* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Chemical Reactions
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Double layer forces wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear transmutation wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Supramolecular catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
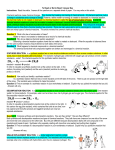
Unit 4 Lesson 4 Pages 199-203; Text section 7.2 Types of Chemical Reactions Chemical reactions can be classified into one of four categories depending on what type and how many reactants are present. We can use a generalized equation to represent each. In the generalized equation, the letters A and B represent positive ions (elements that lose electrons). The letters X and Y will represent negative ions (elements that gain electrons). In a synthesis reaction, two or more reactants are combined to form one product. The generalized equation is A + X AX A decomposition reaction is one where one product breaks down into two or more products. It is the opposite of a synthesis reaction. The generalized equation for a decomposition reaction is AX A + X During a single replacement reaction, the reactants are a single element and a compound. The single element will take the place of one of the elements in the compound. The element that was replaced will be off by its self. The generalized equation for a single replacement reaction is A + BX AX + B In a double replacement reaction, the elements in two compounds switch. The generalized equation is AX + BY AY + BX. The following websites presents the same material. If you need more explanation or examples, view it. The site calls double replacement reactions ionic and single replacement, replacement. It also contains problems where you write the products for each type of reaction given only the reactants. If you try some of these (I suggest it- later it will be for a grade), you will need to write the formulas for the reactants. Questions: Describe a synthesis reaction. Describe a decomposition reaction. Describe a single replacement reaction. Describe a double replacement reaction. Identify each type of reaction shown: 2H2O 2H2 + O2 AgNO3 + NaCl 2H2 + O2 AgCl + NaNO3 2H2O Cu + 2AgNO3 Cu(NO3)2 + 2Ag For each problem: 1. Decide what type of reaction is shown 2. Write the products 3. Balance the equation 1. _____Na2S + _____Cl2 _______________ + ______________ Type of reaction= 2. _____ PbO + _____Zn(C2H3O2)2 _____________ + ________________ Type of reaction = 3. _____FeCl3 ______________ + ___________________ Type of reaction = 4. _____ Al(ClO3)3 + _____CaCO3 ________________ + _________________ Type of reaction = 5. _____K2S + _____Ba Type of reaction = ___________________ + __________________