* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
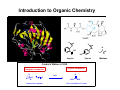
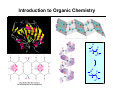
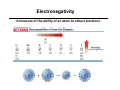
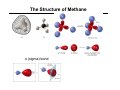
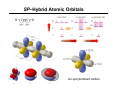
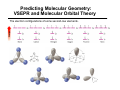
Chapter 1 Important Concepts and Principles Ch1.3: Valence, C–C Bonds (single, double, triple), Isomer (constitutional), Molecular/Structural formula, Connectivity Ch1.4-8: Ionic/covalent bonds, Octet rule, Ions, Electronegativity Lewis structure, Formal charges, Resonance structures, Resonance stabilization Ch1.9-15: Atomic/molecular orbitals Orbital hybridization (sp3, sp2, sp) Sigma(σ)/Pi (π)bonds (structure of ethane/ethene/ethyne) Stereoisomer Ch1.16: Molecular geometry (tetrahedral, trigonal planar, linear, trigonal pyramid, bent) Ch1.17: Representation of structural formulas (dash, condensed, bond line, three-dimensional) Introduction to Organic Chemistry O O O H NH OH H HO O Tylenol Aspirin Friedrich Wöhler in 1828 Organic compound Inorganic compound H H O heat +N H O C N H Ammonium cyanate H2N NH2 Uria (constituent of urine) C H H Methane Introduction to Organic Chemistry O O O H NH OH O Aspirin H HO Tylenol C H H Methane • What is the shape of these molecules? < Structure > • What these molecules do/how they do? < Function/Mechanism > • How they can be obtained? < Synthesis > Introduction to Organic Chemistry H N O R N H H H N O R H N H + Electronegativity A measure of the ability of an atom to attract electrons Formal Charges Indicator of how many electrons are gained/lost by an atom Formal Charges Practice: Find formal charges for the red atoms. Atomic Orbitals Wave Functions: Solutions to Schrödinger's Equation (contains the information of electron’s energy and position (H An orbital is a region of space where the probability of finding an electron is large. Molecular Orbitals Atomic orbitals (AOs) combine to become molecular orbitals (MOs): the number of molecular orbitals that results always equals the number of atomic orbitals that combine. SP3–Hybrid Atomic Orbital Hybridization: A mathematical process combining individual wave functions The shape of an sp3 orbital The Structure of Methane σ (sigma) bond The Structure of Ethane SP2–Hybrid Atomic Orbitals π (pi) bond An sp2-hybridized carbon SP–Hybrid Atomic Orbitals An sp-hybridized carbon Bond Lengths and Angles of Ethyne, Ethene, and Ethane sp-hybridized C sp2-hybridized C sp3-hybridized C s-character 50% 33.3% 25% p-character 50% 66.6% 75% ***The higher s-character of a carbon atom, the higher its electronegativity. Rule of thumb in using hybridized atomic orbitals for actual molecules SP3 hybridization: Any atom in a molecule that is not a part of a double or triple bond – Tetrahedral 109.5° 109.5° H 109.5° O H H N H H H C H H H 109.5° SP2 hybridization: Any atom in a molecule that is a part of a double bond – Trigonal planar H H H N C C C H H H H H H B O C H H H H H C+ H SP hybridization: Any atom in a molecule that is a part of a triple bond – Linear N N N C CH3 Rule of thumb in using hybridized atomic orbitals for actual molecules What is the hybridization of the indicated atom(s) in each molecule? CH3 C C (a) Me (b) Me C (c) + Me O O (d) (e) (f) O (h) (g) (i) N O (j) Me Me Al Me (k) O H (l) N Predicting Molecular Geometry: VSEPR and Molecular Orbital Theory The electron configurations of some second-row elements. Chapter 1 Suggested Problems Ch1.3: Valence, C–C Bonds (single, double, triple), Isomer (constitutional), Molecular/Structural formula, Connectivity: Problems 1,33, 1.36 Ch1.4-8: Lewis structure, Formal charges: Problem 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.18, 1.19 Resonance structures, Resonance stabilization: Problem 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, 1.27, 1.31, 1.32 Ch1.9-15: Sigma(σ)/Pi (π)bonds (structure of ethane/ethene/ethyne) Stereoisomer: Problem 1.8, 1.34 Ch1.16: Molecular geometry (tetrahedral, trigonal planar, linear, trigonal pyramid, bent): Problem 1.10, 1.11, 1.28–30 Ch1.17: Representation of structural formulas (dash, condensed, bond line, three-dimensional): Problem 1.13, 1.16, 1.22, 1.23