Biosynthesis of Nucleotides Biosynthesis of Nucleotides
... formed from ribose-5-P and ATP by PRPP synthetase. PRPP is the donor of the ribose ring of the nucleotides. PRPP also participates in pyrimidine biosynthesis and in the synthesis of histidine and tryptophan. ...
... formed from ribose-5-P and ATP by PRPP synthetase. PRPP is the donor of the ribose ring of the nucleotides. PRPP also participates in pyrimidine biosynthesis and in the synthesis of histidine and tryptophan. ...
Organic Chemistry
... • For short-term energy storage, animals convert glucose into glycogen. • For long-term storage, however, organisms usually convert sugars into fats, or lipids. • Lipids are a diverse group of molecules that includes oils, fats, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. • All lipids are insoluble in water ...
... • For short-term energy storage, animals convert glucose into glycogen. • For long-term storage, however, organisms usually convert sugars into fats, or lipids. • Lipids are a diverse group of molecules that includes oils, fats, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. • All lipids are insoluble in water ...
Biochemistry
... Certain infections caused by bacteria are treated with sulphanilamides that block the synthesis of bacterial growth factor. What is the mechanism of these drugs action? A *They are antivitamins of p-aminobenzoic acid B They inhibit the folic acid absorption C They are allosteric enzyme inhibitors D ...
... Certain infections caused by bacteria are treated with sulphanilamides that block the synthesis of bacterial growth factor. What is the mechanism of these drugs action? A *They are antivitamins of p-aminobenzoic acid B They inhibit the folic acid absorption C They are allosteric enzyme inhibitors D ...
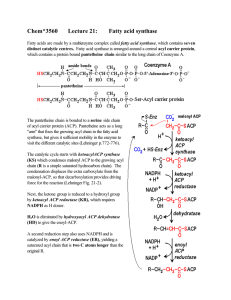
Chem*3560 Lecture 21: Fatty acid synthase
... NADPH. Enz:[oxaloacetate] → pyruvate + CO2 Many organisms also contain an NADP + dependent isozyme of isocitrate dehydrogenase. isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP + dependent) isocitrate + NADP+ → α -ketoglutarate + CO2 + NADPH Unlike the NAD+ dependent isozyme, this isozyme does not require ADP for act ...
... NADPH. Enz:[oxaloacetate] → pyruvate + CO2 Many organisms also contain an NADP + dependent isozyme of isocitrate dehydrogenase. isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP + dependent) isocitrate + NADP+ → α -ketoglutarate + CO2 + NADPH Unlike the NAD+ dependent isozyme, this isozyme does not require ADP for act ...
Muscle Physiology - Home Page | Hermantown Community Schools
... free fatty acids from adipose tissue; amino acids from protein catabolism ...
... free fatty acids from adipose tissue; amino acids from protein catabolism ...
Met1 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... B) lipid metabolism disorders - carnitine palmitoyl transferase deficiencies see p. 750 >> C) purine metabolism disorders - myoadenylate deaminase deficiency see below >> D) mitochondrial myopathies - succinate dehydrogenase deficiency exercise intolerance in childhood; exertion-induced symptoms ( ...
... B) lipid metabolism disorders - carnitine palmitoyl transferase deficiencies see p. 750 >> C) purine metabolism disorders - myoadenylate deaminase deficiency see below >> D) mitochondrial myopathies - succinate dehydrogenase deficiency exercise intolerance in childhood; exertion-induced symptoms ( ...
3. Metabolism - Professor Monzir Abdel
... Biotransformation is a major part of the pathway for elimination of many xenobiotic compounds. Biotransformation can result in either a decrease or an increase (or no change) in toxicity. Biotransformation can result in the formation of reactive metabolites. ...
... Biotransformation is a major part of the pathway for elimination of many xenobiotic compounds. Biotransformation can result in either a decrease or an increase (or no change) in toxicity. Biotransformation can result in the formation of reactive metabolites. ...
