The 11th lecture in molecular biology
... poly peptide protein .it represent 80-85% from total RNA 3- m RNA: not stable type cos it will degraded once it translated thus it represent 5%of total RNA non-coding RNAs are transfer RNA (tRNA ) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), both of which are involved in the process of translation. Structure of m RNA: ...
... poly peptide protein .it represent 80-85% from total RNA 3- m RNA: not stable type cos it will degraded once it translated thus it represent 5%of total RNA non-coding RNAs are transfer RNA (tRNA ) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), both of which are involved in the process of translation. Structure of m RNA: ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Initiation at the promoter site by RNA polymerase opens up the DNA molecule Elongation adds new RNA bases, including Uracil, down the exposed DNA bases Termination occurs when RNA polymerase hits the “stop” signal and detaches the new single strand of RNA ...
... Initiation at the promoter site by RNA polymerase opens up the DNA molecule Elongation adds new RNA bases, including Uracil, down the exposed DNA bases Termination occurs when RNA polymerase hits the “stop” signal and detaches the new single strand of RNA ...
Genetics Practice Questions C 1. Describe transcription
... 6. The genetic code is universal, unambiguous, and redundant. Explain what this means and why it is important. ・Universality・・・・All known living things have the same genetic code. ...
... 6. The genetic code is universal, unambiguous, and redundant. Explain what this means and why it is important. ・Universality・・・・All known living things have the same genetic code. ...
Molecular Genetics - Lake Travis Independent School District
... The “language” of mRNA is sometimes called the genetic code. The genetic code is read 3 letters (or bases) at a time, called codons. A codon is made up of 3 nucleotides that specify for a single amino acid Amino acids are strung together to form proteins (polypeptides) ...
... The “language” of mRNA is sometimes called the genetic code. The genetic code is read 3 letters (or bases) at a time, called codons. A codon is made up of 3 nucleotides that specify for a single amino acid Amino acids are strung together to form proteins (polypeptides) ...
File
... How does RNA polymerase know where to start and stop making an RNA copy of DNA? RNA polymerase binds to places on the DNA molecule known as… PROMOTERS ...
... How does RNA polymerase know where to start and stop making an RNA copy of DNA? RNA polymerase binds to places on the DNA molecule known as… PROMOTERS ...
Chapter 17
... Evolutionary Significance? Non-coding RNA regions were the result of non-coding DNA regions. Longer DNA increased chances of Xover during meiosis. During RNA processing, introns must be cut out (spliced) before a functional polypeptide can be made ...
... Evolutionary Significance? Non-coding RNA regions were the result of non-coding DNA regions. Longer DNA increased chances of Xover during meiosis. During RNA processing, introns must be cut out (spliced) before a functional polypeptide can be made ...
Genetics exam 4
... B. Involves removal of exons C. Involves removal of one or more introns. D. Occurs in prokaryotes E. None of the above _____ Which of the following occurs only in prokaryotes? A. TATA boxes B. Self-terminating transcription C. Polycistronic mRNA D. Coordinate gene regulation ...
... B. Involves removal of exons C. Involves removal of one or more introns. D. Occurs in prokaryotes E. None of the above _____ Which of the following occurs only in prokaryotes? A. TATA boxes B. Self-terminating transcription C. Polycistronic mRNA D. Coordinate gene regulation ...
chapter 3 outline
... Termination is dependent on specific nucleotide sequence signals. A common motif in prokaryotes is the hairpin loop structure, followed by poly-U sequence. Unlike prokaryotes, where there is one principle RNA polymerase, transcription in eukaryotes involves three different RNA polymerases -RNA polym ...
... Termination is dependent on specific nucleotide sequence signals. A common motif in prokaryotes is the hairpin loop structure, followed by poly-U sequence. Unlike prokaryotes, where there is one principle RNA polymerase, transcription in eukaryotes involves three different RNA polymerases -RNA polym ...
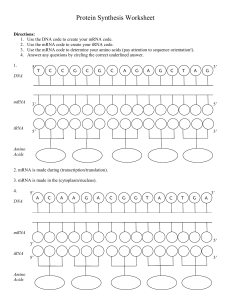
Protein Synthesis Worksheet
... 13. tRNA uses (anticodons/codons) to match to the mRNA. 14. Proteins are made at the (nucleus/ribosome). 15. (tRNA/mRNA) attaches the amino acids into a chain. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 17. (Translation/Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. 18. Translation takes place in t ...
... 13. tRNA uses (anticodons/codons) to match to the mRNA. 14. Proteins are made at the (nucleus/ribosome). 15. (tRNA/mRNA) attaches the amino acids into a chain. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 17. (Translation/Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. 18. Translation takes place in t ...
