protein synthesis
... The tRNA will deliver the appropriate amino acid in the cytoplasm that is coded for by the mRNA messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded to produce a specific protein using specific amino acids ...
... The tRNA will deliver the appropriate amino acid in the cytoplasm that is coded for by the mRNA messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded to produce a specific protein using specific amino acids ...
The Code of Life: Topic 3
... • The 5' cap of mRNA attaches to a a small ribosome subunit. • The initiator tRNA has the anticodon for the start codon (AUG) on mRNA. • The initiator tRNA always carries the amino acid methionine ...
... • The 5' cap of mRNA attaches to a a small ribosome subunit. • The initiator tRNA has the anticodon for the start codon (AUG) on mRNA. • The initiator tRNA always carries the amino acid methionine ...
Slides - University of Sydney
... • So mutations in DNA often don’t affect the amino acid sequence – Especially if in the last nucleotide in the codon – But it’s impossible to deduce the nucleic acid sequence from a protein sequence! ...
... • So mutations in DNA often don’t affect the amino acid sequence – Especially if in the last nucleotide in the codon – But it’s impossible to deduce the nucleic acid sequence from a protein sequence! ...
gene expression - Aurora City Schools
... an anticodon). This process is called initiation. 2 tRNAs can fit at one time. 3. ribosome moves down and matches next codon. 4. Amino acids form peptide bond and protein continues to grow, 1 amino acid at a time. This process is called elongation. 5. ribosome reaches stop codon, mRNA, tRNAs, protei ...
... an anticodon). This process is called initiation. 2 tRNAs can fit at one time. 3. ribosome moves down and matches next codon. 4. Amino acids form peptide bond and protein continues to grow, 1 amino acid at a time. This process is called elongation. 5. ribosome reaches stop codon, mRNA, tRNAs, protei ...
Protein Synthesis Worksheet
... 15. (tRNA / mRNA) brings amino acids to the ribosome. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus / cytoplasm). 17. (Translation / Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. 18. Translation takes place in the (cytoplasm / nucleus). 19. (one / three) codons equals one amino acid. 20. (amino acids / nucleotid ...
... 15. (tRNA / mRNA) brings amino acids to the ribosome. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus / cytoplasm). 17. (Translation / Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. 18. Translation takes place in the (cytoplasm / nucleus). 19. (one / three) codons equals one amino acid. 20. (amino acids / nucleotid ...
Gene Expression Vocabulary
... 3. Gene expression: the process of information from DNA to proteins 4. Transcription: the information in DNA is transferred to mRNA 5. Translation: the information in mRNA is used to make a protein 6. RNA polymerase: an enzyme that begins transcription 7. Promoter: a specific sequence of DNA that ac ...
... 3. Gene expression: the process of information from DNA to proteins 4. Transcription: the information in DNA is transferred to mRNA 5. Translation: the information in mRNA is used to make a protein 6. RNA polymerase: an enzyme that begins transcription 7. Promoter: a specific sequence of DNA that ac ...
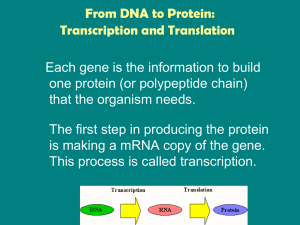
From DNA to Protein: Transcription and Translation
... The process of transcription is similar to DNA replication in that the DNA is unwound and complementary nucleotides are added. Differences: • Only a gene is copied, not the whole chromosome. • RNA nucleotides are added instead of DNA nucleotides. – Uracil is paired with adenine instead of thymine. • ...
... The process of transcription is similar to DNA replication in that the DNA is unwound and complementary nucleotides are added. Differences: • Only a gene is copied, not the whole chromosome. • RNA nucleotides are added instead of DNA nucleotides. – Uracil is paired with adenine instead of thymine. • ...
3.5 Transcription and translation – summary of
... meaning more than one codon can code for a particular amino acid; the genetic code is universal; meaning it is the same in almost all organisms; (AUG is the) start codon; some (nonsense) codons code for the end of translation; ...
... meaning more than one codon can code for a particular amino acid; the genetic code is universal; meaning it is the same in almost all organisms; (AUG is the) start codon; some (nonsense) codons code for the end of translation; ...
Eukaryotic Gene Expression ppt
... Have a nuclear envelope Many are multicellular with specialized cells All cells have full sets of chromosomes Not all genes need to be turned on (expressed) ...
... Have a nuclear envelope Many are multicellular with specialized cells All cells have full sets of chromosomes Not all genes need to be turned on (expressed) ...
DNA Replication, Transcription, and Translation STUDY GUIDE
... The process that makes an exact copy of a cell's DNA is called ___________________. What are the main functions of DNA polymerase? The main function of tRNA is to: What is the term for a three-nucleotide sequence that codes for an amino acid? How many amino acids are used to make up the all of the p ...
... The process that makes an exact copy of a cell's DNA is called ___________________. What are the main functions of DNA polymerase? The main function of tRNA is to: What is the term for a three-nucleotide sequence that codes for an amino acid? How many amino acids are used to make up the all of the p ...
How Proteins are Made
... proteins block RNA polymerase from transcribing a gene. 3. When an inducer (presence of lactose) is present it binds to the repressor and transcription can continue ...
