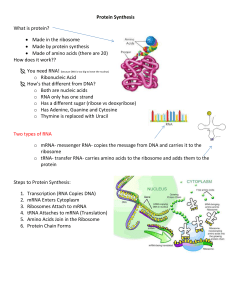
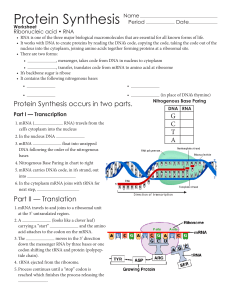
Gene Expression
... Before tRNA can leave the ribosome, the animo acids will bond together to make a polypeptide chain ...
... Before tRNA can leave the ribosome, the animo acids will bond together to make a polypeptide chain ...
File - Mrs. Badger`s Honors Biology Class
... _____ 2. The main function of tRNA is to a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes, a cell’s protein factories. c. string together complementary RNA and DNA strands. d. bring amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. _____ 3. What is the term for ...
... _____ 2. The main function of tRNA is to a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes, a cell’s protein factories. c. string together complementary RNA and DNA strands. d. bring amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. _____ 3. What is the term for ...
Study Guide to Chapter 5 Ð DNA
... __________ a) the nucleus b) the ribosome). Once the strand is complete it detaches from DNA. The second step in making a protein is called __________________ a) transcription b) translation. The molecule of ____________ a) mRNA b) tRNA arrives at the ___________a) ribosome b) nucleus, where complem ...
... __________ a) the nucleus b) the ribosome). Once the strand is complete it detaches from DNA. The second step in making a protein is called __________________ a) transcription b) translation. The molecule of ____________ a) mRNA b) tRNA arrives at the ___________a) ribosome b) nucleus, where complem ...
notes Protein_Synthe.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... - RNA polymerase moves along one strand making a single stranded, complementary copy of the nucleotides required for one gene. - the mRNA detaches and the DNA rezips itself What kind of RNA is there? mRNA – carries a complementary copy of the genetic code information for one gene from the nucleus to ...
... - RNA polymerase moves along one strand making a single stranded, complementary copy of the nucleotides required for one gene. - the mRNA detaches and the DNA rezips itself What kind of RNA is there? mRNA – carries a complementary copy of the genetic code information for one gene from the nucleus to ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS - Gull Lake Community Schools / Overview
... “steps” of the ladder) at the promoter site. Unattached RNA (free) nucleotides bind to their complimentary bases on the DNA strand to form a molecule of mRNA (messenger RNA); RNA polymerase works like a “train moving down the tracks”. This process repeats until DNA signals to STOP! The stop signal m ...
... “steps” of the ladder) at the promoter site. Unattached RNA (free) nucleotides bind to their complimentary bases on the DNA strand to form a molecule of mRNA (messenger RNA); RNA polymerase works like a “train moving down the tracks”. This process repeats until DNA signals to STOP! The stop signal m ...
Protein Synthesis Drawing
... More tRNA molecules transfer correct amino acids to the growing protein chain (by matching the anticodon on tRNA to the codons on mRNA). Remember: One tRNA only carries one kind of A.A. ...
... More tRNA molecules transfer correct amino acids to the growing protein chain (by matching the anticodon on tRNA to the codons on mRNA). Remember: One tRNA only carries one kind of A.A. ...
17-Gene to Protein
... • Introns: noncoding sequences that are removed • Exons: coding sequences that are spliced together • Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs): identify and help bring about the splicing process • Spliceosome: catalyzes splicing reactions ...
... • Introns: noncoding sequences that are removed • Exons: coding sequences that are spliced together • Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs): identify and help bring about the splicing process • Spliceosome: catalyzes splicing reactions ...
Genes and How they work!
... • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – made of several RNA molecules and over 50 proteins • Messenger RNA (mRNA) • Transfer RNA (tRNA) ...
... • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – made of several RNA molecules and over 50 proteins • Messenger RNA (mRNA) • Transfer RNA (tRNA) ...
Protein Synthesis - Helena High School
... 9. What are the two jobs or RNA polymerase in transcription? and 10. What is the goal of translation? 11. In eukaryotic cells translation happens in what location of the cell? structure? ...
... 9. What are the two jobs or RNA polymerase in transcription? and 10. What is the goal of translation? 11. In eukaryotic cells translation happens in what location of the cell? structure? ...
From Gene to Protein
... • Recognize where and why transcription occurs • Recognize where and why translation occurs • Understand relevant vocabulary ...
... • Recognize where and why transcription occurs • Recognize where and why translation occurs • Understand relevant vocabulary ...
1. The term peptidyltransferase relates to A. base additions during
... elongation factors binding to the large ribosomal subunit. ...
... elongation factors binding to the large ribosomal subunit. ...
From Gene to Protein Protein Synthesis
... pries DNA apart and hooks RNA nucleotides together from the DNA code Promoter region on DNA: where RNA polymerase ...
... pries DNA apart and hooks RNA nucleotides together from the DNA code Promoter region on DNA: where RNA polymerase ...
DNA WebQuest NAME___________________________
... 1. Which base in RNA is replaced by uracil? 2. How many mRNA codons are illustrated above? 3. What is the name of the enzyme that creates the mRNA copy from DNA? 4. What is the name of the sugar in the mRNA nucleotides? 5. What is the mRNA transcript for the DNA sequence, TTACGC ...
... 1. Which base in RNA is replaced by uracil? 2. How many mRNA codons are illustrated above? 3. What is the name of the enzyme that creates the mRNA copy from DNA? 4. What is the name of the sugar in the mRNA nucleotides? 5. What is the mRNA transcript for the DNA sequence, TTACGC ...
Word of the Day
... RNA polymerase unzips DNA and copies it into RNA. A’s connect with U’s and G’s connect with C’s. The starting point of transcription is known as the Promoter, the end is known as the terminal signal. After transcription the mRNA moves into the cytosol for protein synthesis. ...
... RNA polymerase unzips DNA and copies it into RNA. A’s connect with U’s and G’s connect with C’s. The starting point of transcription is known as the Promoter, the end is known as the terminal signal. After transcription the mRNA moves into the cytosol for protein synthesis. ...
Study Guide
... How are the functions of mRNA and tRNA different? Describe the process of transcription and translation. What is a codon? What is an anticodon? How are they related? Why is RNA necessary for expressing the code in DNA? How does an organism’s DNA code for its traits? Summarize the process ...
... How are the functions of mRNA and tRNA different? Describe the process of transcription and translation. What is a codon? What is an anticodon? How are they related? Why is RNA necessary for expressing the code in DNA? How does an organism’s DNA code for its traits? Summarize the process ...
The DNA Song
... one of 4 bases: cytosine, guanine, thymine, and adenine. These nucleotides link together by covalent (strong) bonds between the sugars and phosphate groups to form strands. Two of the strands link together at the bases with hydrogen (weak) bonds. During DNA replication, an enzyme, helicase, “unzips” ...
... one of 4 bases: cytosine, guanine, thymine, and adenine. These nucleotides link together by covalent (strong) bonds between the sugars and phosphate groups to form strands. Two of the strands link together at the bases with hydrogen (weak) bonds. During DNA replication, an enzyme, helicase, “unzips” ...
Transcription Factors
... on organism and mRNA b. Other proteins bind to inhibit ribosome—sometimes ribosomes are blocked so that mRNA can’t be used 4. Post-translational Controls a. Protein Processing Cut polypeptides—into functional units to do jobs on their own ...
... on organism and mRNA b. Other proteins bind to inhibit ribosome—sometimes ribosomes are blocked so that mRNA can’t be used 4. Post-translational Controls a. Protein Processing Cut polypeptides—into functional units to do jobs on their own ...