Chemistry Review
... mRNA attaches to ribosome tRNA brings amino acids to ribosome Amino acids attached to each other Continues until a “stop” codon is reached ...
... mRNA attaches to ribosome tRNA brings amino acids to ribosome Amino acids attached to each other Continues until a “stop” codon is reached ...
Features of the genetic code
... in the unusual 5’-5’ direction (phosphate to phosphate bond). Then a methyl thransferase adds methyl groups (-CH3) to the G and one or more of the first few bases of the RNA transcript. Capping and methylation is believed to be critical for efficient translation. • Addition of a poly A tail (100-200 ...
... in the unusual 5’-5’ direction (phosphate to phosphate bond). Then a methyl thransferase adds methyl groups (-CH3) to the G and one or more of the first few bases of the RNA transcript. Capping and methylation is believed to be critical for efficient translation. • Addition of a poly A tail (100-200 ...
purpose - cloudfront.net
... Protein Synthesis Practice 1 PURPOSE To review protein synthesis PROCEDURE Place the steps of protein synthesis in the correct order. _____ DNA rejoins & mRNA leaves the nucleus _____ the mRNA codons pair up with the tRNA anticodons; amino acids are added _____ DNA unzips _____ a mRNA copy of the DN ...
... Protein Synthesis Practice 1 PURPOSE To review protein synthesis PROCEDURE Place the steps of protein synthesis in the correct order. _____ DNA rejoins & mRNA leaves the nucleus _____ the mRNA codons pair up with the tRNA anticodons; amino acids are added _____ DNA unzips _____ a mRNA copy of the DN ...
Transcription and Translation Candy
... Get your original DNA model or rebuild it using the pictures from the DNA structure and replication lab. Transcription is the process of copying the genetic information from DNA into a usable copy of mRNA. Make a model clearly indicating this process make sure to include in your model representation ...
... Get your original DNA model or rebuild it using the pictures from the DNA structure and replication lab. Transcription is the process of copying the genetic information from DNA into a usable copy of mRNA. Make a model clearly indicating this process make sure to include in your model representation ...
DNA Replication - cloudfront.net
... 32. Can you change the order, add, or take an amino acid out and NOT change the protein? 33. What is the mRNA start codon and what amino acid does it code for? 34. What are the 3 mRNA stop codons and what amino acids do they code for? 35. What process makes DNA? 36. What 3 processes in order make pr ...
... 32. Can you change the order, add, or take an amino acid out and NOT change the protein? 33. What is the mRNA start codon and what amino acid does it code for? 34. What are the 3 mRNA stop codons and what amino acids do they code for? 35. What process makes DNA? 36. What 3 processes in order make pr ...
Transcription and Translation
... processing. The initial met is removed and the chain is folded into its final shape. ...
... processing. The initial met is removed and the chain is folded into its final shape. ...
apbio ch 17 test
... A) The tRNA that was in the A site moves into the P site. B) The tRNA that was in the P site moves into the A site. C) The tRNA that was in the A site moves to the E site and is released. D) The tRNA that was in the A site departs from the ribosome via a tunnel. E) The polypeptide enters the E site. ...
... A) The tRNA that was in the A site moves into the P site. B) The tRNA that was in the P site moves into the A site. C) The tRNA that was in the A site moves to the E site and is released. D) The tRNA that was in the A site departs from the ribosome via a tunnel. E) The polypeptide enters the E site. ...
TRANSCRIPTION & TRANSLATION: From DNA to Protein
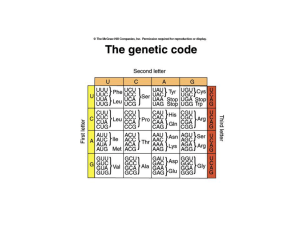
... •An amino acid can be coded for by more than one codon •20 amino acids combine in different combinations to make various proteins ...
... •An amino acid can be coded for by more than one codon •20 amino acids combine in different combinations to make various proteins ...
