Amylase
... Digestive Enzymes: are used in the lumen of the GI tract to break down complex molecules into absorbable subunits Enzymes are biological catalysts which increase the rate of a chemical reaction without themselves becoming part of the product: ...
... Digestive Enzymes: are used in the lumen of the GI tract to break down complex molecules into absorbable subunits Enzymes are biological catalysts which increase the rate of a chemical reaction without themselves becoming part of the product: ...
Basic Biology - NIU Department of Biological Sciences
... • Fats store about twice as much energy per weight as carbohydrates like starch. • Phospholipids are the main component of cell membranes. – they have a glycerol with 2 fatty acids attached, plus a phosphate-containing “head” group instead of a third fatty acid. ...
... • Fats store about twice as much energy per weight as carbohydrates like starch. • Phospholipids are the main component of cell membranes. – they have a glycerol with 2 fatty acids attached, plus a phosphate-containing “head” group instead of a third fatty acid. ...
Carbohydrates lipids and prpoteins 3.2
... A condensation reaction occurs between the amino group (NH2) of one amino acid and the carboxylic acid group (COOH) of another amino acid This reaction forms a dipeptide (plus a molecule of water) that is held together by a peptide bond Multiple amino acids can be joined together to form a polypepti ...
... A condensation reaction occurs between the amino group (NH2) of one amino acid and the carboxylic acid group (COOH) of another amino acid This reaction forms a dipeptide (plus a molecule of water) that is held together by a peptide bond Multiple amino acids can be joined together to form a polypepti ...
Pdf - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... Now here, if we see this pyruvate dehydrogenase enzyme, it has got the core moieties, which is dihydrolipoyl transacetylase enzyme to which that, pyruvate dehydrogenase of 20 such molecules, this another enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase has 20 such molecules, each molecule has the molecular weight of 1 ...
... Now here, if we see this pyruvate dehydrogenase enzyme, it has got the core moieties, which is dihydrolipoyl transacetylase enzyme to which that, pyruvate dehydrogenase of 20 such molecules, this another enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase has 20 such molecules, each molecule has the molecular weight of 1 ...
슬라이드 1
... • The role of the adipose tissue – Buffering the level of fatty acids in the circulation in the postprandial period • by regulation of the release of NEFA into the circulation • according to the conditions of feeding or fasting through a change in the activity of hormone-sensitive lipase. ...
... • The role of the adipose tissue – Buffering the level of fatty acids in the circulation in the postprandial period • by regulation of the release of NEFA into the circulation • according to the conditions of feeding or fasting through a change in the activity of hormone-sensitive lipase. ...
last update was
... 1. First Law of Thermodynamics Energy can be changed from one form into another, but cannot be created nor destroyed. Energy can be stored in various forms then changed into other forms. For example, energy in glucose is oxidized to change the energy stored in chemical bonds into mechanical energy. ...
... 1. First Law of Thermodynamics Energy can be changed from one form into another, but cannot be created nor destroyed. Energy can be stored in various forms then changed into other forms. For example, energy in glucose is oxidized to change the energy stored in chemical bonds into mechanical energy. ...
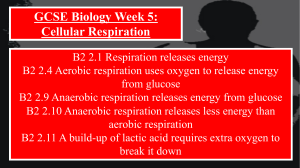
respiration - Learn Biology
... So, anaerobic respiration takes place when there isn’t enough oxygen (O2) available to supply the body (e.g. muscles) with the O2 required for ‘normal’ aerobic respiration. Anaerobic respiration is very useful in emergencies! (think Fight or Flight – which we’ll cover when we cover the nervous sy ...
... So, anaerobic respiration takes place when there isn’t enough oxygen (O2) available to supply the body (e.g. muscles) with the O2 required for ‘normal’ aerobic respiration. Anaerobic respiration is very useful in emergencies! (think Fight or Flight – which we’ll cover when we cover the nervous sy ...
