From gene to protein 2
... Several components of the spliceosome are carried on the phosphorylated tail of RNA polymerase(to keep track of introns and exons). ...
... Several components of the spliceosome are carried on the phosphorylated tail of RNA polymerase(to keep track of introns and exons). ...
aa + aa + aa + aa aa – aa – aa – aa
... 2. Proteins are long chains of _________________ _________________. 3. The long chans of amino acids (known as_________________________) coil up to create a ______________ (working) protein. The protein will not work unless it is folded up. 4. Most amino acids look exactly the same except for the __ ...
... 2. Proteins are long chains of _________________ _________________. 3. The long chans of amino acids (known as_________________________) coil up to create a ______________ (working) protein. The protein will not work unless it is folded up. 4. Most amino acids look exactly the same except for the __ ...
Transcription: Synthesizing RNA from DNA
... ribose sugar (hydroxyl group at 2 C) Nitrogen Base: A,C,G,Uracil (instead of thymine) Single stranded (vs. DNA double stranded) ...
... ribose sugar (hydroxyl group at 2 C) Nitrogen Base: A,C,G,Uracil (instead of thymine) Single stranded (vs. DNA double stranded) ...
Central Dogma WebQuest - Life Science
... 2. What is the basic building block of a protein? _______________________ 3. How many amino acids exist in humans? _______________________ 4. Name one amino acid. _______________________ 5. What type of bond holds amino acids together?_______________________ 6. How many nucleotides code for each ami ...
... 2. What is the basic building block of a protein? _______________________ 3. How many amino acids exist in humans? _______________________ 4. Name one amino acid. _______________________ 5. What type of bond holds amino acids together?_______________________ 6. How many nucleotides code for each ami ...
Gene Expression
... Before tRNA can leave the ribosome, the animo acids will bond together to make a polypeptide chain ...
... Before tRNA can leave the ribosome, the animo acids will bond together to make a polypeptide chain ...
Walk the Dogma - Nutley Public Schools
... information is copied from DNA to RNA • DNA double-strand “unzips” • RNA polymerase (an enzyme) binds to a specific region on DNA called a promoter • RNA polymerase travels along the gene, creating a chain of mRNA that is complementary to the strand of DNA • RNA polymerase reaches the termination si ...
... information is copied from DNA to RNA • DNA double-strand “unzips” • RNA polymerase (an enzyme) binds to a specific region on DNA called a promoter • RNA polymerase travels along the gene, creating a chain of mRNA that is complementary to the strand of DNA • RNA polymerase reaches the termination si ...
Lab Instructions - Translation Please
... in the role of protein synthesis. This activity will also introduce the concept of mutations. Procedure: 1. You will be working in 3 person teams. 2. The teacher’s desk is the nucleus and the DNA templates cannot leave that area. The teacher will designate one team member’s desk for each group as th ...
... in the role of protein synthesis. This activity will also introduce the concept of mutations. Procedure: 1. You will be working in 3 person teams. 2. The teacher’s desk is the nucleus and the DNA templates cannot leave that area. The teacher will designate one team member’s desk for each group as th ...
notes File - selu moodle
... More initiation factors involved Elongation occurs in the same fashion, but eukaryotes have multiple RNA polymerases RNA polymerase I – transcribes rRNA RNA polymerase II – transcribes mRNA and snRNA RNA polymerase III – transcribes tRNA and other small RNA Termination sites are not well defined mRN ...
... More initiation factors involved Elongation occurs in the same fashion, but eukaryotes have multiple RNA polymerases RNA polymerase I – transcribes rRNA RNA polymerase II – transcribes mRNA and snRNA RNA polymerase III – transcribes tRNA and other small RNA Termination sites are not well defined mRN ...
ch04-genetics
... Questions 3-7 (Matching): Match the following terms to their respective statement below. A. Gene B. Genome C. Genetic code D. Base triplet E. Codon 3. _________ All the DNA, both coding and noncoding, in one 23-chromosome set 4. _________ A system that enables 4 nucleotides (A, T, C, G) to code for ...
