Hybridization of atomic orbitals In general VSEPR predicts the
... Four equal bonds with equal HCH angles A covalent bond is formed by sharing two electrons by two atoms Imagine an orbital (containing 1 electron) from one atom overlaps with an orbital from the other atom to form the bond ...
... Four equal bonds with equal HCH angles A covalent bond is formed by sharing two electrons by two atoms Imagine an orbital (containing 1 electron) from one atom overlaps with an orbital from the other atom to form the bond ...
Oxacyclopropane (Epoxide) Synthesis: Epoxidation by
... The mildest reagent capable of breaking both the and bonds in a double bond is ozone, O3. This process is known as “ozonolysis.” Ozone is produced by an electrical discharge in dry oxygen in a instrument called an ozonator. The initial product of the reaction of ozone with an alkene is an ozonid ...
... The mildest reagent capable of breaking both the and bonds in a double bond is ozone, O3. This process is known as “ozonolysis.” Ozone is produced by an electrical discharge in dry oxygen in a instrument called an ozonator. The initial product of the reaction of ozone with an alkene is an ozonid ...
4b. Orbital Diagrams
... Orbital Diagrams • Use individual orbitals • Give subshell arrangement • Each orbital takes one electron before any other orbital in the same subshell can receive a second electron ...
... Orbital Diagrams • Use individual orbitals • Give subshell arrangement • Each orbital takes one electron before any other orbital in the same subshell can receive a second electron ...
Workshop 5
... Draw an atomic orbital model of the type demonstrated in lecture for CH2=C=CH2. Consider first the geometry at each carbon and select the appropriate hybridization. Label the orbitals used and show all valence electrons. The geometry should be clear from your drawing. Draw a dash/wedge structure for ...
... Draw an atomic orbital model of the type demonstrated in lecture for CH2=C=CH2. Consider first the geometry at each carbon and select the appropriate hybridization. Label the orbitals used and show all valence electrons. The geometry should be clear from your drawing. Draw a dash/wedge structure for ...
Chemistry 4021/8021 Computational Chemistry 3/4 Credits Spring
... combination of CN π bonds with a weak antibonding interaction with Ni, and orbital 42 is a symmetric combination of CO π* antibonds with no significant Ni contribution (only a Ni pz orbital would have the right phase behavior to participate in this orbital, and no such orbital is nearby in energy). ...
... combination of CN π bonds with a weak antibonding interaction with Ni, and orbital 42 is a symmetric combination of CO π* antibonds with no significant Ni contribution (only a Ni pz orbital would have the right phase behavior to participate in this orbital, and no such orbital is nearby in energy). ...
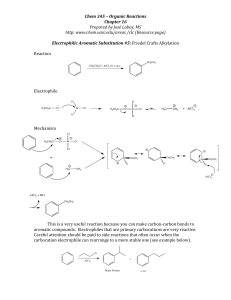
Mechanism
... the scrotum in “chimneyboys.” The connection between cancer and chimney soot was made by Percivall Pott in 1775. ...
... the scrotum in “chimneyboys.” The connection between cancer and chimney soot was made by Percivall Pott in 1775. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 7. What are the important guidelines to be followed while choosing alternate synthetic route? 8. Explain the umpolung concept of synthesis with suitable example. 9. Explain the mechanism of the following reaction. hv ...
... 7. What are the important guidelines to be followed while choosing alternate synthetic route? 8. Explain the umpolung concept of synthesis with suitable example. 9. Explain the mechanism of the following reaction. hv ...
SCH4U Organic Chemistry Portfolio Name: This portfolio is due on
... 5. Nomex is a polymer used to make flame-resistant clothing for firefighters. A portion of its structure is provided below. Write a polymerization reaction showing its production from monomers. What type of reaction is this? ...
... 5. Nomex is a polymer used to make flame-resistant clothing for firefighters. A portion of its structure is provided below. Write a polymerization reaction showing its production from monomers. What type of reaction is this? ...
Solution Key - Chemistry With BT
... (5) None of the methods mentioned here will convert enantiomers into each other ...
... (5) None of the methods mentioned here will convert enantiomers into each other ...
Woodward–Hoffmann rules

The Woodward–Hoffmann rules, devised by Robert Burns Woodward and Roald Hoffmann, are a set of rules in organic chemistry predicting the barrier heights of pericyclic reactions based upon conservation of orbital symmetry. The Woodward–Hoffmann rules can be applied to understand electrocyclic reactions, cycloadditions (including cheletropic reactions), sigmatropic reactions, and group transfer reactions. Reactions are classified as allowed if the electronic barrier is low, and forbidden if the barrier is high. Forbidden reactions can still take place but require significantly more energy.The Woodward–Hoffmann rules were first formulated to explain the striking stereospecificity of electrocyclic reactions under thermal and photochemical control. Thermolysis of the substituted cyclobutene trans-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (1) gave only one diastereomer, the (E,E)-3,4-dimethyl-2,4-hexadiene (2) as shown below; the (Z,Z) and the (E,Z) diastereomers were not detected in the reaction. Similarly, thermolysis of cis-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (3) gave only the (E,Z) diastereomer (4).Due to their elegance and simplicity, the Woodward–Hoffmann rules are credited with first exemplifying the power of molecular orbital theory to experimental chemists. Hoffmann was awarded the 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work, shared with Kenichi Fukui who developed a similar model using frontier molecular orbital (FMO) theory; because Woodward had died two years before, he was not eligible to win what would have been his second Nobel Prize for Chemistry.