COUPLING REACTIONS IN ORGANIC SYNTHESIS
... The addition of dihydrogen to Vaska's complex and other transition metals is a reversible reaction. The hydrogen can be released again if the reaction moves to the left in a reductive elimination. That reversibility makes transition metal compounds useful for hydrogen storage. Hydrogen gas is volumi ...
... The addition of dihydrogen to Vaska's complex and other transition metals is a reversible reaction. The hydrogen can be released again if the reaction moves to the left in a reductive elimination. That reversibility makes transition metal compounds useful for hydrogen storage. Hydrogen gas is volumi ...
CM1121 - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 1
... CM1121 - Organic Chemistry 1 This module is intended for students majoring in Chemistry and Applied Chemistry. It deals primarily with the basic principles to understand the structure and reactivity of organic molecules. Emphasis is on substitution and elimination reactions and chemistry of various ...
... CM1121 - Organic Chemistry 1 This module is intended for students majoring in Chemistry and Applied Chemistry. It deals primarily with the basic principles to understand the structure and reactivity of organic molecules. Emphasis is on substitution and elimination reactions and chemistry of various ...
Eliminations
... Mechanism: The E2 reaction is concerted: the leaving group leaves at the same time as the hydrogen is removed. The reaction obeys second-‐order kinetics: ...
... Mechanism: The E2 reaction is concerted: the leaving group leaves at the same time as the hydrogen is removed. The reaction obeys second-‐order kinetics: ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... ________ 20. The complete combustion of octane (C8H18) would: a. require 25 O2(g). c. produce 18 H2O(g). b. produce 16 CO2(g). d. all of the above ________ 21. Double-replacement reactions are generally driven by the formation of: a. a precipitate. c. water. b. a gaseous product. d. all of the above ...
... ________ 20. The complete combustion of octane (C8H18) would: a. require 25 O2(g). c. produce 18 H2O(g). b. produce 16 CO2(g). d. all of the above ________ 21. Double-replacement reactions are generally driven by the formation of: a. a precipitate. c. water. b. a gaseous product. d. all of the above ...
Chemistry 21 A - El Camino College
... 9. a) endothermic reaction is ___________________________________________________________________ b) exothermic reaction is ___________________________________________________________________ 10. The percentage yield is _____________________________________________________________________ __________ ...
... 9. a) endothermic reaction is ___________________________________________________________________ b) exothermic reaction is ___________________________________________________________________ 10. The percentage yield is _____________________________________________________________________ __________ ...
A Diels-Alder Synthesis
... The Diels-Alder reaction usually proceeds with endo selectivity. This means that the product in which the activating electron-withdrawing group of the dienophile is located in the endo position is formed faster than the alternative exo isomer. This happens even though the exo product is sometimes mo ...
... The Diels-Alder reaction usually proceeds with endo selectivity. This means that the product in which the activating electron-withdrawing group of the dienophile is located in the endo position is formed faster than the alternative exo isomer. This happens even though the exo product is sometimes mo ...
Exam 2 SOLUTION
... Please work in the space provided. Box your answers to set them off. The last page may be torn off and used for scratch paper. Bring all materials up when you are finished with the exam. Good luck! 1. Predict the product, or give the starting material for the following reactions: [12] ...
... Please work in the space provided. Box your answers to set them off. The last page may be torn off and used for scratch paper. Bring all materials up when you are finished with the exam. Good luck! 1. Predict the product, or give the starting material for the following reactions: [12] ...
Chapter 11: Reactions at an sp3 Hybridized Carbon III
... • TBS will replace H of an alcohol to act as a protecting group for the alcohol • Polarize H(+) and RO(-) in the alcohol and TBS(+) and Cl(-) in TBSCl • Si loves F even more than O and will grab F– and spit out RO– when you need to break off the TBS protecting group ...
... • TBS will replace H of an alcohol to act as a protecting group for the alcohol • Polarize H(+) and RO(-) in the alcohol and TBS(+) and Cl(-) in TBSCl • Si loves F even more than O and will grab F– and spit out RO– when you need to break off the TBS protecting group ...