... Questions 3-7 (Matching): Match the following terms to their respective statement below. A. Gene B. Genome C. Genetic code D. Base triplet E. Codon 3. _________ All the DNA, both coding and noncoding, in one 23-chromosome set 4. _________ A system that enables 4 nucleotides (A, T, C, G) to code for ...
Document
... 14.5 Small RNA Molecules Are Present Extensively in Eukaryotes and Participate in a Variety of Functions • Both siRNA and miRNA molecules combine with proteins to form an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). • The RISC pairs with a mRNA molecule that possesses a sequence complementary to its siR ...
... 14.5 Small RNA Molecules Are Present Extensively in Eukaryotes and Participate in a Variety of Functions • Both siRNA and miRNA molecules combine with proteins to form an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). • The RISC pairs with a mRNA molecule that possesses a sequence complementary to its siR ...
Transcription & Translation
... • The steps of translation: • 1. Initiation: mRNA enters the cytoplasm and becomes associated with ribosomes (rRNA + proteins). • tRNAs, each carrying a specific amino acid, pair up with the mRNA codons inside the ribosomes. Base pairing (A-U, G-C) between mRNA codons and tRNA anticodons determines ...
... • The steps of translation: • 1. Initiation: mRNA enters the cytoplasm and becomes associated with ribosomes (rRNA + proteins). • tRNAs, each carrying a specific amino acid, pair up with the mRNA codons inside the ribosomes. Base pairing (A-U, G-C) between mRNA codons and tRNA anticodons determines ...
Gene Action
... 5. After the peptide bond forms, the tRNA detaches from the ribosome and the ribosome shifts the mRNA strand by 1 codon. A new tRNA with amino acid binds to the exposed codon. Steps 3-5 repeat as the polypeptide lengthens ...
... 5. After the peptide bond forms, the tRNA detaches from the ribosome and the ribosome shifts the mRNA strand by 1 codon. A new tRNA with amino acid binds to the exposed codon. Steps 3-5 repeat as the polypeptide lengthens ...
Crossword Puzzle: Protein Synthesis
... 1. The number of codons that exist 3. Sequence of nucleotides on DNA to with RNA polymerase will attach to start transcription 4. mRNA copying DNA's nucleotide sequence 5. 3 nucleotides on tRNA that match to a specific codon on mRNA 6. Type of RNA that helps make up ribosomes 7. Instructions for mak ...
... 1. The number of codons that exist 3. Sequence of nucleotides on DNA to with RNA polymerase will attach to start transcription 4. mRNA copying DNA's nucleotide sequence 5. 3 nucleotides on tRNA that match to a specific codon on mRNA 6. Type of RNA that helps make up ribosomes 7. Instructions for mak ...
Protein Synthesis - Biology Junction
... 23. The site of protein synthesis 24. Start codon 25. Sugar on RNA 26. Chain of amino acids made during translation 27. Ribonucleic acid 28. How mRNA leaves the nucleus after copying DNA 29. DNA strand copied by mRNA 30. Enzyme that attaches RNA nucleotides to the DNA template strand so it can be co ...
... 23. The site of protein synthesis 24. Start codon 25. Sugar on RNA 26. Chain of amino acids made during translation 27. Ribonucleic acid 28. How mRNA leaves the nucleus after copying DNA 29. DNA strand copied by mRNA 30. Enzyme that attaches RNA nucleotides to the DNA template strand so it can be co ...
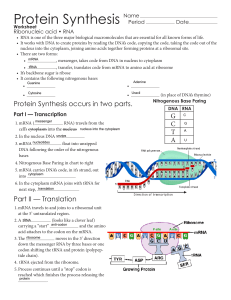
Protein Synthesis - Manhasset Public Schools
... Protein Synthesis Involves two processes: 1. Transcription: the copying of the genetic message (DNA) into a molecule of mRNA 2. Translation: mRNA is used to assemble an amino acid sequence into a polypeptide ...
