whose nucleus contains different numbers of neutrons are called: Atoms ...
... 1. A common isotope of iron has a mass number of 56. How many neutrons does it have? The atomic number tells you the number of… A particle with zero charge found in the nucleus of an atom is called a(n): Atoms of the same element whose nucleus contains different numbers of neutrons are called: Atoms ...
Vocabulary and Section Summary
... Name ______________________________ Class___________________Date__________________ ...
... Name ______________________________ Class___________________Date__________________ ...
chapter_3_study_guide
... __________________ alpha particles. He found that most alpha particles passed through the gold foil but some were mysteriously deflected by something in the gold. Rutherford concluded there must be a ___________________ ____________________ in the center of the gold atoms that deflected the alpha pa ...
... __________________ alpha particles. He found that most alpha particles passed through the gold foil but some were mysteriously deflected by something in the gold. Rutherford concluded there must be a ___________________ ____________________ in the center of the gold atoms that deflected the alpha pa ...
Name ____ Date
... number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the atoms of different elements. 8. What is the mole and how is the concept used in measuring quantities of an element? 9. How is the periodic table used to determine protons, neutrons, and electrons (especially valence electrons)? 10. What is a group or ...
... number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the atoms of different elements. 8. What is the mole and how is the concept used in measuring quantities of an element? 9. How is the periodic table used to determine protons, neutrons, and electrons (especially valence electrons)? 10. What is a group or ...
The Dalton Thompson 1889 Rutherford Niels Bohr Moseley
... The famous ‘gold foil experiment’ by Rutherford proved the ‘Plum Pudding’ model wrong as not all alpha particles passed through the gold atoms, some were deflected. The positively charged alpha particle hit a positive substance which caused it to be deflected, therefore atoms must have a nucleus whe ...
... The famous ‘gold foil experiment’ by Rutherford proved the ‘Plum Pudding’ model wrong as not all alpha particles passed through the gold atoms, some were deflected. The positively charged alpha particle hit a positive substance which caused it to be deflected, therefore atoms must have a nucleus whe ...
Chapter 2 - Speedway High School
... • Atoms of the various elements differ in number of subatomic particles – Atomic number – Mass number – Atomic mass ...
... • Atoms of the various elements differ in number of subatomic particles – Atomic number – Mass number – Atomic mass ...
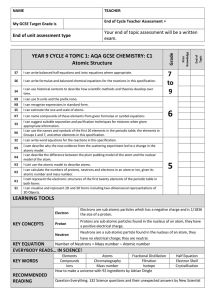
Cycle 4 Topic 1 C1 Atomic Structure Cycle Sheet
... I can use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this specification. I can write word equations for the reactions in this specification. ...
... I can use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this specification. I can write word equations for the reactions in this specification. ...
Chapter 8: Chemical Bonding
... Note: The number of valence e- for the s and p-block elements is given by the element's group number! ...
... Note: The number of valence e- for the s and p-block elements is given by the element's group number! ...
section_2_review_set
... creates the chemical bonds 3. What is the claim to fame for the neutron? stabilizes the nucleus 4. What is the mass of each of the following particles?: proton 1; neutron 1; electron 0. 5. What is the charge for each of the following particles?: proton +1; neutron 0; electron -1. 6. What two things ...
... creates the chemical bonds 3. What is the claim to fame for the neutron? stabilizes the nucleus 4. What is the mass of each of the following particles?: proton 1; neutron 1; electron 0. 5. What is the charge for each of the following particles?: proton +1; neutron 0; electron -1. 6. What two things ...
Chapter 18: Atoms and Elements
... and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the mass number. ...
... and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the mass number. ...
Document
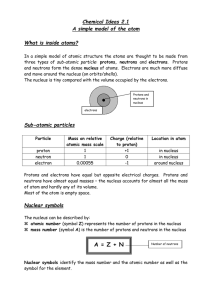
... three types of sub-atomic particle: protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons form the dense nucleus of atoms. Electrons are much more diffuse and move around the nucleus (on orbits/shells). The nucleus is tiny compared with the volume occupied by the electrons. Protons and neutrons in n ...