END OF SEMESTER EXAM PREPARATION AND REVISION
... • Lagging strand: Okazaki fragments to form daughter strand (discontinuous) • RNA replication requires primers ...
... • Lagging strand: Okazaki fragments to form daughter strand (discontinuous) • RNA replication requires primers ...
Molecular Genetics
... • aka Post-transcriptional Modifications • The primary transcript is called hnRNA – 5’ cap (methylated G) – added and a poly-A tail added to the 3’ end – (Note: cap and tail are protection from degradation and recognition by ribosome) – Spliced out introns (non-coding segments; the coding segments a ...
... • aka Post-transcriptional Modifications • The primary transcript is called hnRNA – 5’ cap (methylated G) – added and a poly-A tail added to the 3’ end – (Note: cap and tail are protection from degradation and recognition by ribosome) – Spliced out introns (non-coding segments; the coding segments a ...
Science Notebook DNA, RNA, and Protein
... process in which RNA is synthesized from DNA a group of three nitrogenous bases in DNA or mRNA that code for one amino acid nucleic acid made of ribose, phosphate, and one of four nitrogenous bases—adenine, cytosine, guanine, or uracil intervening DNA sequences that are transcribed and then removed ...
... process in which RNA is synthesized from DNA a group of three nitrogenous bases in DNA or mRNA that code for one amino acid nucleic acid made of ribose, phosphate, and one of four nitrogenous bases—adenine, cytosine, guanine, or uracil intervening DNA sequences that are transcribed and then removed ...
Chapter 14
... DNA is like a book of instructions in each cell • The instructions are written in the alphabet of A,T,G,C. But merely knowing the letter does not tell us how the genes work • DNA consist of two strands of nucleotides twisted together in a double helix. – In replication, the two strands unwind to se ...
... DNA is like a book of instructions in each cell • The instructions are written in the alphabet of A,T,G,C. But merely knowing the letter does not tell us how the genes work • DNA consist of two strands of nucleotides twisted together in a double helix. – In replication, the two strands unwind to se ...
Protein Synthesis
... The mRNA then enters the cytoplasm and attaches to a ribosome. Translation begins at AUG, the start codon. Each transfer RNA has an anticodon whose bases are complementary to a codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions the start codon to attract its anticodon, which is part of the tRNA that b ...
... The mRNA then enters the cytoplasm and attaches to a ribosome. Translation begins at AUG, the start codon. Each transfer RNA has an anticodon whose bases are complementary to a codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions the start codon to attract its anticodon, which is part of the tRNA that b ...
DNA Transcription
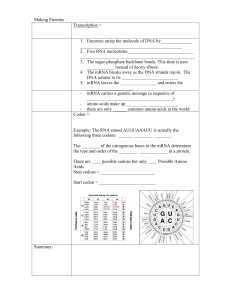
... The genetic code is ______________. (i.e. all organisms use this code and follow it to make proteins) Translation = Translation happens in the ___________________ 1. The strand of mRNA attaches to the ________________. 2. A ___________ molecule brings the first amino acid to the mRNA strand that is ...
... The genetic code is ______________. (i.e. all organisms use this code and follow it to make proteins) Translation = Translation happens in the ___________________ 1. The strand of mRNA attaches to the ________________. 2. A ___________ molecule brings the first amino acid to the mRNA strand that is ...
How does DNA store and transmit cell information?
... the same as mRNA except the Ts are replaced with Us ...
... the same as mRNA except the Ts are replaced with Us ...
Central Dogma! - Cloudfront.net
... polymerase II • RNA polymerase binds on promoter (nucleotide), reads DNA from 3’ to 5’ ...
... polymerase II • RNA polymerase binds on promoter (nucleotide), reads DNA from 3’ to 5’ ...
protein synthesis notes
... No operons…b/c genes w/similar functions are scattered among different chromosomes Multicellular organisms have different types of cells, all somatic cells contain the same DNA…but what makes them different is which genes are turned on/off Ex. Every cell has hemoglobin genes, but only turned “ ...