... proteins block RNA polymerase from transcribing a gene. 3. When an inducer (presence of lactose) is present it binds to the repressor and transcription can continue ...
Chapter 3 Protein Synthesis
... Each codon specifies a particular amino acid There are 20 different amino acids There are 64 different combinations of A, U, G, and C that a codon could have ( 4x4x4) There are three “stop” codons acting as a “period” in a sentence The “sentence” is that strip of mRNA produced by the section of ...
... Each codon specifies a particular amino acid There are 20 different amino acids There are 64 different combinations of A, U, G, and C that a codon could have ( 4x4x4) There are three “stop” codons acting as a “period” in a sentence The “sentence” is that strip of mRNA produced by the section of ...
DNA & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... - The “Middle-Man” between DNA (nucleus) & the ribosomes (cytoplasm). 2. Structure a. Ribose (Sugar) b. Single-stranded, not double. c. Thymine is replaced by URACIL. - Adenine binds with Uracil. d. RNA can be found inside and outside of the nucleus (DNA is always inside!) ...
... - The “Middle-Man” between DNA (nucleus) & the ribosomes (cytoplasm). 2. Structure a. Ribose (Sugar) b. Single-stranded, not double. c. Thymine is replaced by URACIL. - Adenine binds with Uracil. d. RNA can be found inside and outside of the nucleus (DNA is always inside!) ...
Ch. 17 Protein Synthesis
... out of nucleus to the cytoplasm Each 3 bases on mRNA is a “codon” tRNA (transfer RNA) –The anticodon that matches with the codon from mRNA to determine which amino acid joins the protein ...
... out of nucleus to the cytoplasm Each 3 bases on mRNA is a “codon” tRNA (transfer RNA) –The anticodon that matches with the codon from mRNA to determine which amino acid joins the protein ...
DNA to Protein - Seabreeze High School
... Things to think About & Discuss 1. What if a mutation occurs in the DNA? Explain how could that affect the organism’s protein? 2. What if a mutation occurs in 3rd base of the codon? Will it always code for a different amino acid? Explain. ...
... Things to think About & Discuss 1. What if a mutation occurs in the DNA? Explain how could that affect the organism’s protein? 2. What if a mutation occurs in 3rd base of the codon? Will it always code for a different amino acid? Explain. ...
Protein Synthesis Notes
... (the “chefs”) to send these recipes to the ribosomes (“kitchen”) so they can be made. 1. The basic unit of a protein is an amino acid a. we use 20 amino acids to make all of our proteins 2. A chain of amino acids together is a protein 3. Types of proteins include: hormones, enzymes, structural prote ...
... (the “chefs”) to send these recipes to the ribosomes (“kitchen”) so they can be made. 1. The basic unit of a protein is an amino acid a. we use 20 amino acids to make all of our proteins 2. A chain of amino acids together is a protein 3. Types of proteins include: hormones, enzymes, structural prote ...
Chapter 17 - HCC Learning Web
... A) proteins, triglycerides, and testosterone B) proteins, carbohydrates, and ATP C) ATP, RNA, and DNA D) α glucose, ATP, and DNA E) proteins, ATP, and DNA 2) A particular triplet of bases in the template strand of DNA is 5' AGT 3'. The corresponding codon for the mRNA transcribed is 2) _______ A) 3' ...
... A) proteins, triglycerides, and testosterone B) proteins, carbohydrates, and ATP C) ATP, RNA, and DNA D) α glucose, ATP, and DNA E) proteins, ATP, and DNA 2) A particular triplet of bases in the template strand of DNA is 5' AGT 3'. The corresponding codon for the mRNA transcribed is 2) _______ A) 3' ...
Protein Synthesis: Part I: Transcription
... p mRNA copies DNA p mRNA leaves the nucleus and travels through the cytoplasm to the ribosome p mRNA complements known as codons ...
... p mRNA copies DNA p mRNA leaves the nucleus and travels through the cytoplasm to the ribosome p mRNA complements known as codons ...
Protein Synthesis
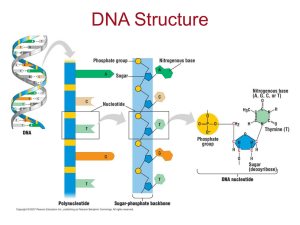
... - The sugar-phosphate backbone is made of deoxyribose sugar - Double stranded ...
... - The sugar-phosphate backbone is made of deoxyribose sugar - Double stranded ...
The process of copying a gene`s DNA sequence into a sequence of
... true regarding introns? 1. Introns are the parts of mRNA that are translated 2. Introns have no function. 3. In general, human genes have fewer introns than genes of other organisms. 4. Introns may be involved in exon shuffling ...
... true regarding introns? 1. Introns are the parts of mRNA that are translated 2. Introns have no function. 3. In general, human genes have fewer introns than genes of other organisms. 4. Introns may be involved in exon shuffling ...
Study Questions for Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein
... RNA splicing takes out sections of mRNA that are not coding for a section of the protein; introns are spliced out and exons are then joined together to make a continuous coding sequence 12) Introns (non-coding regions) were once thought to be “junk DNA” but now it is thought that they do have biolog ...
... RNA splicing takes out sections of mRNA that are not coding for a section of the protein; introns are spliced out and exons are then joined together to make a continuous coding sequence 12) Introns (non-coding regions) were once thought to be “junk DNA” but now it is thought that they do have biolog ...