The Energy Requirement for Growth: An A ~ ~ lication of
... The synthesis of a triglyceride from fatty acids and glycerol requires 6 ATP Eq. It has been assumed that fatty acids are supplied in adequate amounts, b u t that glycerol 1-phosphate must be synthesized from glucose at the expense of 8 ATP Eq/mol glycerol 1-phosphate. The synthesis of 1 mol triglyc ...
... The synthesis of a triglyceride from fatty acids and glycerol requires 6 ATP Eq. It has been assumed that fatty acids are supplied in adequate amounts, b u t that glycerol 1-phosphate must be synthesized from glucose at the expense of 8 ATP Eq/mol glycerol 1-phosphate. The synthesis of 1 mol triglyc ...
Revision Questions What is the definition of energy and what are the
... This is necessary to meet the increase in muscle oxygen requirements during intense exercise. Increases in blood flow to the muscles is due to redistribution of blood flow from inactive organs to the contracting skeletal muscle. Vasodilation occurs in the arterioles to the contracting skeletal muscl ...
... This is necessary to meet the increase in muscle oxygen requirements during intense exercise. Increases in blood flow to the muscles is due to redistribution of blood flow from inactive organs to the contracting skeletal muscle. Vasodilation occurs in the arterioles to the contracting skeletal muscl ...
Structure
... submaximal speeds the majority of energy is produced by aerobic metabolism. As the speed of exercise increases so does the energy demand placed on the muscle. More muscle fibers are recruited including type 2B fibers and more oxygen is consumed by the horse until it reaches a speed where the deliver ...
... submaximal speeds the majority of energy is produced by aerobic metabolism. As the speed of exercise increases so does the energy demand placed on the muscle. More muscle fibers are recruited including type 2B fibers and more oxygen is consumed by the horse until it reaches a speed where the deliver ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5/e
... Two enzymes are key to the coordination of fatty acid metabolism: acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), the first enzyme in the synthesis of fatty acids, and carnitine acyltransferase I, which limits the transport of fatty acids into the mitochondrial matrix for b-oxidation. Ingestion of a high-carbohydrate ...
... Two enzymes are key to the coordination of fatty acid metabolism: acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), the first enzyme in the synthesis of fatty acids, and carnitine acyltransferase I, which limits the transport of fatty acids into the mitochondrial matrix for b-oxidation. Ingestion of a high-carbohydrate ...
Metabolic diseases of the liver
... Metabolic dysfunction : inherited disease • Essential product deficit e.g. G-6-P deficiency (Glycogen storage I) • Precursor accumulation e.g. OTC deficiency (Hyperammonaemia) • Alternative pathway activation e.g. Aminoacidopathy • Combinations of above ...
... Metabolic dysfunction : inherited disease • Essential product deficit e.g. G-6-P deficiency (Glycogen storage I) • Precursor accumulation e.g. OTC deficiency (Hyperammonaemia) • Alternative pathway activation e.g. Aminoacidopathy • Combinations of above ...
UNIT 5 I. Energy and the Cell Module 5.1 Energy is the capacity to
... B. Review the overall equation for photosynthesis, and note that it is the reverse of cellular respiration (figure at top of left page). 6CO2 + 6H2O → Light → C6H12O6 + 6O2 I. An Overview of Photosynthesis Module 7.1 Autotrophs are the producers of the biosphere. A. Autotroph means “self-feeder,” an ...
... B. Review the overall equation for photosynthesis, and note that it is the reverse of cellular respiration (figure at top of left page). 6CO2 + 6H2O → Light → C6H12O6 + 6O2 I. An Overview of Photosynthesis Module 7.1 Autotrophs are the producers of the biosphere. A. Autotroph means “self-feeder,” an ...
Measurement of Enzymes and Their Clinical Significance
... • Using Enzyme Mass – Measure protein mass NOT catalytic activity ...
... • Using Enzyme Mass – Measure protein mass NOT catalytic activity ...
Transamination, Deamination,urea cycle
... • Glutamate ---the only amino acid that undergoes rapid oxidative deamination ...
... • Glutamate ---the only amino acid that undergoes rapid oxidative deamination ...