... Protein Synthesis Involves two processes: 1. Transcription: the copying of the genetic message (DNA) into a molecule of mRNA 2. Translation: mRNA is used to assemble an amino acid sequence into a polypeptide ...
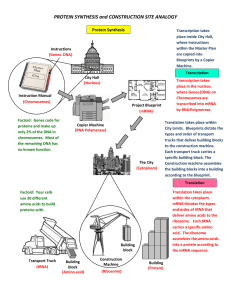
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS and CONSTRUCTION SITE ANALOGY
... within the Master Plan are copied into Blueprints by a Copier Machine. ...
... within the Master Plan are copied into Blueprints by a Copier Machine. ...
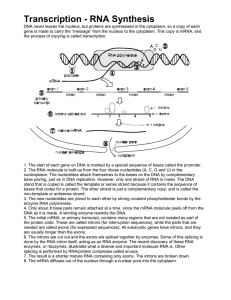
Transcription
... non-template or antisense strand. 3. The new nucleotides are joined to each other by strong covalent phosphodiester bonds by the enzyme RNA polymerase. 4. Only about 8 base pairs remain attached at a time, since the mRNA molecule peels off from the DNA as it is made. A winding enzyme rewinds the DNA ...
... non-template or antisense strand. 3. The new nucleotides are joined to each other by strong covalent phosphodiester bonds by the enzyme RNA polymerase. 4. Only about 8 base pairs remain attached at a time, since the mRNA molecule peels off from the DNA as it is made. A winding enzyme rewinds the DNA ...
RNA, Protein Synthesis, Transcription, and Translation
... • Decoding of instructions found on mRNA is called translation. • Occurs in the cytoplasm, where mRNA attaches to ribosomes. ...
... • Decoding of instructions found on mRNA is called translation. • Occurs in the cytoplasm, where mRNA attaches to ribosomes. ...
Transcription
... initially synthesized‐‐a cut‐and‐paste job called RNA splicing. The average length of a transcription unit along a eukaryotic DNA molecule is about 8,000 nucleotides, so the primary RNA transcript is also that long. But it takes only about 1,200 nucleotides to code for an average‐sized protein of ...
... initially synthesized‐‐a cut‐and‐paste job called RNA splicing. The average length of a transcription unit along a eukaryotic DNA molecule is about 8,000 nucleotides, so the primary RNA transcript is also that long. But it takes only about 1,200 nucleotides to code for an average‐sized protein of ...
1. What is the Central Dogma of Biology? Draw and label a diagram
... Explain how transcription occurs. Use the terms: hairpin loop, promoter, template. Explain how translation occurs. Use the terms: A-site, P-site, tRNA, mRNA, rRNA, codon, anticodon, nonsense codon. ...
... Explain how transcription occurs. Use the terms: hairpin loop, promoter, template. Explain how translation occurs. Use the terms: A-site, P-site, tRNA, mRNA, rRNA, codon, anticodon, nonsense codon. ...
Mutation
... • Binding of Basal Transcription Factors required for euk. RNA Pol II binding. • “Processing” of mRNA in eukaryotes, no processing in prokaryotes ...
... • Binding of Basal Transcription Factors required for euk. RNA Pol II binding. • “Processing” of mRNA in eukaryotes, no processing in prokaryotes ...
DNA/RNA.lecture
... C. Overview: information flow & gene expression II. Transcription A. Structure 1. nucleotide differences 2. RNA 3. short B. When does this happen? C. 3 main kinds of RNA 1. messenger RNAs (mRNA) 2. Other 2 types of RNA - protein-producing machinery a. transfer RNAs (tRNA) b. ribosomal RNAs (rRNA) D. ...
... C. Overview: information flow & gene expression II. Transcription A. Structure 1. nucleotide differences 2. RNA 3. short B. When does this happen? C. 3 main kinds of RNA 1. messenger RNAs (mRNA) 2. Other 2 types of RNA - protein-producing machinery a. transfer RNAs (tRNA) b. ribosomal RNAs (rRNA) D. ...