outline File - selu moodle
... Begins at a promoter transcribes the transcription unit ends at the terminator Promoter – sequence within DNA Elongation uses RNA polymerase to add ribonucleotides that are complementary to the template strand Most common mechanism for termination is the formation of a hairpin structure In proka ...
... Begins at a promoter transcribes the transcription unit ends at the terminator Promoter – sequence within DNA Elongation uses RNA polymerase to add ribonucleotides that are complementary to the template strand Most common mechanism for termination is the formation of a hairpin structure In proka ...
Biology: Protein Synthesis, Extra Credit Name: Place these
... Place these events in the correct order defining protein synthesis. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. m. n. o. ...
... Place these events in the correct order defining protein synthesis. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. m. n. o. ...
transcription - moleculesoflife1
... amino acid sequences (Refer to Genetic code) that have been left blank. If several sequences might work choose any one. 1. DNA mRNA ...
... amino acid sequences (Refer to Genetic code) that have been left blank. If several sequences might work choose any one. 1. DNA mRNA ...
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein
... mechanism for the correct tRNA to pair with the mRNA in the ribosome. At the top (3’ end) there is an amino acid attached to the tRNA Think of the tRNA as a translator, it is the molecule that knows two languages the mRNA language and the amino acid language. The ribosome is the location for protein ...
... mechanism for the correct tRNA to pair with the mRNA in the ribosome. At the top (3’ end) there is an amino acid attached to the tRNA Think of the tRNA as a translator, it is the molecule that knows two languages the mRNA language and the amino acid language. The ribosome is the location for protein ...
TRANSCRIPTION TRANSLATION
... Translation The process of forming peptide bonds between amino acids in a sequence defined by mRNA is called translation. Involves: (i) charging of the tRNA with the specific amino acids and (ii) synthesis of polypeptide chain by the ribosomes. ...
... Translation The process of forming peptide bonds between amino acids in a sequence defined by mRNA is called translation. Involves: (i) charging of the tRNA with the specific amino acids and (ii) synthesis of polypeptide chain by the ribosomes. ...
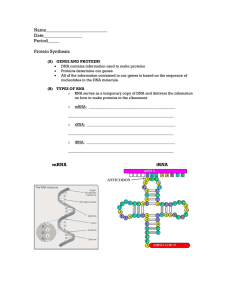
Protein Synthesis and Mutations Review Sheet 2014
... either use them in your answers or separately define or describe their relation to the concepts of protein synthesis or mutations. Protein Synthesis: Chapter 8.4 and 8.5 1. What are three differences between DNA and RNA? 2. Where does transcription take place and describe each step. Use the followin ...
... either use them in your answers or separately define or describe their relation to the concepts of protein synthesis or mutations. Protein Synthesis: Chapter 8.4 and 8.5 1. What are three differences between DNA and RNA? 2. Where does transcription take place and describe each step. Use the followin ...
Review for Molecular Genetics Quest
... 5. Where does this happen? Make sure to label location and type of cell. There are two answers for this!! ...
... 5. Where does this happen? Make sure to label location and type of cell. There are two answers for this!! ...
Modification of Genes and Proteins - sharonap-cellrepro-p3
... After the mRNA is synthesized and released, it is fed through tRNA and creates a chain of amino acids based on codons in the mRNA ...
... After the mRNA is synthesized and released, it is fed through tRNA and creates a chain of amino acids based on codons in the mRNA ...
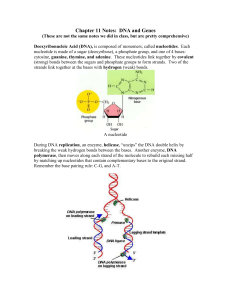
Chapter 11 Notes: DNA and Genes
... In transcription, a single strand of mRNA is copied from DNA, by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. In this case, however, thymine is replaced with uracil, so the “new” base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA i ...
... In transcription, a single strand of mRNA is copied from DNA, by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. In this case, however, thymine is replaced with uracil, so the “new” base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA i ...
Energy Unit SG Key
... rRNA stands for ribosomal RNA. This RNA makes up the ribosome and is the place where mRNA is translated into a protein. tRNA stands for transfer RNA. This RNA has an anti-codon on one end and the amino acid on the other. tRNA matches its anti-codon with the codon on the mRNA during translation, “dro ...
... rRNA stands for ribosomal RNA. This RNA makes up the ribosome and is the place where mRNA is translated into a protein. tRNA stands for transfer RNA. This RNA has an anti-codon on one end and the amino acid on the other. tRNA matches its anti-codon with the codon on the mRNA during translation, “dro ...
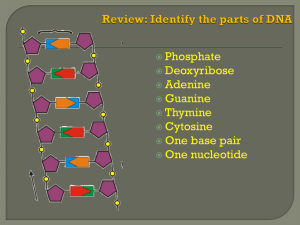
Name___________________________ Date_________________ Period_____
... RNA Polymerase knows where to bind on the DNA due to spots on the DNA called promoters, which act as start point signals for transcription. ...
... RNA Polymerase knows where to bind on the DNA due to spots on the DNA called promoters, which act as start point signals for transcription. ...
Transcription and Translation
... different amounts of molecules) I.e. difference in antibodies (some get sick more often or from different things) ...
... different amounts of molecules) I.e. difference in antibodies (some get sick more often or from different things) ...
Three Types of RNA and Their Functions
... Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA is more often found in nature as a single-strand composition. There are three main types of RNA, mRNA, tRNA and rRNA, and they play active roles within p ...
... Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA is more often found in nature as a single-strand composition. There are three main types of RNA, mRNA, tRNA and rRNA, and they play active roles within p ...
Chapter 17 Powerpoint
... • RNA splicing – Initial RNA sequence is approximately 8,000 nucleotides – Generally, only approx. 1,200 are needed, though. – Noncoding areas are found in between coding areas ...
... • RNA splicing – Initial RNA sequence is approximately 8,000 nucleotides – Generally, only approx. 1,200 are needed, though. – Noncoding areas are found in between coding areas ...
“Translation” means : Ribosomes in the cell cytoplasm read the
... 3. As the ribosome moves along mRNA, codons of bases are read, each one is matched up with the right tRNA and amino acid combo. As the ribosome keeps reading, and tRNA’s are being lined up, a string of amino acids are lined up. They are joined with “peptide bonds” and voila ! You have a protein. ...
... 3. As the ribosome moves along mRNA, codons of bases are read, each one is matched up with the right tRNA and amino acid combo. As the ribosome keeps reading, and tRNA’s are being lined up, a string of amino acids are lined up. They are joined with “peptide bonds” and voila ! You have a protein. ...