DNA Transcription Translation The Central Dogma Trait RNA
... Genes are made of parts represented in the mRNA (exons) and parts that are transcribed but not present in the mRNA (introns). Introns are removed from the primary transcript and exons are spliced together to ...
... Genes are made of parts represented in the mRNA (exons) and parts that are transcribed but not present in the mRNA (introns). Introns are removed from the primary transcript and exons are spliced together to ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... circle and move outward! • UCG = Serine • CAC = • GGU = • UAA = There are 64 codons but only 20 amino acids. So, different codons can code for the same amino acid. ...
... circle and move outward! • UCG = Serine • CAC = • GGU = • UAA = There are 64 codons but only 20 amino acids. So, different codons can code for the same amino acid. ...
DNA structure
... • 1 ‘parent’ DNA strand produces 2 new ‘daughter’ strands • Occurs rapidly, both strands simultaneously – Humans with 6 billion pairs a few hours, with only about 1 error every 10 billion nucleotides ...
... • 1 ‘parent’ DNA strand produces 2 new ‘daughter’ strands • Occurs rapidly, both strands simultaneously – Humans with 6 billion pairs a few hours, with only about 1 error every 10 billion nucleotides ...
RNA
... The mRNA then enters the cytoplasm and attaches to a ribosome. Translation begins at AUG, the start codon. Each transfer RNA has an anticodon whose bases are complementary to a codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions the start codon to attract its anticodon, which is part of the tRNA that b ...
... The mRNA then enters the cytoplasm and attaches to a ribosome. Translation begins at AUG, the start codon. Each transfer RNA has an anticodon whose bases are complementary to a codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions the start codon to attract its anticodon, which is part of the tRNA that b ...
Protein Synthesis
... 1. __________ - separates DNA helix 2. __________________– brings RNA nucleotides over to be synthesized into mRNA _________________: the side of DNA that will be used to create an mRNA strand The genetic code is read _________________________ called ___________on the mRNA strand The genetic c ...
... 1. __________ - separates DNA helix 2. __________________– brings RNA nucleotides over to be synthesized into mRNA _________________: the side of DNA that will be used to create an mRNA strand The genetic code is read _________________________ called ___________on the mRNA strand The genetic c ...
Unit 4: Genetics Name: Date: Aim #23 Translation: How does DNA
... Once transcription in the nucleus occurs, the mRNA that is created travels to a ribosome. Step 1: ___________ leaves the ____________________ and travels to a __________________ Step 2: The ribosome travels along the mRNA strand as a specific _______________________ is carried to the mRNA ...
... Once transcription in the nucleus occurs, the mRNA that is created travels to a ribosome. Step 1: ___________ leaves the ____________________ and travels to a __________________ Step 2: The ribosome travels along the mRNA strand as a specific _______________________ is carried to the mRNA ...
PowerPoint
... The storage of genetic information in DNA, the use of an RNA intermediate that is read in three letter words, and the mechanism of protein synthesis are essentially the same in all ...
... The storage of genetic information in DNA, the use of an RNA intermediate that is read in three letter words, and the mechanism of protein synthesis are essentially the same in all ...
File
... A string of ribosomes carrying out multiple translation on the same mRNA strand is called a polyribosome ...
... A string of ribosomes carrying out multiple translation on the same mRNA strand is called a polyribosome ...
MTC19: transcription and gene expression 02/10/07
... RNA polymerases do not need a primer; however, they do need a gene promoter (control region) within the DNA to identify the starting point (and direction) for transcription The transcript is synthesised using A/C/G/UTP molecules as sources of ribonucleotide monomers When RNA polymerase reaches and r ...
... RNA polymerases do not need a primer; however, they do need a gene promoter (control region) within the DNA to identify the starting point (and direction) for transcription The transcript is synthesised using A/C/G/UTP molecules as sources of ribonucleotide monomers When RNA polymerase reaches and r ...
Chapter 15 - Translation of mRNA
... its anticodon b. Common structural features are shared by all tRNAs c. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases charge tRNAs by attaching the appropriate amino acid d. Mismatches that follow the wobble rule can occur at the third position in codonanticodon pairing 5. Ribosome structure and assembly a. Bacterial a ...
... its anticodon b. Common structural features are shared by all tRNAs c. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases charge tRNAs by attaching the appropriate amino acid d. Mismatches that follow the wobble rule can occur at the third position in codonanticodon pairing 5. Ribosome structure and assembly a. Bacterial a ...