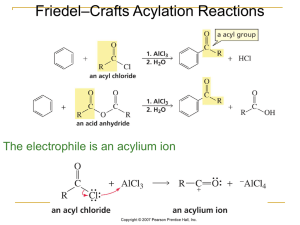
File - Kheriaty Chemistry
... b. What is the chemical formula of that new product? c. What element will O bond to? d. What is the chemical formula of that new product? 16. Potassium oxide reacts with magnesium bromide. a. What element will potassium bond to? b. What is the chemical formula of that new product? c. What element wi ...
... b. What is the chemical formula of that new product? c. What element will O bond to? d. What is the chemical formula of that new product? 16. Potassium oxide reacts with magnesium bromide. a. What element will potassium bond to? b. What is the chemical formula of that new product? c. What element wi ...
Synthesis of a Family of Chiral Asymmetric Schiff - Blogs at H-SC
... trial two. Deprotection yielded spectra that plausibly matched chemical shifts for the intended molecule, even though the product remained an oil. The initial target reaction was not straight out of literature but was rather inspired by work done by Hoveyda’s group. Thus, the target compound, under ...
... trial two. Deprotection yielded spectra that plausibly matched chemical shifts for the intended molecule, even though the product remained an oil. The initial target reaction was not straight out of literature but was rather inspired by work done by Hoveyda’s group. Thus, the target compound, under ...
Electronic Spectroscopy Application of Group Theory
... to occur then we refer to the transition as vibronic. We can understand the process as a state mixing of higher lying states into the excited state. In this case the symmetry of the vibronic mode also enters into consideration. The symmetry of vibronic states given by the direct product of the orbit ...
... to occur then we refer to the transition as vibronic. We can understand the process as a state mixing of higher lying states into the excited state. In this case the symmetry of the vibronic mode also enters into consideration. The symmetry of vibronic states given by the direct product of the orbit ...
chapter 2: reactions of organic compounds
... 4) OXIDATION & 5) REDUCTION REACTIONS • Change in the number of H or O atoms bonded to C • Always occur together • One reactant is oxidized while the other is reduced • For now, lets focus on reactant only… ...
... 4) OXIDATION & 5) REDUCTION REACTIONS • Change in the number of H or O atoms bonded to C • Always occur together • One reactant is oxidized while the other is reduced • For now, lets focus on reactant only… ...
Chem1101 – Semester 1
... When two 1s orbitals in opposite phase, mix, the anti-‐bonding MO (σ*), which has a node, forms with a higher energy ...
... When two 1s orbitals in opposite phase, mix, the anti-‐bonding MO (σ*), which has a node, forms with a higher energy ...
32 . R $ [ ~ % % + l
... down the stairs and finally comes to a rest by the outside door. Which sequence best describes the energy transformations for the piano form the moment it is being brought upstairs, to when it stops by the door? (a) Potential energy Kinetic energy 3 Thermal energy of the ground and piano (b) Ground ...
... down the stairs and finally comes to a rest by the outside door. Which sequence best describes the energy transformations for the piano form the moment it is being brought upstairs, to when it stops by the door? (a) Potential energy Kinetic energy 3 Thermal energy of the ground and piano (b) Ground ...
Slide 1
... *To gain some knowledge about the applications & recent literatures related to the reaction. ...
... *To gain some knowledge about the applications & recent literatures related to the reaction. ...
Exercises Chem Eqm
... 7.1(a) K = 2.85 x 10-6; (b) ∆rGo = +240 kJ mol-1; (c) ∆rG = 0 7.4(a) Mole fractions A: 0.087, B: 0.370, C: 0.196, D: 0.348, Total: 1.001; (b) Kx – 0.33; (c) p = 0.33; (d) ∆rGo = + 2.8 x 103 J mol-1. 7.6(a) ∆rHo = +2.77 kJ mol-1, ∆rSo = -16.5 J K-1 mol-1 7.9(a) χB = 0.904, χI = 0.096 7.11(a) ∆rGo = – ...
... 7.1(a) K = 2.85 x 10-6; (b) ∆rGo = +240 kJ mol-1; (c) ∆rG = 0 7.4(a) Mole fractions A: 0.087, B: 0.370, C: 0.196, D: 0.348, Total: 1.001; (b) Kx – 0.33; (c) p = 0.33; (d) ∆rGo = + 2.8 x 103 J mol-1. 7.6(a) ∆rHo = +2.77 kJ mol-1, ∆rSo = -16.5 J K-1 mol-1 7.9(a) χB = 0.904, χI = 0.096 7.11(a) ∆rGo = – ...
organic lab questions
... (most reactive to least reactive) for the alcohols used in this reaction. Present your ranking in the form of simplified organic structures separated by greater than signs. Show the degree of each alcohol below each structure. ...
... (most reactive to least reactive) for the alcohols used in this reaction. Present your ranking in the form of simplified organic structures separated by greater than signs. Show the degree of each alcohol below each structure. ...
File
... c) Reaction of 1-bromo-3-methylpropane with sodium hydroxide. 2. Write balanced equations and name the reactants and products for: a) dehydration (elimination) reaction of ethanol b) complete combustion of ethanol c) complete combustion of 1-propanol 3. Draw structural diagrams and write IUPAC names ...
