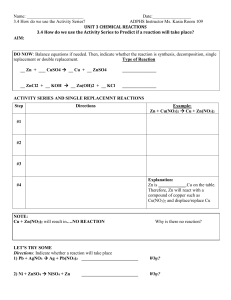
3.4 How do we use the Activity Series
... 3. Will the above reaction take place?_____________________________________________________ 4. Will the reverse reaction take place, Cl2 + 2NaF? __________________________________________ ...
... 3. Will the above reaction take place?_____________________________________________________ 4. Will the reverse reaction take place, Cl2 + 2NaF? __________________________________________ ...
File
... The reaction between bromoethane, CH3CH2Br, and potassium cyanide is an example of a nucleophilic substitution reaction. (i) ...
... The reaction between bromoethane, CH3CH2Br, and potassium cyanide is an example of a nucleophilic substitution reaction. (i) ...
Calculating Percent Yield
... All five specific types of EAS follow the same reaction mechanism. The general mechanism is as follows: ...
... All five specific types of EAS follow the same reaction mechanism. The general mechanism is as follows: ...
South Pasadena · Chemistry
... n=4 and l =3 is ____. e) The maximum number of orbitals that may be associated with the quantum number set n=3, l =2, and ml = -2 is ___. f) Label each of the orbital pictures found in question 78 (page 329)with the appropriate letter: g) When n=5, the possible values of l are ______. h) The maximum ...
... n=4 and l =3 is ____. e) The maximum number of orbitals that may be associated with the quantum number set n=3, l =2, and ml = -2 is ___. f) Label each of the orbital pictures found in question 78 (page 329)with the appropriate letter: g) When n=5, the possible values of l are ______. h) The maximum ...
apch07_quantum
... n=4 and l =3 is ____. e) The maximum number of orbitals that may be associated with the quantum number set n=3, l =2, and ml = -2 is ___. f) Label each of the orbital pictures found in question 78 (page 329)with the appropriate letter: g) When n=5, the possible values of l are ______. h) The maximum ...
... n=4 and l =3 is ____. e) The maximum number of orbitals that may be associated with the quantum number set n=3, l =2, and ml = -2 is ___. f) Label each of the orbital pictures found in question 78 (page 329)with the appropriate letter: g) When n=5, the possible values of l are ______. h) The maximum ...
RTF
... No - this is a very exothermic reaction, releasing a lot of heat (methane, natural gas, is used as a heating fuel). The reverse reaction would be therefore be highly endothermic, requiring a lot of energy to make it go. Thus it is not likely to be reversible. ...
... No - this is a very exothermic reaction, releasing a lot of heat (methane, natural gas, is used as a heating fuel). The reverse reaction would be therefore be highly endothermic, requiring a lot of energy to make it go. Thus it is not likely to be reversible. ...
Slide 1 - Mrs. Reed Science Classes
... products. b.relative numbers of moles of reactants and products. c.number of atoms in each compound in a reaction. d.number of valence electrons involved in the reaction. ...
... products. b.relative numbers of moles of reactants and products. c.number of atoms in each compound in a reaction. d.number of valence electrons involved in the reaction. ...
TYPES OF REACTIONS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... A chlorine atom attacks the methane molecule to form hydrogen chloride and a methyl free radical. ...
... A chlorine atom attacks the methane molecule to form hydrogen chloride and a methyl free radical. ...
Chap Thirteen: Alcohols
... ii. Reduction of Esters and Carboxylic Acids with LiAlH4 only LEARNING OUTCOMES: Understand the formation of alcohols through use of organometallics in carboncarbon bond forming reactions with electrophiles Predict the stereochemistry and optical activity of a product from an understanding of it ...
... ii. Reduction of Esters and Carboxylic Acids with LiAlH4 only LEARNING OUTCOMES: Understand the formation of alcohols through use of organometallics in carboncarbon bond forming reactions with electrophiles Predict the stereochemistry and optical activity of a product from an understanding of it ...
3.8 ADDITION OF WATER TO AN ALKENE H or enzyme + H-O
... Our example just shows one molecule of monomer as a reactant, although in fact there are large numbers of them that will react with each other to form the polymer: The one sided arrows indicate that one electron goes to each C atom. This is in contrast to the previous reaction pathways where both el ...
... Our example just shows one molecule of monomer as a reactant, although in fact there are large numbers of them that will react with each other to form the polymer: The one sided arrows indicate that one electron goes to each C atom. This is in contrast to the previous reaction pathways where both el ...
CH 6
... • If carbocation intermediate is more stable than another, why is the reaction through the more stable one faster? – The relative stability of the intermediate is related to an equilibrium constant (Gº) – The relative stability of the transition state (which describes the size of the rate constant) ...
