Problem 3: Why do pre-mRNAs get smaller during RNA processing?
... C. RNA synthesis and protein synthesis are coupled as in prokaryotes D. mRNA is often extensively modified before translation E. multiple copies of nuclear genes, and pseudogenes can occur ...
... C. RNA synthesis and protein synthesis are coupled as in prokaryotes D. mRNA is often extensively modified before translation E. multiple copies of nuclear genes, and pseudogenes can occur ...
protein synthesis
... List below are the steps involved in the attachment of the amino acid to its tRNA. Put them in the correct order. ______ ATP loses phosphates ______ AMP attaches to amino acid ______ Enzyme active site binds to amino acid and ATP ______ tRNA displaces AMP and binds to amino acid The attachment of an ...
... List below are the steps involved in the attachment of the amino acid to its tRNA. Put them in the correct order. ______ ATP loses phosphates ______ AMP attaches to amino acid ______ Enzyme active site binds to amino acid and ATP ______ tRNA displaces AMP and binds to amino acid The attachment of an ...
2009 WH Freeman and Company
... • Intron removal, mRNA processing, and transcription take place at the same site in the nucleus. • Self-splicing introns happen in some rRNA genes in protists and in mitochondria genes in fungi. • There are alternative processing pathways for processing pre-mRNA. ...
... • Intron removal, mRNA processing, and transcription take place at the same site in the nucleus. • Self-splicing introns happen in some rRNA genes in protists and in mitochondria genes in fungi. • There are alternative processing pathways for processing pre-mRNA. ...
From DNA to Protein
... Allows one gene to encode different proteins Some exons are removed from RNA and others are spliced together in various combinations ...
... Allows one gene to encode different proteins Some exons are removed from RNA and others are spliced together in various combinations ...
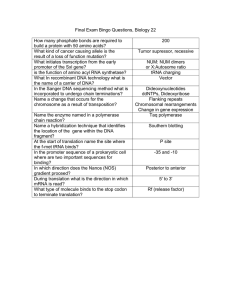
How many phosphate bonds are required to build a protein with 50
... incorporated to undergo chain terminations? Name a change that occurs for the chromosome as a result of transposition? Name the enzyme named in a polymerase chain reaction? Name a hybridization technique that identifies the location of the gene within the DNA fragment? At the start of translation na ...
... incorporated to undergo chain terminations? Name a change that occurs for the chromosome as a result of transposition? Name the enzyme named in a polymerase chain reaction? Name a hybridization technique that identifies the location of the gene within the DNA fragment? At the start of translation na ...
Ch. 11 - Gene Action and protein synthesis
... Genes are made up of different regions: – Coding region – part that contains information for producing the protein – Flanking regions – the regions before (upstream) and after (downstream) the coding region ...
... Genes are made up of different regions: – Coding region – part that contains information for producing the protein – Flanking regions – the regions before (upstream) and after (downstream) the coding region ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... • Transcribe = to write/copy down • When DNA’s instructions are copied by mRNA ...
... • Transcribe = to write/copy down • When DNA’s instructions are copied by mRNA ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... of the cell – the instructions tell the cell how to assemble the amino acids for making proteins ...
... of the cell – the instructions tell the cell how to assemble the amino acids for making proteins ...
Protein Synthesis
... The sequence (order) of bases in a strand of DNA makes the code for building proteins. EX: The three bases “CCA” form the code for the amino acid proline. A long string of amino acids forms a protein. Each gene is usually a set of instructions for making a protein. Proteins are responsible for most ...
... The sequence (order) of bases in a strand of DNA makes the code for building proteins. EX: The three bases “CCA” form the code for the amino acid proline. A long string of amino acids forms a protein. Each gene is usually a set of instructions for making a protein. Proteins are responsible for most ...
Bio 1 Unit Objectives Protein Synthesis Readings
... A gene provides the information for making a specific protein Explain the “one-gene-one-polypeptide” hypothesis Trace the information flow from DNA to protein Describe how amino acids are coded ...
... A gene provides the information for making a specific protein Explain the “one-gene-one-polypeptide” hypothesis Trace the information flow from DNA to protein Describe how amino acids are coded ...