Insulin-Transferrin-Selenium 100X
... • Insulin has pleiotropic anabolic effects on mammalian cells, promoting glucose and amino acid uptake, lipogenesis, monovalent cation and phosphate transport, protein, and nucleic acid synthesis. • Transferrin serves as a carrier for iron and may also help to reduce toxic levels of oxygen radicals ...
... • Insulin has pleiotropic anabolic effects on mammalian cells, promoting glucose and amino acid uptake, lipogenesis, monovalent cation and phosphate transport, protein, and nucleic acid synthesis. • Transferrin serves as a carrier for iron and may also help to reduce toxic levels of oxygen radicals ...
Dear students, Under Boston`s asking, I persude the leader to agree
... (B) One-carbon fragments are donated by folic acid derivatives (C) Carbamoyl phosphate donates a carbamoyl group (D) The entire glycine molecule is incorporated into a precursor of the base (E) Glutamine is a nitrogen donor 68. Which of the following hormones decreases the level of blood sugar? (A) ...
... (B) One-carbon fragments are donated by folic acid derivatives (C) Carbamoyl phosphate donates a carbamoyl group (D) The entire glycine molecule is incorporated into a precursor of the base (E) Glutamine is a nitrogen donor 68. Which of the following hormones decreases the level of blood sugar? (A) ...
Ch13.doc
... below, -32.5kJ/mole in the EOC problem) which is clearly more than ATP + H2O ADP + Pi (30 kJ/mole) which means the usually ATP hydrolysis reaction can not drive the synthesis of acetyl-CoA from acetate + CoA. So, now check out Table 13-6, see below.. The ΔGo’ for ATP + H2O AMP + PPi is -45.6 kJ/ ...
... below, -32.5kJ/mole in the EOC problem) which is clearly more than ATP + H2O ADP + Pi (30 kJ/mole) which means the usually ATP hydrolysis reaction can not drive the synthesis of acetyl-CoA from acetate + CoA. So, now check out Table 13-6, see below.. The ΔGo’ for ATP + H2O AMP + PPi is -45.6 kJ/ ...
Teacher shi 18940209087 Email: QQ
... 63. one carbon unit does not include (A) –CH3 (B) -CH2(C) -CH= (D) -CHO (E) CO2 64. The product which is formed from the reaction catalyzed by pyruvate kinase is : (A) fructose-6-phosphate (B)fructose-1-phosphate (C) fructose-1,6-diphosphate (D) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (E) pyruvate 65. How many m ...
... 63. one carbon unit does not include (A) –CH3 (B) -CH2(C) -CH= (D) -CHO (E) CO2 64. The product which is formed from the reaction catalyzed by pyruvate kinase is : (A) fructose-6-phosphate (B)fructose-1-phosphate (C) fructose-1,6-diphosphate (D) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (E) pyruvate 65. How many m ...
Biogeochemical cycles – Important Biomolecules
... adenosine triphosphate, or ATP. The ATP molecule is composed of three components. At the centre is a sugar molecule, ribose (same sugaras found in DNA). Attached to one side of this is the purine base adenine. The other side of the sugar is attached to a string of phosphate groups. The phosphates ar ...
... adenosine triphosphate, or ATP. The ATP molecule is composed of three components. At the centre is a sugar molecule, ribose (same sugaras found in DNA). Attached to one side of this is the purine base adenine. The other side of the sugar is attached to a string of phosphate groups. The phosphates ar ...
File - Living Environment
... How does Glucose and O2 get to the Mitochondria? Glucose is absorbed by the digestive system Oxygen is taken in by the respiratory system Both systems are connected to the circulatory system which moves materials to and from the cell? ...
... How does Glucose and O2 get to the Mitochondria? Glucose is absorbed by the digestive system Oxygen is taken in by the respiratory system Both systems are connected to the circulatory system which moves materials to and from the cell? ...
