Review L14 Gene to Protein L15 Gene Reg
... What is the difference between genotype & phenotype? What is gene expression? Why is the phrase “one gene, one protein” inaccurate? Provide a definition for transcription and translation that clearly distinguishes between the two terms. What is a codon? Why is redundancy important in codons? Make a ...
... What is the difference between genotype & phenotype? What is gene expression? Why is the phrase “one gene, one protein” inaccurate? Provide a definition for transcription and translation that clearly distinguishes between the two terms. What is a codon? Why is redundancy important in codons? Make a ...
浙江万里学院《基因工程》试题(二)参考答案
... 1. 1). Prokaryotes initiate translation at an AUG codon just downstream of the Shine-Dalgamo sequence (ribosome-binding site) AGGAGGU, which base-pairs with a section of the 16S rRNA near its 3' end. The eukaryotic ribosomal small subunit binds at the 5' cap of mRNA, and the first AUG encountered is ...
... 1. 1). Prokaryotes initiate translation at an AUG codon just downstream of the Shine-Dalgamo sequence (ribosome-binding site) AGGAGGU, which base-pairs with a section of the 16S rRNA near its 3' end. The eukaryotic ribosomal small subunit binds at the 5' cap of mRNA, and the first AUG encountered is ...
Protein Synthesis Notes: Transcription and Translation
... o Transcription Practice: Transcribe this strand of DNA into RNA (no T‟s in RNA!) DNA: A A T C T A G A T C A T T A RNA:______________________________ Step 2- Translation o Function: Pieces of RNA make _____________________, which then make ___________. o Location: In the ____________________________ ...
... o Transcription Practice: Transcribe this strand of DNA into RNA (no T‟s in RNA!) DNA: A A T C T A G A T C A T T A RNA:______________________________ Step 2- Translation o Function: Pieces of RNA make _____________________, which then make ___________. o Location: In the ____________________________ ...
Protein Synthesis
... “The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific traits by dictating the synthesis of proteins.” ...
... “The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific traits by dictating the synthesis of proteins.” ...
From Gene to Protein Genes code for... Proteins RNAs Remember
... mRNA transcript is brought to the ribosome Initiation = the rRNA, mRNA transcript, and tRNA carrying methionine bind together Elongation = amino acids are added one by one to create the polypeptide Termination = when a stop codon is reached on the mRNA ...
... mRNA transcript is brought to the ribosome Initiation = the rRNA, mRNA transcript, and tRNA carrying methionine bind together Elongation = amino acids are added one by one to create the polypeptide Termination = when a stop codon is reached on the mRNA ...
Remember, transcription copies the DNA into mRNA
... This is an enzyme that attaches amino acids to tRNAs (that is how it uses the tRNA). ...
... This is an enzyme that attaches amino acids to tRNAs (that is how it uses the tRNA). ...
Protein Synthesis Webquest
... Use the keyboard to type the bases that would form the mRNA. 1. List your bases from mRNA: ...
... Use the keyboard to type the bases that would form the mRNA. 1. List your bases from mRNA: ...
Slide 1
... (20 AAs) – chain of AAs is a polypeptide •Bond between amino acids called peptide bond •After protein is formed it is shaped and folded in order to carry out a specific function ...
... (20 AAs) – chain of AAs is a polypeptide •Bond between amino acids called peptide bond •After protein is formed it is shaped and folded in order to carry out a specific function ...
Q on Genetic Control of Protein Structure and function – Chapter 5
... Which enzyme turns DNA nucleotides into a polynucleotide? Explain what is meant by “complementary base pairing”. What type of bond holds the two DNA strands together? What are the 2 essential functions of DNA? What are the 2 main types of RNA and what are their similarities and ...
... Which enzyme turns DNA nucleotides into a polynucleotide? Explain what is meant by “complementary base pairing”. What type of bond holds the two DNA strands together? What are the 2 essential functions of DNA? What are the 2 main types of RNA and what are their similarities and ...
A20-Protein Synthesis
... reads it 3 bases at a time, and matches these with bases on tRNA attached to an amino acid. An amino acid chain is formed from many peptide bonds. ...
... reads it 3 bases at a time, and matches these with bases on tRNA attached to an amino acid. An amino acid chain is formed from many peptide bonds. ...
The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics
... • Each “word” in the mRNA strand is composed of a 3-letter sequence called a CODON. • Each CODON specifies a SINGLE Amino Acid. • There is 1 start codon for initiation of protein synthesis and 3 stop codons for ending protein synthesis for a specific protein. • A given amino acid can have more than ...
... • Each “word” in the mRNA strand is composed of a 3-letter sequence called a CODON. • Each CODON specifies a SINGLE Amino Acid. • There is 1 start codon for initiation of protein synthesis and 3 stop codons for ending protein synthesis for a specific protein. • A given amino acid can have more than ...
General Biology Notes CH 12: TRANSLATION A.K.A. PROTEIN
... into a sequence of amino acids that makes up proteins. ...
... into a sequence of amino acids that makes up proteins. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - No Slide Title
... Ribosomes are large protein / RNA complexes that are the site of translation. The structure of ribosomes reflects ribosomal function. Each ribosome consists of large and small subunits, with binding sites for mRNA and three tRNA molecules. During translation, the growing polypeptide is atached to t ...
