Ch 11 Atoms etc GNC
... Electrons—negatively charged; protons—positively charged; neutrons—electrically neutral Section 2 The Simplest Matter A. Elements—materials that cannot be broken down into simpler materials 1. There are 115 known elements. 2. 90 naturally occurring elements, 25 synthetic elements—made in laboratorie ...
... Electrons—negatively charged; protons—positively charged; neutrons—electrically neutral Section 2 The Simplest Matter A. Elements—materials that cannot be broken down into simpler materials 1. There are 115 known elements. 2. 90 naturally occurring elements, 25 synthetic elements—made in laboratorie ...
and the atomic
... Try it Yourself! In the following pictures, there is a target hidden by a cloud. To figure out the shape of the target, we shot some beams into the cloud and recorded where the beams came out. Can you figure out the shape of the target? ...
... Try it Yourself! In the following pictures, there is a target hidden by a cloud. To figure out the shape of the target, we shot some beams into the cloud and recorded where the beams came out. Can you figure out the shape of the target? ...
Chemistry Content Standards
... Chemistry Content SC1 Students will analyze the nature of matter and its classifications. a. Relate the role of nuclear fusion in producing essentially all elements heavier than helium. b. Identify substances based on chemical and physical properties. c. Predict formulas for stable ionic compounds ( ...
... Chemistry Content SC1 Students will analyze the nature of matter and its classifications. a. Relate the role of nuclear fusion in producing essentially all elements heavier than helium. b. Identify substances based on chemical and physical properties. c. Predict formulas for stable ionic compounds ( ...
Key Concepts - Chemistry Classes of Professor Alba
... simple, whole-number ratios to form compounds; and (4) atoms of one element cannot change into atoms of another element. In a chemical reaction, atoms change the way that they are bound together with other atoms to form a new substance. Although it was only 200 years ago that John Dalton proposed hi ...
... simple, whole-number ratios to form compounds; and (4) atoms of one element cannot change into atoms of another element. In a chemical reaction, atoms change the way that they are bound together with other atoms to form a new substance. Although it was only 200 years ago that John Dalton proposed hi ...
Chemistry Fall Semester Review Sheet
... 19. Define the law of multiple proportions. Elements form compounds in simple whole number ratios 20. What do isotopes of the same element have in common and what is different? Isotopes have the same number of protons, electrons and atomic number Isotopes have a different mass number and number of ...
... 19. Define the law of multiple proportions. Elements form compounds in simple whole number ratios 20. What do isotopes of the same element have in common and what is different? Isotopes have the same number of protons, electrons and atomic number Isotopes have a different mass number and number of ...
Midterm Review Packet - Mrs. McKenzie`s Chemistry and ICP Classes
... In what type of orbitals are the actinide and lanthanide electrons found? ...
... In what type of orbitals are the actinide and lanthanide electrons found? ...
Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... Atomic Structure Subatomic Location Charge Amu Importance ...
... Atomic Structure Subatomic Location Charge Amu Importance ...
a) air c) milk f) beer
... compounds for a fixed mass of the other element are in ratios of small whole numbers. ...
... compounds for a fixed mass of the other element are in ratios of small whole numbers. ...
Matter Review
... • In your notes, use your periodic tables to determine the following for the elements at the bottom. – The number of protons – The number of neutrons – The number of shells – The number of electrons on the outer most shell (valence electrons) – Draw the atoms for each ...
... • In your notes, use your periodic tables to determine the following for the elements at the bottom. – The number of protons – The number of neutrons – The number of shells – The number of electrons on the outer most shell (valence electrons) – Draw the atoms for each ...
Elements, mixtures and compounds lecture
... I. Element (ie: oxygen, hydrogen, lead, gold, krypton): A. exists as only one type of atom: it is, therefore a pure substance (This does not often occur in nature); gold necklace? Oxygen is the most common pure element on Earth (occurs as a dioxide: O2 , what does “di” mean?) B. cannot be broken do ...
... I. Element (ie: oxygen, hydrogen, lead, gold, krypton): A. exists as only one type of atom: it is, therefore a pure substance (This does not often occur in nature); gold necklace? Oxygen is the most common pure element on Earth (occurs as a dioxide: O2 , what does “di” mean?) B. cannot be broken do ...
Diapositiva 1
... – Some particles were deflected at large angles – Discovery: atoms have a very dense positive (+) center, called the nucleus ...
... – Some particles were deflected at large angles – Discovery: atoms have a very dense positive (+) center, called the nucleus ...
Chemistry Midterm Exam 2015 (Study Guide) Unit 1: Measurement
... What is important about the electron configurations of the noble gases? They all have full energy levels. What subatomic particle plays the greatest part in determining the properties of an element? electron Where are the transition metals located? Columns 3-12 (B=group) How does atomic radius chang ...
... What is important about the electron configurations of the noble gases? They all have full energy levels. What subatomic particle plays the greatest part in determining the properties of an element? electron Where are the transition metals located? Columns 3-12 (B=group) How does atomic radius chang ...
Atomic Structure
... Early Atomic Theory “Cosmic substance is made up of an infinite number of elements or particles ...