... c) Reaction of 1-bromo-3-methylpropane with sodium hydroxide. 2. Write balanced equations and name the reactants and products for: a) dehydration (elimination) reaction of ethanol b) complete combustion of ethanol c) complete combustion of 1-propanol 3. Draw structural diagrams and write IUPAC names ...
Exam 2 Fall 2005 Chemsitry 1211
... This exam is twenty five questions long. Each question is worth 4 points. Please read through all of the questions first and ask about anything you do not understand. You will have one hour and 15 minutes to complete this exam. Exams will be picked up at the end of the class period. No late exams wi ...
... This exam is twenty five questions long. Each question is worth 4 points. Please read through all of the questions first and ask about anything you do not understand. You will have one hour and 15 minutes to complete this exam. Exams will be picked up at the end of the class period. No late exams wi ...
Chemistry Final Test
... Which of the following statements is correct regarding this reaction? (A) This reaction is a nucleophilic reaction. (B) This reaction is a substitution reaction. (C) A negatively charged intermediate is involved in this reaction. (D) A cyclic bromonium ion is an intermediate in this reaction. 6-2、Wh ...
... Which of the following statements is correct regarding this reaction? (A) This reaction is a nucleophilic reaction. (B) This reaction is a substitution reaction. (C) A negatively charged intermediate is involved in this reaction. (D) A cyclic bromonium ion is an intermediate in this reaction. 6-2、Wh ...
Chem 1a Midterm Review
... particularly the shape, nodes and sign of the orbitals. Note that the s and d orbitals are symmetric to inversion through the origin while the p is anti-symmetric toward inversions. Orbital energy: one electron atoms the energy only dependents on n multi-electron atoms: Penetration for orbitals of s ...
... particularly the shape, nodes and sign of the orbitals. Note that the s and d orbitals are symmetric to inversion through the origin while the p is anti-symmetric toward inversions. Orbital energy: one electron atoms the energy only dependents on n multi-electron atoms: Penetration for orbitals of s ...
Assignment 4 Task 1a
... Scenario: You are working as a CSI in a forensic biochemistry laboratory. You have been assigned to a new case and are working as part of a team to solve the case. Working in the laboratory you will need to have a good understanding of the conventions adopted to ensure that all chemical compounds ha ...
... Scenario: You are working as a CSI in a forensic biochemistry laboratory. You have been assigned to a new case and are working as part of a team to solve the case. Working in the laboratory you will need to have a good understanding of the conventions adopted to ensure that all chemical compounds ha ...
Fall Exam 4 - Chemistry - University of Kentucky
... A molecule containing a central atom with sp2 hybridization has which one of the following electron geometries? ...
... A molecule containing a central atom with sp2 hybridization has which one of the following electron geometries? ...
Exam 3 Answer Key
... Which of the following statements are true? A. In Bohr’s atomic theory, when an electron moves from one energy level to another energy level more distant from the nucleus, energy is emitted. B. The principal quantum number determines the size and the shape of the orbitals. C. Mendeleev assembled the ...
... Which of the following statements are true? A. In Bohr’s atomic theory, when an electron moves from one energy level to another energy level more distant from the nucleus, energy is emitted. B. The principal quantum number determines the size and the shape of the orbitals. C. Mendeleev assembled the ...
CHEM1405 2012-J-2 June 2012 • What is the ground state electron
... • The radioactive isotopes 131I and 137Cs have been detected in drinking water near the Japanese Fukushima nuclear reactor. They have half lives of 8 days and 30 years, respectively. What is the definition of half-life? Half-life is the amount of time required for the amount (or activity) of a sampl ...
... • The radioactive isotopes 131I and 137Cs have been detected in drinking water near the Japanese Fukushima nuclear reactor. They have half lives of 8 days and 30 years, respectively. What is the definition of half-life? Half-life is the amount of time required for the amount (or activity) of a sampl ...
Woodward–Hoffmann rules

The Woodward–Hoffmann rules, devised by Robert Burns Woodward and Roald Hoffmann, are a set of rules in organic chemistry predicting the barrier heights of pericyclic reactions based upon conservation of orbital symmetry. The Woodward–Hoffmann rules can be applied to understand electrocyclic reactions, cycloadditions (including cheletropic reactions), sigmatropic reactions, and group transfer reactions. Reactions are classified as allowed if the electronic barrier is low, and forbidden if the barrier is high. Forbidden reactions can still take place but require significantly more energy.The Woodward–Hoffmann rules were first formulated to explain the striking stereospecificity of electrocyclic reactions under thermal and photochemical control. Thermolysis of the substituted cyclobutene trans-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (1) gave only one diastereomer, the (E,E)-3,4-dimethyl-2,4-hexadiene (2) as shown below; the (Z,Z) and the (E,Z) diastereomers were not detected in the reaction. Similarly, thermolysis of cis-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (3) gave only the (E,Z) diastereomer (4).Due to their elegance and simplicity, the Woodward–Hoffmann rules are credited with first exemplifying the power of molecular orbital theory to experimental chemists. Hoffmann was awarded the 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work, shared with Kenichi Fukui who developed a similar model using frontier molecular orbital (FMO) theory; because Woodward had died two years before, he was not eligible to win what would have been his second Nobel Prize for Chemistry.