* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1 Review Sheet
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
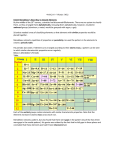
Chapter 1 Review Sheet Definitions: 1. element – the most simple form of matter that can’t be broken down by either chemical or physical means 2. compound – two or more elements that are chemically combined 3. atom – the smallest representative part of an element 4. atomic mass unit – the unit used to measure the relative mass of atoms 5. physical property – a property that can be observed without changing the substances identity 6. chemical property – a property that is displayed when matter undergoes a change in composition Identify the following as either a physical or a chemical property: 7. color PHYSICAL 8. state of matter PHYSICAL 9. ability to rust CHEMICAL 10. magnetic PHYSICAL 11. boiling point PHYSICAL 12. ability to react CHEMICAL 13. ability to tarnish CHEMICAL 14. pH PHYSICAL 15. density PHYSICAL Element Names & Symbols: Carbon C Calcium Ca Copper Cu Chlorine Cl Sulfur S Silicon Si Gold Au Silver Ag Neon Ne Nitrogen N Sodium Na Nickel Ni Identify the following scientists: 16. Joseph Proust 17. JJ Thomspon developed the Law of Definite Proportions. discovered the electron and developed the Plum Pudding Model. 18. Democritus believed that matter was made of tiny particles and there was space between them. 19. Dmitri Mendeleev first organized the periodic table. 20. Ernest Rutherford discovered the nucleus of the atom during his Gold Foil Experiment. 21. Niels Bohr developed a model of the atom in which the electrons orbit the nucleus similar to the way planets orbit the sun. 22. John Dalton possible relationship. believed that atoms combine in the simplest Short Answer: 23. How was Mendeleev’s original periodic table of elements different from our current periodic table? Mendeleev’s table only had about 30 elements and it was ordered by increasing atomic mass, our current table has 118 elements and is ordered by increasing atomic number 24. How was Mendeleev’s original periodic table of elements similar to our current periodic table? Mendeleev grouped elements based on their common properties and our current table does the same 25. Describe Ernest Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment. How did we simulate this experiment in a lab? Rutherford shot particles through a thin piece of gold foil. Most particles went through but some bounced back. We simulated this experiment with wooden boards and marbles. 26. Describe the pH scale. Identify the pH values for acids, bases and neutral solutions. The pH scale goes from 0-14. Acids are from 0-6.9, Bases are from 7.1-14 and neutral solutions are at 7. 27. What were the 3 indicators of a chemical reaction that were observed in Chapter 1 Activity 2? bubbles (gas produced), heat produced, color change 28. Draw a transverse wave and label the following parts: crest, trough & wavelength 29. List the 7 parts of the electromagnetic spectrum in order of lowest to highest energy. radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, UV, x-rays, gamma rays 30. List the 7 colors of the visible spectrum in order of lowest to highest energy. Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, Violet Calculations: f=C λ E=hxf C = 3.00 x 108 m/s h = 6.63 x 10-34 Jּs 31. What is the velocity of a wave that has a wavelength of 5.92 x 10-6 m? f=C f = 3.00 x 108 f = 5.07 x 1013 m/s -6 λ 5.92 x 10 32. What is the wavelength of a wave that has a velocity of 2.13 x 1013 m/s? λ=C λ = 3.00 x 108 λ = 1.41 x 10-5 m V 2.13 x 1013 33. How much energy is released from a wave with a frequency of 7.5 x 1013 Hz? E=hxf E = 6.63 x 10-34 Jּs x 7.5 x 1013 Hz E = 5.0 x 10-20 J 34. How much energy is released when an electron jumps from E4 to E2? 2.55 eV