Selected Solutions to End of Chapter 13 Problems
... below, -32.5kJ/mole in the EOC problem) which is clearly more than ATP + H2O ADP + Pi (30 kJ/mole) which means the usually ATP hydrolysis reaction can not drive the synthesis of acetyl-CoA from acetate + CoA. So, now check out Table 13-6, see below.. The ΔGo’ for ATP + H2O AMP + PPi is -45.6 kJ/ ...
... below, -32.5kJ/mole in the EOC problem) which is clearly more than ATP + H2O ADP + Pi (30 kJ/mole) which means the usually ATP hydrolysis reaction can not drive the synthesis of acetyl-CoA from acetate + CoA. So, now check out Table 13-6, see below.. The ΔGo’ for ATP + H2O AMP + PPi is -45.6 kJ/ ...
Biochemie jater
... The high levels of NADH and acetyl-CoA inhibit citric acid cycle activity and ketogenesis, whereas they exert a stimulatory effect on the synthesis of neutral fats and cholesterol (an increase in the storage of lipids leads to a fatty liver- it is reversible) In chronic alcoholism- liver cell deat ...
... The high levels of NADH and acetyl-CoA inhibit citric acid cycle activity and ketogenesis, whereas they exert a stimulatory effect on the synthesis of neutral fats and cholesterol (an increase in the storage of lipids leads to a fatty liver- it is reversible) In chronic alcoholism- liver cell deat ...
Overview of metabolism
... • It must obtain carbon from their environment in the form of relatively complex organic molecules such as glucose. • Multicellular animals and most microorganisms are heterotrophic. • It must subsist on the products of other organisms. ...
... • It must obtain carbon from their environment in the form of relatively complex organic molecules such as glucose. • Multicellular animals and most microorganisms are heterotrophic. • It must subsist on the products of other organisms. ...
New COMPARTMENT ORGANIZATION
... communication by allowing for the flow of information between compartments in the cell and between cells and their environment. • The presence of specific molecules in membranes allows recognition of stimuli in the form of chemical signals (eg hormones, local mediators and neurotransmitters), electr ...
... communication by allowing for the flow of information between compartments in the cell and between cells and their environment. • The presence of specific molecules in membranes allows recognition of stimuli in the form of chemical signals (eg hormones, local mediators and neurotransmitters), electr ...
Lecture 3: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
... executing “programmed cell death” or “apoptosis”. Matrix is the liquid part present in the inner most compartment of the mitochondria and it contains ribosome, DNA, RNA, enzymes to run Kreb’s cycle and other proteins. Mitochondrial DNA is circular and it has full machinery to synthesize its own RNA ...
... executing “programmed cell death” or “apoptosis”. Matrix is the liquid part present in the inner most compartment of the mitochondria and it contains ribosome, DNA, RNA, enzymes to run Kreb’s cycle and other proteins. Mitochondrial DNA is circular and it has full machinery to synthesize its own RNA ...
Chapter 8 Review Sheet
... 36. Why use ATP? Why not just use glucose or amino acids or triglycerides or sucrose or fatty acids directly as a source of energy? ...
... 36. Why use ATP? Why not just use glucose or amino acids or triglycerides or sucrose or fatty acids directly as a source of energy? ...
Inborn Errors of Metabolism
... • Usually IVF’s with glucose to give 12-15 mg/kg/min glu and at least 60 kcal/kg to prevent catabolism (may ...
... • Usually IVF’s with glucose to give 12-15 mg/kg/min glu and at least 60 kcal/kg to prevent catabolism (may ...
Biology: Concepts and Connections, 6e (Campbell)
... B) Extremely stable bonds link the second and third phosphate groups. C) It contains the six-carbon sugar hexose. يحتوي على جزيء من قاعدة نيتروجينية يسمى االدنين ...
... B) Extremely stable bonds link the second and third phosphate groups. C) It contains the six-carbon sugar hexose. يحتوي على جزيء من قاعدة نيتروجينية يسمى االدنين ...