E2 reactions
... Relative rates for E2: 3°>2°>1°. The base must be strong. The LG should be good. The solvent should be polar. Coplanar (usually anti) transition state is ...
... Relative rates for E2: 3°>2°>1°. The base must be strong. The LG should be good. The solvent should be polar. Coplanar (usually anti) transition state is ...
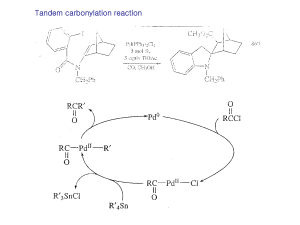
18 Important and sometimes forgotten) organic transformations
... •Phosphines can also be used •DMAP and DBU are better in some cases ...
... •Phosphines can also be used •DMAP and DBU are better in some cases ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... Molecular Orbitals One model of molecular bonding pictures a molecular orbital that is a combination of individual atomic orbitals. A bonding orbital can be occupied by a pair of electrons. In a sigma (σ) bond, the molecular orbital is symmetrical around the axis connecting ...
... Molecular Orbitals One model of molecular bonding pictures a molecular orbital that is a combination of individual atomic orbitals. A bonding orbital can be occupied by a pair of electrons. In a sigma (σ) bond, the molecular orbital is symmetrical around the axis connecting ...
Lecture 9. Redox chemistry
... •Iron, a common construction metal often used in forming steel alloys, corrodes by being oxidized to ions of iron by oxygen. •This corrosion is even faster in the presence of salts and acids, because these materials make electrically conductive solutions that make electron transfer easy ...
... •Iron, a common construction metal often used in forming steel alloys, corrodes by being oxidized to ions of iron by oxygen. •This corrosion is even faster in the presence of salts and acids, because these materials make electrically conductive solutions that make electron transfer easy ...
C h e m g u i d e ... ALCOHOLS: THE REACTION WITH SODIUM
... 1. The reaction between alcohols and sodium is sometimes used as a test for the -OH group in the compound. a) Why is it important to test the pH of the liquid before adding the sodium? b) What would you observe if the liquid was actually an alcohol? c) Observing this isn’t enough to be sure that you ...
... 1. The reaction between alcohols and sodium is sometimes used as a test for the -OH group in the compound. a) Why is it important to test the pH of the liquid before adding the sodium? b) What would you observe if the liquid was actually an alcohol? c) Observing this isn’t enough to be sure that you ...
Unit 3: Reactions of Alkenes. Thermodynamics and Kinetics
... H3C—CH3 rotational barrier = 2.9 kcal/mol ...
... H3C—CH3 rotational barrier = 2.9 kcal/mol ...
Woodward–Hoffmann rules

The Woodward–Hoffmann rules, devised by Robert Burns Woodward and Roald Hoffmann, are a set of rules in organic chemistry predicting the barrier heights of pericyclic reactions based upon conservation of orbital symmetry. The Woodward–Hoffmann rules can be applied to understand electrocyclic reactions, cycloadditions (including cheletropic reactions), sigmatropic reactions, and group transfer reactions. Reactions are classified as allowed if the electronic barrier is low, and forbidden if the barrier is high. Forbidden reactions can still take place but require significantly more energy.The Woodward–Hoffmann rules were first formulated to explain the striking stereospecificity of electrocyclic reactions under thermal and photochemical control. Thermolysis of the substituted cyclobutene trans-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (1) gave only one diastereomer, the (E,E)-3,4-dimethyl-2,4-hexadiene (2) as shown below; the (Z,Z) and the (E,Z) diastereomers were not detected in the reaction. Similarly, thermolysis of cis-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (3) gave only the (E,Z) diastereomer (4).Due to their elegance and simplicity, the Woodward–Hoffmann rules are credited with first exemplifying the power of molecular orbital theory to experimental chemists. Hoffmann was awarded the 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work, shared with Kenichi Fukui who developed a similar model using frontier molecular orbital (FMO) theory; because Woodward had died two years before, he was not eligible to win what would have been his second Nobel Prize for Chemistry.