Chapter 17: RNA
... C. Transcription- the process of copying the genetic message on the DNA into a messenger RNA, mRNA. a. The sequence of nucleotides in a gene carries the information for the primary structure of a protein. ie, the linear sequence of a.a. on the protein b. In transcription, a gene on the DNA strand pr ...
... C. Transcription- the process of copying the genetic message on the DNA into a messenger RNA, mRNA. a. The sequence of nucleotides in a gene carries the information for the primary structure of a protein. ie, the linear sequence of a.a. on the protein b. In transcription, a gene on the DNA strand pr ...
Terminator
... • The segment of DNA that contains the gene for a specific protein or RNA that the cell wants to produce will unwind and the complementary RNA strand will be made by incorporation the RNA nucleotides ...
... • The segment of DNA that contains the gene for a specific protein or RNA that the cell wants to produce will unwind and the complementary RNA strand will be made by incorporation the RNA nucleotides ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS What is a gene?
... • The segment of DNA that contains the gene for a specific protein or RNA that the cell wants to produce will unwind and the complementary RNA strand will be made by incorporation the RNA nucleotides ...
... • The segment of DNA that contains the gene for a specific protein or RNA that the cell wants to produce will unwind and the complementary RNA strand will be made by incorporation the RNA nucleotides ...
Unit 7 Study Guide ANSWERS 2014
... 16. Give an example of a mutagen? UV light, radiation 17. Define gene. A segment of DNA that contains the information necessary to produce a protein 18. Where are genes located? Chromosomes 19 Where is DNA located in the cell? Nucleus 20. What cell organelle is responsible for assembling proteins? R ...
... 16. Give an example of a mutagen? UV light, radiation 17. Define gene. A segment of DNA that contains the information necessary to produce a protein 18. Where are genes located? Chromosomes 19 Where is DNA located in the cell? Nucleus 20. What cell organelle is responsible for assembling proteins? R ...
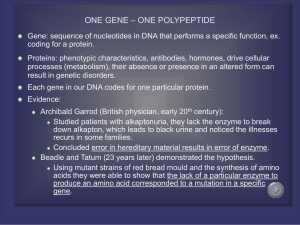
ONE GENE – ONE POLYPEPTIDE
... GENETIC CODE There are 20 amino acids found in proteins, only 4 bases in mRNA (U C A G) Codons: sequences of three bases used to code for an a.a. 43=64 possible codons (some amino acids have more than one codon) Ex. UUU UUC, UCU, UCC all code for phenylalanine (a.a.) This redundancy helps to reduce ...
... GENETIC CODE There are 20 amino acids found in proteins, only 4 bases in mRNA (U C A G) Codons: sequences of three bases used to code for an a.a. 43=64 possible codons (some amino acids have more than one codon) Ex. UUU UUC, UCU, UCC all code for phenylalanine (a.a.) This redundancy helps to reduce ...
Answers section 4
... 6. if you are given 3’-CAT-5’ as the template strand of DNA, then the mRNA will be 5’GUA-3’. The mRNA will be 5’-CAU-3’ if it is the coding strand of DNA that you are given. 7. A 8. B 9. A 10. B 11. C 12. D 13. B 14. A 15. C 16. E 17. D 18. E 19. D 20. C 21. A 22. E 23. B 24. ribose vs. deoxyribose ...
... 6. if you are given 3’-CAT-5’ as the template strand of DNA, then the mRNA will be 5’GUA-3’. The mRNA will be 5’-CAU-3’ if it is the coding strand of DNA that you are given. 7. A 8. B 9. A 10. B 11. C 12. D 13. B 14. A 15. C 16. E 17. D 18. E 19. D 20. C 21. A 22. E 23. B 24. ribose vs. deoxyribose ...
Science 103: Outline 17
... (v) A tRNA (plus amino acid) with the anticodon corresponding to the third codon binds and the first tRNA (empty) leaves. (v) The ribosomes move down the mRNA until they reach a stop codon. The ribosomes detach from the mRNA and the protein is released. 4. Fate of Proteins Where in the cell would tr ...
... (v) A tRNA (plus amino acid) with the anticodon corresponding to the third codon binds and the first tRNA (empty) leaves. (v) The ribosomes move down the mRNA until they reach a stop codon. The ribosomes detach from the mRNA and the protein is released. 4. Fate of Proteins Where in the cell would tr ...
BIO 101: Transcription and Translation
... In eukaryotes, pre-mRNA must be further processed to mRNA before it leaves the nucleus ...
... In eukaryotes, pre-mRNA must be further processed to mRNA before it leaves the nucleus ...
Gene Expression - the Biology Department
... – complexity increases resulting from transcription control and transcription and post-transcription ...