... No operons…b/c genes w/similar functions are scattered among different chromosomes Multicellular organisms have different types of cells, all somatic cells contain the same DNA…but what makes them different is which genes are turned on/off Ex. Every cell has hemoglobin genes, but only turned “ ...
3D-structure of bacterial ribosomes, the machines that make
... codon. The first position of the anticodon on tRNA matches the third position of the codon. Biotechnology by Clark and Pazdernik Copyright © 2012 by Academic Press. All rights reserved. ...
... codon. The first position of the anticodon on tRNA matches the third position of the codon. Biotechnology by Clark and Pazdernik Copyright © 2012 by Academic Press. All rights reserved. ...
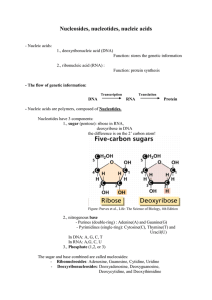
Nucleosides, nucleotides, nucleic acids
... The nucleotide sequence (=base sequence) carries the genetic information, this information will be translated into amino-acid sequence during protein synthesis. - Types and structure of RNA: - messenger RNA = mRNA: carries the information from the DNA to the site of protein synthesis. Single strande ...
... The nucleotide sequence (=base sequence) carries the genetic information, this information will be translated into amino-acid sequence during protein synthesis. - Types and structure of RNA: - messenger RNA = mRNA: carries the information from the DNA to the site of protein synthesis. Single strande ...
Document
... c.) in the promoter? Ask yourself—What acts at the promoter?! RNA Polymerase…Okay, there are some critical regions in the promoter (namely –10 and –35) that serve as binding sites for RNA Polymerase. If those were mutated, could that possibly result inproduction of a non-functional protein? YES! Mut ...
... c.) in the promoter? Ask yourself—What acts at the promoter?! RNA Polymerase…Okay, there are some critical regions in the promoter (namely –10 and –35) that serve as binding sites for RNA Polymerase. If those were mutated, could that possibly result inproduction of a non-functional protein? YES! Mut ...
Study Guide Foldable .Answer Key
... form along a gene and direct what type of protein will be made is called the ______ _______. The molecule that copies the coded message from the DNA in the nucleus and delivers it to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. ...
... form along a gene and direct what type of protein will be made is called the ______ _______. The molecule that copies the coded message from the DNA in the nucleus and delivers it to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. ...
Transcription andTranslation Flip Book
... A gene mutation is a change in one gene on an individual chromosome. This may nucleotide result in a change in only one _________ or many nucleotides making up that gene might be altered. The incidence of gene mutations is relatively low due to the enzymes proofread action of _________ that ________ ...
... A gene mutation is a change in one gene on an individual chromosome. This may nucleotide result in a change in only one _________ or many nucleotides making up that gene might be altered. The incidence of gene mutations is relatively low due to the enzymes proofread action of _________ that ________ ...
Expressing Genetic Information
... 2. What is stored in the chromatin, the genetic material of DNA? 3. Genes are discrete units of DNA that act in a certain way. What is that way? 4. Compare and contrast DNA with RNA. 5. What is the genetic code? 6. What is the Human Genome Project? 7. What percentage of RNA is rRNA? Why is it so hig ...
... 2. What is stored in the chromatin, the genetic material of DNA? 3. Genes are discrete units of DNA that act in a certain way. What is that way? 4. Compare and contrast DNA with RNA. 5. What is the genetic code? 6. What is the Human Genome Project? 7. What percentage of RNA is rRNA? Why is it so hig ...
DNA - Ellis Benjamin
... RNA • 3 types of RNA – Messenger RNA (mRNA) – carries info. specific to a protein, 3 RNA bases form a codon specifying an amino acid – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – combines with proteins to form a ribosome – Transfer RNA (tRNA) – carries specific amino acid to ribosome ...
... RNA • 3 types of RNA – Messenger RNA (mRNA) – carries info. specific to a protein, 3 RNA bases form a codon specifying an amino acid – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – combines with proteins to form a ribosome – Transfer RNA (tRNA) – carries specific amino acid to ribosome ...