Chapter 2b Packet
... 23. Temperature and _________ can affect enzyme activity. 24. ________________ a class of organic compounds that includes fats, steroids, and waxes. 25. The building blocks of proteins are ________________; carbohydrates are _______________; nucleic acids are ___________________; and lipids are ____ ...
... 23. Temperature and _________ can affect enzyme activity. 24. ________________ a class of organic compounds that includes fats, steroids, and waxes. 25. The building blocks of proteins are ________________; carbohydrates are _______________; nucleic acids are ___________________; and lipids are ____ ...
Created with Sketch. Fermentation (word : 990 KB)
... Fermentation is a process by which the living cell is able to obtain energy through the breakdown of glucose and other simple sugar molecules without requiring oxygen. It is an anaerobic (without oxygen) process. Within the cell cytoplasm, glucose or other simple sugars are broken down in a series o ...
... Fermentation is a process by which the living cell is able to obtain energy through the breakdown of glucose and other simple sugar molecules without requiring oxygen. It is an anaerobic (without oxygen) process. Within the cell cytoplasm, glucose or other simple sugars are broken down in a series o ...
Citric acid cycle - Imperial College London
... sugars). Glycolysis breaks glucose (a six-carbon-molecule) down into pyruvate (a three-carbon molecule). In eukaryotes, pyruvate moves into the mitochondria. It is converted into acetyl-CoA by decarboxylation and enters the citric acid cycle. In protein catabolism, proteins are broken down by protea ...
... sugars). Glycolysis breaks glucose (a six-carbon-molecule) down into pyruvate (a three-carbon molecule). In eukaryotes, pyruvate moves into the mitochondria. It is converted into acetyl-CoA by decarboxylation and enters the citric acid cycle. In protein catabolism, proteins are broken down by protea ...
Unit 1 Chemistry Study Guide
... In what 2 membranes in plant cells is ATP synthetase found? Is oxygen released in the light or dark reactions of photosynthesis? Does photophosphorylation occur in Photosystem II? In which photosystem is water split? Which process does not give a net gain in ATP ---glycolysis, aerobic respiration, o ...
... In what 2 membranes in plant cells is ATP synthetase found? Is oxygen released in the light or dark reactions of photosynthesis? Does photophosphorylation occur in Photosystem II? In which photosystem is water split? Which process does not give a net gain in ATP ---glycolysis, aerobic respiration, o ...
Glycolysis
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).Glycolysis is a determined sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The intermediates provide entry points to glycolysis. For example, most monosaccharides, such as fructose and galactose, can be converted to one of these intermediates. The intermediates may also be directly useful. For example, the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a source of the glycerol that combines with fatty acids to form fat.Glycolysis is an oxygen independent metabolic pathway, meaning that it does not use molecular oxygen (i.e. atmospheric oxygen) for any of its reactions. However the products of glycolysis (pyruvate and NADH + H+) are sometimes disposed of using atmospheric oxygen. When molecular oxygen is used in the disposal of the products of glycolysis the process is usually referred to as aerobic, whereas if the disposal uses no oxygen the process is said to be anaerobic. Thus, glycolysis occurs, with variations, in nearly all organisms, both aerobic and anaerobic. The wide occurrence of glycolysis indicates that it is one of the most ancient metabolic pathways. Indeed, the reactions that constitute glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, occur metal-catalyzed under the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes. Glycolysis could thus have originated from chemical constraints of the prebiotic world.Glycolysis occurs in most organisms in the cytosol of the cell. The most common type of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP pathway), which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. Glycolysis also refers to other pathways, such as the Entner–Doudoroff pathway and various heterofermentative and homofermentative pathways. However, the discussion here will be limited to the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway.The entire glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases: The Preparatory Phase – in which ATP is consumed and is hence also known as the investment phase The Pay Off Phase – in which ATP is produced.↑ ↑ 2.0 2.1 ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