Transcription - Effingham County Schools
... make a copy of it for your own use, put the reference material back on the shelf so that others can use it too. Can you imagine if DNA was physically lost? That’s why chromosomes never leave the nucleus. ...
... make a copy of it for your own use, put the reference material back on the shelf so that others can use it too. Can you imagine if DNA was physically lost? That’s why chromosomes never leave the nucleus. ...
Chapter 3 Protein Synthesis Life Science RNA – Ribonucleic Acid
... Each codon specifies a particular amino acid There are 20 different amino acids There are 64 different combinations of A, U, G, and C that a codon could have ( 4x4x4) There are three “stop” codons acting as a “period” in a sentence The “sentence” is that strip of mRNA produced by the section of expo ...
... Each codon specifies a particular amino acid There are 20 different amino acids There are 64 different combinations of A, U, G, and C that a codon could have ( 4x4x4) There are three “stop” codons acting as a “period” in a sentence The “sentence” is that strip of mRNA produced by the section of expo ...
Gene Expression - Phillips Scientific Methods
... _____ GTP is used to attach the large subunit of the ribosome to the mRNA initiation complex. _____ The next tRNA matches its anti-codon to the codon of the “A” site. _____ Spliceosome adheres to snRNPs and excises introns while sealing exons into a continuous strand of mRNA. _____ Two GTPs are used ...
... _____ GTP is used to attach the large subunit of the ribosome to the mRNA initiation complex. _____ The next tRNA matches its anti-codon to the codon of the “A” site. _____ Spliceosome adheres to snRNPs and excises introns while sealing exons into a continuous strand of mRNA. _____ Two GTPs are used ...
sample genetic code exercises
... Given the following DNA sequences, derive the (a) complementary mRNA, and the (b) resulting protein: 1. 5’ TTTCATGCCCCGATAUGTACCC 3’ a. to derive the complementary RNA, we simply take note of the pairing rules (A with T/U, and C with G). Also, the DNA and RNA strands must be antiparallel (i.e. 5’ an ...
... Given the following DNA sequences, derive the (a) complementary mRNA, and the (b) resulting protein: 1. 5’ TTTCATGCCCCGATAUGTACCC 3’ a. to derive the complementary RNA, we simply take note of the pairing rules (A with T/U, and C with G). Also, the DNA and RNA strands must be antiparallel (i.e. 5’ an ...
Biology Pre-Learning Check
... We will also study the process where RNA is used to make proteins. Specifically, we will study each part (transcription and translation), the steps involved and the enzymes involved. We will also look more specifically at mutations; how they can occur and what effects they might have. Pages in the b ...
... We will also study the process where RNA is used to make proteins. Specifically, we will study each part (transcription and translation), the steps involved and the enzymes involved. We will also look more specifically at mutations; how they can occur and what effects they might have. Pages in the b ...
Chapter 17 - Denton ISD
... sections called _______, and leaving exons. Some genes can produce multiple polypeptides depending on what is spliced; this is called ___________________. Exon shuffling during cross-over may also be useful in evolution. ...
... sections called _______, and leaving exons. Some genes can produce multiple polypeptides depending on what is spliced; this is called ___________________. Exon shuffling during cross-over may also be useful in evolution. ...
Biology 211 Intro Molecular and Cell Biology
... There are two sites on the ribosome for binding tRNAs, the P site and the A site. The growing protein chain is attached to the tRNA in the P site. An incoming charged tRNA binds to the codon of the mRNA in the A site. The ribosome catalyzes formation of a peptide bond. Translocation of the ribosome ...
... There are two sites on the ribosome for binding tRNAs, the P site and the A site. The growing protein chain is attached to the tRNA in the P site. An incoming charged tRNA binds to the codon of the mRNA in the A site. The ribosome catalyzes formation of a peptide bond. Translocation of the ribosome ...
4. Transcription in Detail
... Process is repeated until __________________________________is reached Complex is dismantled and ________________________________is released. ...
... Process is repeated until __________________________________is reached Complex is dismantled and ________________________________is released. ...
protein synthesis - Ms. Dooley`s Science Class
... of one DNA strand (“master strand”) to form mRNA. (Remember that uracil replaces thymine in the RNA formation; therefore, uracil pairs with thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine.) The nucleotides on the new mRNA are complimentary (opposite) to the nucleotides in the master strand of DNA. After the ...
... of one DNA strand (“master strand”) to form mRNA. (Remember that uracil replaces thymine in the RNA formation; therefore, uracil pairs with thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine.) The nucleotides on the new mRNA are complimentary (opposite) to the nucleotides in the master strand of DNA. After the ...
Protein Synthesis
... stranded molecule, we only need to copy one side of the DNA. The side we use is the 3’ side. (NO lagging strand!!!) • Tell a partner WHY you thing we use the 3’ side of the DNA, be ready to share. • The 3’ side of DNA is called the antisense strand. The 5’ (uncopied) side is called the sense strand. ...
... stranded molecule, we only need to copy one side of the DNA. The side we use is the 3’ side. (NO lagging strand!!!) • Tell a partner WHY you thing we use the 3’ side of the DNA, be ready to share. • The 3’ side of DNA is called the antisense strand. The 5’ (uncopied) side is called the sense strand. ...