... – complexity increases resulting from transcription control and transcription and post-transcription ...
Translation
... In order for a cell to make a protein, DNA must be transcribed into ____________ and the mRNA must then be translated into _____________. The processes of transcription and translation together are called _________________________. The process of transcription occurs in the ____________ of a cell. T ...
... In order for a cell to make a protein, DNA must be transcribed into ____________ and the mRNA must then be translated into _____________. The processes of transcription and translation together are called _________________________. The process of transcription occurs in the ____________ of a cell. T ...
From Gene to Protein
... gene codes for one enzyme • Not all proteins are enzymes, so refined to be one-gene-onepolypeptide hypothesis Crick – Central Dogma of Genetics • DNA RNA Protein •Modified since ...
... gene codes for one enzyme • Not all proteins are enzymes, so refined to be one-gene-onepolypeptide hypothesis Crick – Central Dogma of Genetics • DNA RNA Protein •Modified since ...
Document
... The storage of genetic information in DNA, the use of an RNA intermediate that is read in three letter words, and the mechanism of protein synthesis are essentially the same in all organisms. ...
... The storage of genetic information in DNA, the use of an RNA intermediate that is read in three letter words, and the mechanism of protein synthesis are essentially the same in all organisms. ...
Chapter 9 – Genetically Modified Organisms
... coded for by a particular codon can be determined using the genetic code • What is the relationship between the genetic code and genetic modification? ...
... coded for by a particular codon can be determined using the genetic code • What is the relationship between the genetic code and genetic modification? ...
Protein Synthesis - Overview
... • this recognition by tRNA of mRNA is facilitated through complimentary base pairing. every tRNA carries only one specific amino acid • therefore there must be at least 20 (20-64) different tRNA’s ...
... • this recognition by tRNA of mRNA is facilitated through complimentary base pairing. every tRNA carries only one specific amino acid • therefore there must be at least 20 (20-64) different tRNA’s ...
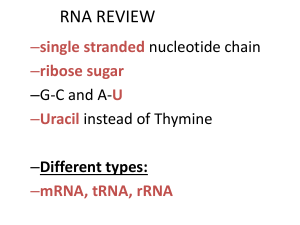
RNA and protein synthesis
... and translation. 1. Transcription: Process where DNA serves as a template to produce complementary mRNA 2. Translation: Process in which mRNA is used to link amino acids together to synthesize proteins. Involves tRNA and rRNA DNA ...
... and translation. 1. Transcription: Process where DNA serves as a template to produce complementary mRNA 2. Translation: Process in which mRNA is used to link amino acids together to synthesize proteins. Involves tRNA and rRNA DNA ...
Central Dogma.pptx
... (turned on) by first being transcribed into RNA (mRNA, tRNA or rRNA) mRNA=messenger RNA, carries DNA’s message to be later translated into proteins with the help of tRNA and the ribosome. ...
... (turned on) by first being transcribed into RNA (mRNA, tRNA or rRNA) mRNA=messenger RNA, carries DNA’s message to be later translated into proteins with the help of tRNA and the ribosome. ...
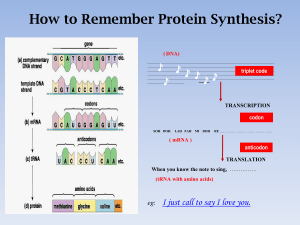
How to remember Protein Synthesis
... • DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. • During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. • The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. • The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position ...
... • DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. • During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. • The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. • The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position ...
Protein Synthesis
... i. Gene = a segment of DNA coding for a RNA segment. These RNA segments will be used to produce a polypeptide (structural or enzymatic protein) ii. Each strand of DNA can contain thousands of genes iii. Each gene has a beginning and an end b. DNA is used as the blueprint to direct the production of ...
... i. Gene = a segment of DNA coding for a RNA segment. These RNA segments will be used to produce a polypeptide (structural or enzymatic protein) ii. Each strand of DNA can contain thousands of genes iii. Each gene has a beginning and an end b. DNA is used as the blueprint to direct the production of ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... i. Gene = a segment of DNA coding for a RNA segment. These RNA segments will be used to produce a polypeptide (structural or enzymatic protein) ii. Each strand of DNA can contain thousands of genes iii. Each gene has a beginning and an end b. DNA is used as the blueprint to direct the production of ...
... i. Gene = a segment of DNA coding for a RNA segment. These RNA segments will be used to produce a polypeptide (structural or enzymatic protein) ii. Each strand of DNA can contain thousands of genes iii. Each gene has a beginning and an end b. DNA is used as the blueprint to direct the production of ...
DNA RNA-Protein Synthesis Homework
... must send it’s information to the cell to make the proteins that support the cell. ...
... must send it’s information to the cell to make the proteins that support the cell. ...