... • If carbocation intermediate is more stable than another, why is the reaction through the more stable one faster? – The relative stability of the intermediate is related to an equilibrium constant (Gº) – The relative stability of the transition state (which describes the size of the rate constant) ...
study note 3 33
... An addition of a molecule to a double or triple bond. The molecule is broken down in the reaction; the two parts of the molecule are added to either side of the double bond, leaving a single bond (or leaving a double bond when the addition is to a triple bond). Halogenation, and hydrogenation are ty ...
... An addition of a molecule to a double or triple bond. The molecule is broken down in the reaction; the two parts of the molecule are added to either side of the double bond, leaving a single bond (or leaving a double bond when the addition is to a triple bond). Halogenation, and hydrogenation are ty ...
8. Chemistry of cooking
... (a) Name the two products formed by the dehydration of butan-2-ol (b) Name a reagent which could be used to oxidise butan-2-ol to butanone. ...
... (a) Name the two products formed by the dehydration of butan-2-ol (b) Name a reagent which could be used to oxidise butan-2-ol to butanone. ...
South Pasadena · Chemistry
... The principal quantum number, n, can have the values of: ___ ___ ___ ___ ___, etc. The angular momentum quantum number, l, can have integer values from ______ to ______. The magnetic quantum number, ml, can have integer values from _____ to _____. 2. When n = 3, l can have values of ________________ ...
... The principal quantum number, n, can have the values of: ___ ___ ___ ___ ___, etc. The angular momentum quantum number, l, can have integer values from ______ to ______. The magnetic quantum number, ml, can have integer values from _____ to _____. 2. When n = 3, l can have values of ________________ ...
Exam 2-Answer Key
... two pi bonds and a sigma bond, each formed by a lateral overlap of two p orbitals. a sigma bond formed by overlap of two s orbitals and two pi bonds, each formed by lateral overlap of two p orbitals. a sigma bond formed by end-on overlap of two sp" orbitals and a pi bond formed by lateral overlap of ...
... two pi bonds and a sigma bond, each formed by a lateral overlap of two p orbitals. a sigma bond formed by overlap of two s orbitals and two pi bonds, each formed by lateral overlap of two p orbitals. a sigma bond formed by end-on overlap of two sp" orbitals and a pi bond formed by lateral overlap of ...
- professional publication
... Reaction. Mechanism and Stereochemistry of S N2 reaction, Mechanism and Stereochemistry of SN1 Reaction. Rearrangement of Carbocation, S N2 versus SN1 Reactions, Reactivity of Alkyl Halides in SN1 and SN2, Factors Affecting SN1 and SN2. ...
... Reaction. Mechanism and Stereochemistry of S N2 reaction, Mechanism and Stereochemistry of SN1 Reaction. Rearrangement of Carbocation, S N2 versus SN1 Reactions, Reactivity of Alkyl Halides in SN1 and SN2, Factors Affecting SN1 and SN2. ...
Topic 16 IB Chemistry Definitions
... The rate is always proportional to the concentration of a reactant raised to a power, where the power is the order of the reaction with respect to that reactant. The constant of proportionality in the rate expression. Unit is: (mol dm-3)1 – overall order ...
... The rate is always proportional to the concentration of a reactant raised to a power, where the power is the order of the reaction with respect to that reactant. The constant of proportionality in the rate expression. Unit is: (mol dm-3)1 – overall order ...
Woodward–Hoffmann rules

The Woodward–Hoffmann rules, devised by Robert Burns Woodward and Roald Hoffmann, are a set of rules in organic chemistry predicting the barrier heights of pericyclic reactions based upon conservation of orbital symmetry. The Woodward–Hoffmann rules can be applied to understand electrocyclic reactions, cycloadditions (including cheletropic reactions), sigmatropic reactions, and group transfer reactions. Reactions are classified as allowed if the electronic barrier is low, and forbidden if the barrier is high. Forbidden reactions can still take place but require significantly more energy.The Woodward–Hoffmann rules were first formulated to explain the striking stereospecificity of electrocyclic reactions under thermal and photochemical control. Thermolysis of the substituted cyclobutene trans-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (1) gave only one diastereomer, the (E,E)-3,4-dimethyl-2,4-hexadiene (2) as shown below; the (Z,Z) and the (E,Z) diastereomers were not detected in the reaction. Similarly, thermolysis of cis-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (3) gave only the (E,Z) diastereomer (4).Due to their elegance and simplicity, the Woodward–Hoffmann rules are credited with first exemplifying the power of molecular orbital theory to experimental chemists. Hoffmann was awarded the 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work, shared with Kenichi Fukui who developed a similar model using frontier molecular orbital (FMO) theory; because Woodward had died two years before, he was not eligible to win what would have been his second Nobel Prize for Chemistry.