Nucleic acid chemistry lecture 3
... Differentiate between different types of RNA List differences between DNA and RNA Mention free nucleotides of biological impotances ...
... Differentiate between different types of RNA List differences between DNA and RNA Mention free nucleotides of biological impotances ...
013368718X_CH13_193
... DNA template is RNA polymerase. 6. The region of DNA where the production of an RNA strand begins is called the intron. 7. Exons are spliced together in forming messenger RNA. For Questions 8–16, match the term with its definition. ...
... DNA template is RNA polymerase. 6. The region of DNA where the production of an RNA strand begins is called the intron. 7. Exons are spliced together in forming messenger RNA. For Questions 8–16, match the term with its definition. ...
DNA RNA Protein Hwk KEY
... 8. … A scientist uses biotech methods to insert a human gene into bacterial cells, hoping the cells will express it and synthesize functional human protein. Instead, the protein produced is found to contain many fewer amino acids and doesn't work. What could have gone wrong? Perhaps the human gene c ...
... 8. … A scientist uses biotech methods to insert a human gene into bacterial cells, hoping the cells will express it and synthesize functional human protein. Instead, the protein produced is found to contain many fewer amino acids and doesn't work. What could have gone wrong? Perhaps the human gene c ...
DNA - hdueck
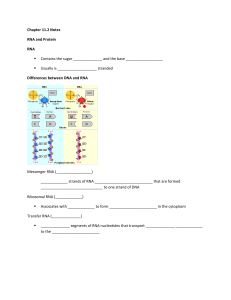
... Ribonucleic Acid Types (p 288-295) There are several types. We will focus on the main 3 types: rRNA: large, makes up structure of ribosomes. - Large globular structure, forms structure with proteins to form ribosome tRNA: smaller, contains amino acid to match code of mRNA. Compact 3-D structure mRN ...
... Ribonucleic Acid Types (p 288-295) There are several types. We will focus on the main 3 types: rRNA: large, makes up structure of ribosomes. - Large globular structure, forms structure with proteins to form ribosome tRNA: smaller, contains amino acid to match code of mRNA. Compact 3-D structure mRN ...
GENE to PROTEIN
... • First codon decipher was UUU • There are 64 codons • A codon codes for only 1 amino acid The genetic code must have evolved very early in the history of life because it is nearly universal among living organisms. ...
... • First codon decipher was UUU • There are 64 codons • A codon codes for only 1 amino acid The genetic code must have evolved very early in the history of life because it is nearly universal among living organisms. ...
GENE to PROTEIN
... • First codon decipher was UUU • There are 64 codons • A codon codes for only 1 amino acid The genetic code must have evolved very early in the history of life because it is nearly universal among living organisms. ...
... • First codon decipher was UUU • There are 64 codons • A codon codes for only 1 amino acid The genetic code must have evolved very early in the history of life because it is nearly universal among living organisms. ...
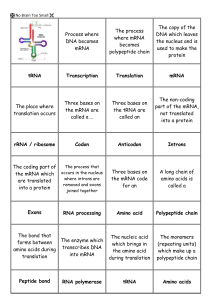
Gene expression flash cards
... The process that The coding part of the mRNA which occurs in the nucleus where introns are are translated removed and exons into a protein joined together ...
... The process that The coding part of the mRNA which occurs in the nucleus where introns are are translated removed and exons into a protein joined together ...
Lecture outlines: RNA to proteins
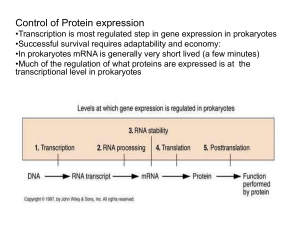
... rRNA and tRNA generally called “stable RNAs” (have long half-lives) while mRNAs are degraded fairly rapidly (in E. coli, typical mRNA with half-life of a few minutes). Generally, do not see processing of mRNAs in bacterial cells (as seen in eukaryotes; Fig. 8.12). Exception to this are the RNAs tran ...
... rRNA and tRNA generally called “stable RNAs” (have long half-lives) while mRNAs are degraded fairly rapidly (in E. coli, typical mRNA with half-life of a few minutes). Generally, do not see processing of mRNAs in bacterial cells (as seen in eukaryotes; Fig. 8.12). Exception to this are the RNAs tran ...
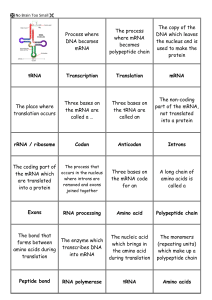
Gene expression flash cards
... The process that The coding part of the mRNA which occurs in the nucleus where introns are are translated removed and exons into a protein joined together ...
... The process that The coding part of the mRNA which occurs in the nucleus where introns are are translated removed and exons into a protein joined together ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS AND PROCESSING Protein biosynthesis is
... strictly regulated at multiple steps. They are principally during transcription (phenomena of RNA synthesis from DNA template) and translation (phenomena of amino acid assembly from RNA). The cistron DNA is transcribed into the first of a series of RNA intermediates. The last version is used as a te ...
... strictly regulated at multiple steps. They are principally during transcription (phenomena of RNA synthesis from DNA template) and translation (phenomena of amino acid assembly from RNA). The cistron DNA is transcribed into the first of a series of RNA intermediates. The last version is used as a te ...