Ch17_note_summary
... leaving exons. Some genes can produce multiple polypeptides depending on what is spliced; this is called alternative RNA splicing. Exon shuffling during cross-over may also be useful in evolution. ...
... leaving exons. Some genes can produce multiple polypeptides depending on what is spliced; this is called alternative RNA splicing. Exon shuffling during cross-over may also be useful in evolution. ...
3.4: Transcription and Translation
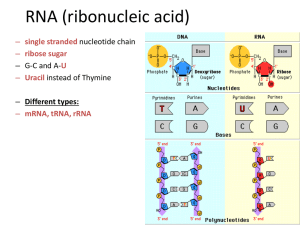
... sugar is deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA; DNA is double stranded and RNA is single stranded; DNA has a (double) helix; DNA has thymine while RNA has uracil; (require full names written out) both contain four nitrogenous bases / A, G, C, T for DNA and A, G, C, U for RNA; [4 max] ...
... sugar is deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA; DNA is double stranded and RNA is single stranded; DNA has a (double) helix; DNA has thymine while RNA has uracil; (require full names written out) both contain four nitrogenous bases / A, G, C, T for DNA and A, G, C, U for RNA; [4 max] ...
Decoding mRNA
... DNA. This copy is called 5. _________________________ and can leave the cell’s nucleus. It travels to the 6.___________________ in the cytoplasm of the cell where DNA’s message can be decoded into a sequence of amino acids. The steps of creating an mRNA transcript need to be put in order. 7. Place t ...
... DNA. This copy is called 5. _________________________ and can leave the cell’s nucleus. It travels to the 6.___________________ in the cytoplasm of the cell where DNA’s message can be decoded into a sequence of amino acids. The steps of creating an mRNA transcript need to be put in order. 7. Place t ...
Making Proteins
... nucleotide bases to DNA, using one side as a template. 3. The mRNA strand is created. It now compliments the original DNA strand (G-C and A-U). 4. Ligase helps the strand of DNA to close and again. 5. mRNA strand moves out of nucleus to ribosomes, and the DNA zips up. ...
... nucleotide bases to DNA, using one side as a template. 3. The mRNA strand is created. It now compliments the original DNA strand (G-C and A-U). 4. Ligase helps the strand of DNA to close and again. 5. mRNA strand moves out of nucleus to ribosomes, and the DNA zips up. ...
DNA WebQuest
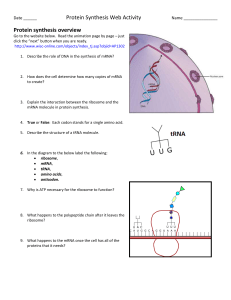
... Go to the website below. Read the animation page by page – just click the “next” button when you are ready. http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP1302 1. Describe the role of DNA in the synthesis of mRNA? ...
... Go to the website below. Read the animation page by page – just click the “next” button when you are ready. http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP1302 1. Describe the role of DNA in the synthesis of mRNA? ...
Protein Synthesis (Translation)
... Translation or protein synthesis is the process of making a protein Proteins are made up of amino acids (small building blocks) There are 20 different types of amino acids ...
... Translation or protein synthesis is the process of making a protein Proteins are made up of amino acids (small building blocks) There are 20 different types of amino acids ...
No Slide Title
... Types / Function of RNA mRNA rRNA and tRNA snRNA : splicing, telomere maintenance RNA enzyme / ribozyme : catalytic activity RNA genome : genetic material (ss / ds) RNA gene : RNA as final product ...
... Types / Function of RNA mRNA rRNA and tRNA snRNA : splicing, telomere maintenance RNA enzyme / ribozyme : catalytic activity RNA genome : genetic material (ss / ds) RNA gene : RNA as final product ...
transcription translation mutation lesson ppt
... together to make the mature mRNA transcript intron = noncoding (inbetween) sequence ~10,000 bases eukaryotic DNA exon = coding (expressed) sequence ...
... together to make the mature mRNA transcript intron = noncoding (inbetween) sequence ~10,000 bases eukaryotic DNA exon = coding (expressed) sequence ...
9 - Transcription and Translation
... tRNA Structure tRNA is like a “_______________” with a "nucleic acid word" (________________) on one side and a "protein word" (___________________) on the other side Specific amino acids are added to each tRNA molecule with a specific enzyme called ___________________________ _____________________ ...