... Early Atomic Theory “Cosmic substance is made up of an infinite number of elements or particles ...
1 Chapter 4 Atomic Structure 4.1 Defining the Atom Early Models of
... Chapter 4 Atomic Structure 4.1 Defining the Atom Early Models of the Atom An _____________ is the smallest particle of an element that retains it identity in a chemical reaction. The Greek philosopher Democritus (460 B.C. - 370 B.C) was among the first to suggest the existence of atoms. Democritus b ...
... Chapter 4 Atomic Structure 4.1 Defining the Atom Early Models of the Atom An _____________ is the smallest particle of an element that retains it identity in a chemical reaction. The Greek philosopher Democritus (460 B.C. - 370 B.C) was among the first to suggest the existence of atoms. Democritus b ...
matter crct/final exam review
... 26. All of the elements in a column are members of a _________________ and they all have the same number of _______________________________________________________. 27. What information does the atomic mass give you? 28. How can you calculate the number of neutrons in an atom? 29. The majority of th ...
... 26. All of the elements in a column are members of a _________________ and they all have the same number of _______________________________________________________. 27. What information does the atomic mass give you? 28. How can you calculate the number of neutrons in an atom? 29. The majority of th ...
Cornell notes template
... - Take sufficient notes with selective (not too many words) & accurate paraphrasing - Skip a line between ideas and topics - Use bulleted lists and abbreviations - Correctly sequence information - Include diagrams or tables if needed for clarification or length The atomic number of proton and electr ...
... - Take sufficient notes with selective (not too many words) & accurate paraphrasing - Skip a line between ideas and topics - Use bulleted lists and abbreviations - Correctly sequence information - Include diagrams or tables if needed for clarification or length The atomic number of proton and electr ...
Chemistry 1 – Tollett Chapter 5 – Atomic Structure & The Periodic
... negatively charged particles which he called electrons. • He also calculated the charge-to-mass ratio of the electron. ...
... negatively charged particles which he called electrons. • He also calculated the charge-to-mass ratio of the electron. ...
File
... of radioactive decay. - Radioactive decay: the atomic nuclei of radioactive isotopes release fast-moving particles and energy. - Example of a nuclear reaction: process that involves the particles of an atom’s nucleus. - Radioactivity: The spontaneous emission of radiation by an unstable atomic nucle ...
... of radioactive decay. - Radioactive decay: the atomic nuclei of radioactive isotopes release fast-moving particles and energy. - Example of a nuclear reaction: process that involves the particles of an atom’s nucleus. - Radioactivity: The spontaneous emission of radiation by an unstable atomic nucle ...
chapter2 - AlvarezHChem
... 2. Emit other particles and are transformed into other elements • Particles emitted 1. Beta (β) particles: High speed electrons 2. Alpha (α) particles: helium nuclei 3. Gamma (γ) rays: high energy light ...
... 2. Emit other particles and are transformed into other elements • Particles emitted 1. Beta (β) particles: High speed electrons 2. Alpha (α) particles: helium nuclei 3. Gamma (γ) rays: high energy light ...
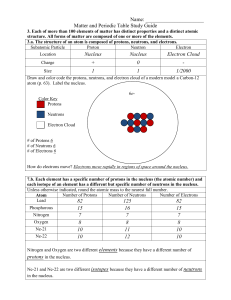
Matter and the Periodic Table Study Guide Answer Key
... Semimetals/Metalloids have properties of both metals and non-metals. 3.b. Compounds are formed by combining two or more different elements and compounds have properties that are different from their constituent elements. 3.f. Use the periodic table to identify elements in simple compounds. Compound ...
... Semimetals/Metalloids have properties of both metals and non-metals. 3.b. Compounds are formed by combining two or more different elements and compounds have properties that are different from their constituent elements. 3.f. Use the periodic table to identify elements in simple compounds. Compound ...
1 - M*W
... d) B & C 34) Halogens, like fluorine, are very reactive because a) They want to gain an electron to complete their outer energy level b) They want to lose an electron to complete their outer energy level c) They want to gain a proton in their nucleus d) They want to lose a proton from their nucleus ...
... d) B & C 34) Halogens, like fluorine, are very reactive because a) They want to gain an electron to complete their outer energy level b) They want to lose an electron to complete their outer energy level c) They want to gain a proton in their nucleus d) They want to lose a proton from their nucleus ...
Elements Compounds Mixtures
... salad, BLT; PB&J HOMOGENEOUS • Two or more substances evenly mixed. • You can NOT see the different substances, even with a microscope! • Examples: gatorade, salt water, brass, air ...
... salad, BLT; PB&J HOMOGENEOUS • Two or more substances evenly mixed. • You can NOT see the different substances, even with a microscope! • Examples: gatorade, salt water, brass, air ...
Atomic Structure
... ________________________ Atoms (he called them atomos). ________________________ Elements. ________________________ Ions. ________________________ Electrons. ________________________ Nucleus. ...
... ________________________ Atoms (he called them atomos). ________________________ Elements. ________________________ Ions. ________________________ Electrons. ________________________ Nucleus. ...