06a Organic Acids 2
... Citric acid synthesis during idiophase 1 mol glucose can result in 1 mol citric acid! 6 electrons need to be disposed of (oxygen) How can citrate be synthesised when pyruvate is not available (e.g. when lipids are the substrate (ß-oxidation))? ...
... Citric acid synthesis during idiophase 1 mol glucose can result in 1 mol citric acid! 6 electrons need to be disposed of (oxygen) How can citrate be synthesised when pyruvate is not available (e.g. when lipids are the substrate (ß-oxidation))? ...
Reading Guide
... 25. Glycine can be broken down by the glycine cleavage system to give a methylene group to the vitamin ____________________. 26. Branched amino acids that are glucogenic yield ______________; branched amino acids that are ketogenic yield _______________. ...
... 25. Glycine can be broken down by the glycine cleavage system to give a methylene group to the vitamin ____________________. 26. Branched amino acids that are glucogenic yield ______________; branched amino acids that are ketogenic yield _______________. ...
9) Several oxygen saturation curves are shown in the figure below
... upon binding the enzyme at a site other than the active site. This is an example of: A) negative cooperatively B) product inhibition C) allosteric regulation D) the saturation effect E) competitive inhibition 31) The metabolic process that produces cellular energy sources, molecular building blocks, ...
... upon binding the enzyme at a site other than the active site. This is an example of: A) negative cooperatively B) product inhibition C) allosteric regulation D) the saturation effect E) competitive inhibition 31) The metabolic process that produces cellular energy sources, molecular building blocks, ...
2010 Ruminant Carbohydrate Digestion
... – Acrylate pathways • Important on high grain diets – Accounts of 40% of propionate production ...
... – Acrylate pathways • Important on high grain diets – Accounts of 40% of propionate production ...
CASE 37
... from the blood (high insulin/glucagon ratio) or produces and adds glucose to the blood (low insulin/glucagon ratio). The responses can be divided into short-term ones such as the changes occurring during a normal daily cycle of feeding and long-term adaptive responses to prolonged fasting. In the sh ...
... from the blood (high insulin/glucagon ratio) or produces and adds glucose to the blood (low insulin/glucagon ratio). The responses can be divided into short-term ones such as the changes occurring during a normal daily cycle of feeding and long-term adaptive responses to prolonged fasting. In the sh ...
Insulin Signaling
... ----Adenine-----Adenosine--------------Adenosine monophosphate(AMP) ----Adenosine diphosphate(ADP)-----------Adenosine triphosphate(ATP)--------------- ...
... ----Adenine-----Adenosine--------------Adenosine monophosphate(AMP) ----Adenosine diphosphate(ADP)-----------Adenosine triphosphate(ATP)--------------- ...
Glycolysis
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).Glycolysis is a determined sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The intermediates provide entry points to glycolysis. For example, most monosaccharides, such as fructose and galactose, can be converted to one of these intermediates. The intermediates may also be directly useful. For example, the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a source of the glycerol that combines with fatty acids to form fat.Glycolysis is an oxygen independent metabolic pathway, meaning that it does not use molecular oxygen (i.e. atmospheric oxygen) for any of its reactions. However the products of glycolysis (pyruvate and NADH + H+) are sometimes disposed of using atmospheric oxygen. When molecular oxygen is used in the disposal of the products of glycolysis the process is usually referred to as aerobic, whereas if the disposal uses no oxygen the process is said to be anaerobic. Thus, glycolysis occurs, with variations, in nearly all organisms, both aerobic and anaerobic. The wide occurrence of glycolysis indicates that it is one of the most ancient metabolic pathways. Indeed, the reactions that constitute glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, occur metal-catalyzed under the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes. Glycolysis could thus have originated from chemical constraints of the prebiotic world.Glycolysis occurs in most organisms in the cytosol of the cell. The most common type of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP pathway), which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. Glycolysis also refers to other pathways, such as the Entner–Doudoroff pathway and various heterofermentative and homofermentative pathways. However, the discussion here will be limited to the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway.The entire glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases: The Preparatory Phase – in which ATP is consumed and is hence also known as the investment phase The Pay Off Phase – in which ATP is produced.↑ ↑ 2.0 2.1 ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