... tRNA Structure tRNA is like a “_______________” with a "nucleic acid word" (________________) on one side and a "protein word" (___________________) on the other side Specific amino acids are added to each tRNA molecule with a specific enzyme called ___________________________ _____________________ ...
From DNA to Protein
... Gene expression A multistep process in which genetic information is converted into a structural or functional part of a cell or body ...
... Gene expression A multistep process in which genetic information is converted into a structural or functional part of a cell or body ...
Regulation of gene expression: Eukaryotic
... II. Transcription: RNA from DNA What is the enzyme that can direct RNA synthesis? RNA polymerase - first isolated in liver of rats - requires NTPs with ribose as sugar - NO primer is needed ...
... II. Transcription: RNA from DNA What is the enzyme that can direct RNA synthesis? RNA polymerase - first isolated in liver of rats - requires NTPs with ribose as sugar - NO primer is needed ...
Chapter 3 Section 4 Protein Synthesis
... • Transcription – the DNA strand is unzipped to allow a strand of mRNA to be created from its exposed nitrogen bases • The new strand of mRNA are made by matching new nitrogen bases with the exposed nitrogen bases from the unzipped strand of DNA. ...
... • Transcription – the DNA strand is unzipped to allow a strand of mRNA to be created from its exposed nitrogen bases • The new strand of mRNA are made by matching new nitrogen bases with the exposed nitrogen bases from the unzipped strand of DNA. ...
Part 4 Transcription
... 9. Understand transcription and the role that RNA polymerase plays in it. ...
... 9. Understand transcription and the role that RNA polymerase plays in it. ...
Translation (Protein Synthesis)
... • mRNA from nucleus Through cytoplasm to the ribosome mRNA start codon AUG signals beginning of protein ...
... • mRNA from nucleus Through cytoplasm to the ribosome mRNA start codon AUG signals beginning of protein ...
Name
... 4. What nucleotides are found in RNA? 5. Where in the eukaryotic cell does transcription take place? 6. What are the differences between DNA and RNA (include at least 3 differences)? 7. What are the differences between replication and transcription (include at least 3 differences)? 8. Draw a picture ...
... 4. What nucleotides are found in RNA? 5. Where in the eukaryotic cell does transcription take place? 6. What are the differences between DNA and RNA (include at least 3 differences)? 7. What are the differences between replication and transcription (include at least 3 differences)? 8. Draw a picture ...
Biology Topics, Venn diagrams
... • Provides instructions for protein synthesis • 2 stranded, double helix structure • Sequence of three bases calls for particular amino acid • Found in nucleus • Replicates • Eukaryote ...
... • Provides instructions for protein synthesis • 2 stranded, double helix structure • Sequence of three bases calls for particular amino acid • Found in nucleus • Replicates • Eukaryote ...
DNA, RNA, Protein Graphic Organizer
... Sickle Cell DNA/RNA Mutation Worksheet Sickle cell anemia is a disease that is passed down through families. Normal red blood cells are shaped like a disc, while sickle blood cells are shaped in a crescent shape. Sickle cell anemia is caused by an abnormal type of hemoglobin. Hemoglobin helps carry ...
... Sickle Cell DNA/RNA Mutation Worksheet Sickle cell anemia is a disease that is passed down through families. Normal red blood cells are shaped like a disc, while sickle blood cells are shaped in a crescent shape. Sickle cell anemia is caused by an abnormal type of hemoglobin. Hemoglobin helps carry ...
Central Dogma PPT
... together to make the mature mRNA transcript intron = noncoding (inbetween) sequence ~10,000 bases eukaryotic DNA exon = coding (expressed) sequence ...
... together to make the mature mRNA transcript intron = noncoding (inbetween) sequence ~10,000 bases eukaryotic DNA exon = coding (expressed) sequence ...
Step two: Translation from mRNA to protein
... the bonds that link bases into strands the bonds that make strands into double helix RNA: basic parts and bonds differences between it and DNA types of RNA in the cell Transcription: Copying genetic information from DNA to mRNA what are the steps? (transcription and processing) where does it occur? ...
... the bonds that link bases into strands the bonds that make strands into double helix RNA: basic parts and bonds differences between it and DNA types of RNA in the cell Transcription: Copying genetic information from DNA to mRNA what are the steps? (transcription and processing) where does it occur? ...