... Ribosomes are large protein / RNA complexes that are the site of translation. The structure of ribosomes reflects ribosomal function. Each ribosome consists of large and small subunits, with binding sites for mRNA and three tRNA molecules. During translation, the growing polypeptide is atached to t ...
CH 9 cont
... Single ringed N Bases = Pyrimidines are C and T 2X ringed N Bases = Purines are A and G Scientists Watson and Crick proposed structure of DNA as a ____________, held together by H Bonds and __________ These complementary bases were A bonded w/ ____ G bonded w/ _______ II. DNA REPLICATION What is it? ...
... Single ringed N Bases = Pyrimidines are C and T 2X ringed N Bases = Purines are A and G Scientists Watson and Crick proposed structure of DNA as a ____________, held together by H Bonds and __________ These complementary bases were A bonded w/ ____ G bonded w/ _______ II. DNA REPLICATION What is it? ...
Section 1.5 Name:
... ii. Also, RNA does not have thymine, instead it has the pyrimidine of _______________ iii. RNA is only a _________________ strand -‐ DNA is a double strand b. Types of RNA i. _____________________ RNA – ...
... ii. Also, RNA does not have thymine, instead it has the pyrimidine of _______________ iii. RNA is only a _________________ strand -‐ DNA is a double strand b. Types of RNA i. _____________________ RNA – ...
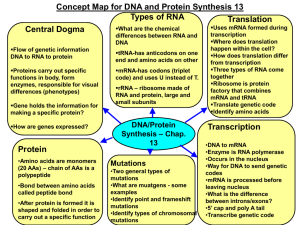
CENTRAL DOGMA AND GENE REGULATION
... sequences) and introns (insertion sequences) 2. The pre-mRNA is edited; the intron are removed. 3. A cap is added at the start site and a poly A++ tail is added at to the termination site. 4. The resulting mRNA is called “transcript”. Translation occurs in the cytoplasm on the ribosomes (rER) and re ...
... sequences) and introns (insertion sequences) 2. The pre-mRNA is edited; the intron are removed. 3. A cap is added at the start site and a poly A++ tail is added at to the termination site. 4. The resulting mRNA is called “transcript”. Translation occurs in the cytoplasm on the ribosomes (rER) and re ...
Packet 9: Transcription and Translation Name: Hour: _____ Notes
... • DNA: The _______________ for _____ _______ _____________ • RNA: The _______________ system that takes the instructions _____ ______ and makes ______________ for the cell. • Gene: are ________ ______ instructions that control the production of ...
... • DNA: The _______________ for _____ _______ _____________ • RNA: The _______________ system that takes the instructions _____ ______ and makes ______________ for the cell. • Gene: are ________ ______ instructions that control the production of ...
TRANSLATION NOTES - Randolph High School
... Definition of Translation The decoding of mRNA’s message into a protein Happens in the ribosome Also known as Protein Synthesis, which is when proteins are made by stringing amino acids together to form long chains (20+ types of amino acids in humans) ...
... Definition of Translation The decoding of mRNA’s message into a protein Happens in the ribosome Also known as Protein Synthesis, which is when proteins are made by stringing amino acids together to form long chains (20+ types of amino acids in humans) ...
Transcription & Translation
... • Rho-Independent: here two G+C regions rich slow RNA polymerase; a hairpin forms in the mRNA weakening the mRNA-DNA template association; which is further weakened by poly-A stretch. ...
... • Rho-Independent: here two G+C regions rich slow RNA polymerase; a hairpin forms in the mRNA weakening the mRNA-DNA template association; which is further weakened by poly-A stretch. ...
The Central Dogma of Biology Classroom Copy
... The central dogma of molecular biology explains the flow of genetic information, from DNA to RNA, to make a functional protein also known as a polypeptide. DNA contains the information needed (code) to make all of our proteins, and messenger RNA (mRNA) is a messenger that carrier the information to ...
... The central dogma of molecular biology explains the flow of genetic information, from DNA to RNA, to make a functional protein also known as a polypeptide. DNA contains the information needed (code) to make all of our proteins, and messenger RNA (mRNA) is a messenger that carrier the information to ...
PG1005 Lecture 17 Gene Transcription
... -Linear polymer composed of 4 nucleotide subunits --Nucleotides are ribonucleotides (ribose sugar) -AGCU (adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil) -Intramolecular complimentary sequences found in RNA Can form intramolecular bonds permitting folding and generation of precise 3D structures ...
... -Linear polymer composed of 4 nucleotide subunits --Nucleotides are ribonucleotides (ribose sugar) -AGCU (adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil) -Intramolecular complimentary sequences found in RNA Can form intramolecular bonds permitting folding and generation of precise 3D structures ...
RNA
... • Phenotype = physical and chemical state • The phenotype is determined by the proteins synthesised when the genes are expressed ...
... • Phenotype = physical and chemical state • The phenotype is determined by the proteins synthesised when the genes are expressed ...
PP-Protein Synthesis
... DNA contains the sequence of nucleotides that codes for the synthesis of proteins. DNA ...
... DNA contains the sequence of nucleotides that codes for the synthesis of proteins. DNA ...