* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemical reactions cause chemical changes. They involve the
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
California Green Chemistry Initiative wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Fine chemical wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Al-Shifa pharmaceutical factory wikipedia , lookup
Determination of equilibrium constants wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon proliferation wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Supramolecular catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
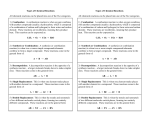
To React or Not to React! Answer Key Instructions: Read the article. Answer all the questions on a separate sheet of paper. You may write on this article. Chemical reactions cause chemical changes. They involve the breaking and making of chemical bonds. All chemical reactions involve a change in substances and a change in energy. However, neither matter nor energy is created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. The fact that matter is not created or destroyed in a chemical reaction is called the law of conservation of mass. In order for chemical reaction equations to show that no matter is created or destroyed, chemical reaction equations must be balanced. In other words, chemical reaction equations must show all the same atoms in the reactants and the products. They will just be arranged in different ways to show that a chemical reaction has occurred. There are many ways atoms can be rearranged in compounds. Thus, there are many types of chemical reactions. This article reviews five common chemical reactions. Question 1: What is the law of conservation of mass? Matter or mass is not created or destroyed as a result of a chemical reaction. Question 2: Why do we balance chemical reaction equations? Balancing a chemical reaction equation shows that no matter is created or destroyed. When the equation is balanced there are the same number of atoms of each element on both sides of the arrow. Question 3: What happens to chemical compounds in a chemical reaction? The chemical bonds that hold compounds together are broken and rearranged in a chemical reaction. SYNTHESIS REACTION: In a synthesis reaction two or more simple substances combine to form a more complex substance. In other words, two or more reactants yield one product. For example, hydrogen gas combined with oxygen gas can produce a more complex substance…water! The chemical equation for this synthesis reaction looks like: reactant + reactant product In order to visualize a synthesis reaction look at the cartoon to the right. In the cartoon, the skinny bird (reactant) and the worm (reactant) combine to make one product, a fat bird. Question 4: How could you identify a synthesis reaction? In a synthesis reaction there are two or more reactants on the left side of the arrow. There is just one product on the right side of the arrow. The reactants were combined to make the product. Question 5: Find an example of a synthesis reaction in your worksheets or textbook. Explain why you picked the reaction that you did. Answers will vary. DECOMPOSITION REACTION: In a decomposition reaction a more complex substance breaks down into simpler parts. One reactant yields 2 or more products. For example, water can be broken down into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. The chemical equation for this decomposition reaction looks like: reactant product + product In order to visualize a decomposition reaction look at the cartoon to the right. In this cartoon the egg (the reactant), which contained the turtle at one time, now has opened and the turtle (product) and eggshell (product) are now two separate substances. Question 6: Compare synthesis and decomposition reactions. How are they similar? How are they different? Both synthesis and decomposition reactions are types of chemical reactions. They both have one compound on one side of the arrow and more than one compound on the other side. But, they are different because decomposition starts with one compound in the reactants and breaks it apart. Synthesis is the opposite, starting with more than one reactant and putting them together. Question 7: Find an example of a decomposition reaction in your worksheets or textbook. Explain why you picked the reaction that you did. Answers will vary. SINGLE REPLACEMENT REACTION: In a single replacement reaction a single uncombined element replaces another in a compound. Two reactants yield two products. For example when zinc combines with hydrochloric acid, the zinc replaces hydrogen. The chemical equation for this single replacement reaction looks like: reactant + reactant product + product In order to visualize a single replacement reaction look at the cartoon to the right. Notice, the guy in the dark shirt steals the dance partner of the guy in the white shirt. So, the lone reactant traded places with one of the atoms that were part of a compound. Question 8: How could you identify a single replacement reaction? In a single replacement reaction there are two reactants and two products. One of the reactants is a single element and it trades places with one element in a compound. Question 9: Find an example of a single replacement reaction in your worksheets or textbook. Explain why you picked the reaction that you did. Answers will vary. DOUBLE REPLACEMENT REACTION: In a double replacement reaction parts of two compounds switch places to form two new compounds. Two reactants yield two products. For example when silver nitrate combines with sodium chloride, two new compounds-silver chloride and sodium nitrate are formed because the sodium and silver switched places. The chemical equation for this double replacement reaction looks like: reactant + reactant product + product In order to visualize a double replacement reaction look at the cartoon to the right. In the cartoon there are two different men with different hats on the reactants side. The men switch hats. Question 10: Compare single and double replacement reactions. How are they similar? How are they different? Both single replacement and double replacement reactions involve two reactants and two products. They are both types of chemical reactions involving a substance switching places with another. They are different because a single replacement starts with a compound and a single element and ends with a compound and a single element, but a double-replacement has two compounds on both sides of the arrow and a part of both compounds switch places. Question 11: Find an example of a double replacement reaction in your worksheets or textbook. Explain why you picked the reaction that you did. Answers will vary. COMBUSTION REACTION: Combustion means burning. In a combustion reaction a hydrocarbon and oxygen gas react to form carbon dioxide and water. A hydrocarbon is a compound made primarily of carbon and hydrogen. For example, when propane reacts with oxygen, carbon dioxide and water are formed. The chemical equation for this combustion reaction look like: Question 12: How could you identify a combustion reaction? In a combustion reaction the reactants are always some hydrocarbon (carbon and hydrogen compound) and oxygen. The products are always carbon dioxide and water. Question 13: Find an example of a combustion reaction in your worksheets or textbook. Explain why you picked the reaction you did. Answers will vary. ENERGY OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS: Chemical reactions always involve a change in energy because energy is required to break and make chemical bonds. However, energy is neither created nor destroyed. Energy is absorbed or released in chemical reactions. Chemical reactions in which energy is absorbed are called endothermic. This means that energy is required for the reaction to occur. The energy absorbed is often heat energy or electrical energy. Chemical reactions in which energy is released are called exothermic. The energy that is released was originally stored in the chemical bonds of the reactants. Often the heat given off causes the product(s) to feel hot. Any reaction that involves combustion (burning) is an exothermic chemical reaction.