Protein Synthesis Review
... Enzymes, which speed up chemical reactions Build and repair cell structures Determine the structure & function of living organisms ...
... Enzymes, which speed up chemical reactions Build and repair cell structures Determine the structure & function of living organisms ...
Protein Synthesis - Building Directory
... Amino acids are added one by one by the following process: ...
... Amino acids are added one by one by the following process: ...
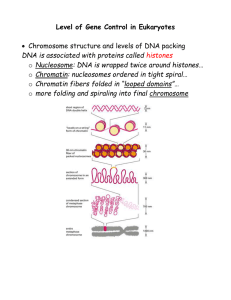
Genetic Controls in Eukaryotes
... Regulation at post-transcriptional level - RNA processing o Alternative RNA splicing = different segments of RNA are treated as exons and introns = different mRNA o Controlled by regulatory proteins specific to each cell type o Consequence = a single gene can code for more than one polypeptide = ...
... Regulation at post-transcriptional level - RNA processing o Alternative RNA splicing = different segments of RNA are treated as exons and introns = different mRNA o Controlled by regulatory proteins specific to each cell type o Consequence = a single gene can code for more than one polypeptide = ...
MS Word worksheet
... 2. Draw a diagram that illustrates the flow of information within a eukaryotic cell from a gene to a polypeptide chain and then: Indicate the places where transcription and translation occur and define these two terms. ...
... 2. Draw a diagram that illustrates the flow of information within a eukaryotic cell from a gene to a polypeptide chain and then: Indicate the places where transcription and translation occur and define these two terms. ...
What Is the Genetic Code? 1. Explain, in general terms, how the
... 2. Draw a diagram that illustrates the flow of information within a eukaryotic cell from a gene to a polypeptide chain and then: Indicate the places where transcription and translation occur and define these two terms. ...
... 2. Draw a diagram that illustrates the flow of information within a eukaryotic cell from a gene to a polypeptide chain and then: Indicate the places where transcription and translation occur and define these two terms. ...
Eukaryotic mRNA translation: Ribosome structure, function, and
... mRNP remodeling occurs during nucleocytoplasmic transport ...
... mRNP remodeling occurs during nucleocytoplasmic transport ...
From Gene to Protein
... Sequences are UAG, UAA, and UGA Don’t code for AA’s Polypeptide cleaved from last tRNA (P site) and leaves the ...
... Sequences are UAG, UAA, and UGA Don’t code for AA’s Polypeptide cleaved from last tRNA (P site) and leaves the ...
Topic 3 The Chemistry of Life - wfs
... 6. It is at the ribosomes where the process of translation occurs. Translation is the process that leads to the formation of polypeptides, proteins. 7. In the cytoplasm tRNA molecules contain anticodons. The tRNA anticodons pair with the mRNA codons through base pairing. Because each tRNA with a par ...
... 6. It is at the ribosomes where the process of translation occurs. Translation is the process that leads to the formation of polypeptides, proteins. 7. In the cytoplasm tRNA molecules contain anticodons. The tRNA anticodons pair with the mRNA codons through base pairing. Because each tRNA with a par ...
RNA STRUCTURE - mbbsclub.com
... Transcription produces messenger RNAs that are translated into sequences of amino acids (polypeptide chains or proteins), and ribosomal RNAs, transfer RNAs, and additional small RNA molecules that perform specialized structural, catalytic, and regulatory functions and are not translated. ...
... Transcription produces messenger RNAs that are translated into sequences of amino acids (polypeptide chains or proteins), and ribosomal RNAs, transfer RNAs, and additional small RNA molecules that perform specialized structural, catalytic, and regulatory functions and are not translated. ...
Mentor: James A. MacKay Students: Amanda Williams, Holly Sofka
... Students: Amanda Williams, Holly Sofka Project Description: Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is believed to be an important molecule in the evolution of life and has functionally taken on many important biological roles. Given the many functions of RNA, molecular recognition of RNA represents an attractive go ...
... Students: Amanda Williams, Holly Sofka Project Description: Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is believed to be an important molecule in the evolution of life and has functionally taken on many important biological roles. Given the many functions of RNA, molecular recognition of RNA represents an attractive go ...