... three types of sub-atomic particle: protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons form the dense nucleus of atoms. Electrons are much more diffuse and move around the nucleus (on orbits/shells). The nucleus is tiny compared with the volume occupied by the electrons. Protons and neutrons in n ...
atom - Images
... How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are present in (a) 27Al3+ (b) 79Se2 Write the isotope notation for an ion that contains 20 protons, 21 neutrons, and 18 electrons. Write the isotope notation for an atom of lead that has 128 neutrons. Write the isotope notation for the following: ...
... How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are present in (a) 27Al3+ (b) 79Se2 Write the isotope notation for an ion that contains 20 protons, 21 neutrons, and 18 electrons. Write the isotope notation for an atom of lead that has 128 neutrons. Write the isotope notation for the following: ...
Getting to Know: Periodic Table
... element do not have the same number of neutrons. For example, most atoms of the element carbon, C, have 6 neutrons in their nucleus. There are some atoms of carbon that have 7 or even 8 neutrons in their nucleus. Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. ...
... element do not have the same number of neutrons. For example, most atoms of the element carbon, C, have 6 neutrons in their nucleus. There are some atoms of carbon that have 7 or even 8 neutrons in their nucleus. Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) (Listed on p 203) 1. Elements are composed of extremely small particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. 3. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements. 4. C ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) (Listed on p 203) 1. Elements are composed of extremely small particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. 3. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements. 4. C ...
Sem 1 Final
... • In two isotopes of the same element, which of the following would be the same and which would be different? – Atomic number – Number of protons – Number of neutrons – Number of electrons – Element symbol – Atomic mass ...
... • In two isotopes of the same element, which of the following would be the same and which would be different? – Atomic number – Number of protons – Number of neutrons – Number of electrons – Element symbol – Atomic mass ...
Chapter 2
... • Types of elements • Metals – left side; majority of elements; good conductors; lose electrons (+ ions) • Nonmetals – right side; poor conductors; gain electrons (- ions) • Metalloids – stair-step line • Groups – columns; grouped by similar properties • 18 – each has a name ...
... • Types of elements • Metals – left side; majority of elements; good conductors; lose electrons (+ ions) • Nonmetals – right side; poor conductors; gain electrons (- ions) • Metalloids – stair-step line • Groups – columns; grouped by similar properties • 18 – each has a name ...
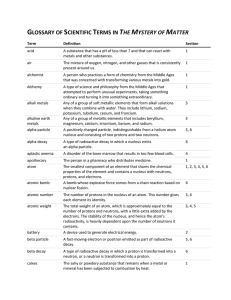
GLOSSARY OF SCIENTIFIC TERMS IN THE MYSTERY OF MATTER
... person. A group of two or more atoms linked together by sharing electrons in a chemical bond. A heavy, neutral particle in an atom’s nucleus that accounts for almost all of each atom’s mass, in addition to protons. Any of the six gases helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon. Because the oute ...
... person. A group of two or more atoms linked together by sharing electrons in a chemical bond. A heavy, neutral particle in an atom’s nucleus that accounts for almost all of each atom’s mass, in addition to protons. Any of the six gases helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon. Because the oute ...
Test Review Answers File
... 8. Why are the Noble Gases considered “inert” gases? List all the elements in this group. -undergo fewest chemical reactions, low chemical reactivity -helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, radon 9. List which elements are chemically similar to Beryllium. Explain why. Magnesium, calcium, strontium, ba ...
... 8. Why are the Noble Gases considered “inert” gases? List all the elements in this group. -undergo fewest chemical reactions, low chemical reactivity -helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, radon 9. List which elements are chemically similar to Beryllium. Explain why. Magnesium, calcium, strontium, ba ...
What does an elements atomic # tell us about the element?
... Potassium - K Atomic # = 19 Atomic mass = 39 K nucleus contains 19 protons 39 – 19 = 20 neutrons How many electrons? Same as # Protons (19) ...
... Potassium - K Atomic # = 19 Atomic mass = 39 K nucleus contains 19 protons 39 – 19 = 20 neutrons How many electrons? Same as # Protons (19) ...
Atomic Structure ppt
... • Protons and neutrons have essentially the same mass. • The mass of an electron is so small we ignore it. ...
... • Protons and neutrons have essentially the same mass. • The mass of an electron is so small we ignore it. ...