Biomolecule Review Worksheet
... even others form chains and rings. The sequence and shapes of the “R” groups control the shape and function of the protein. ...
... even others form chains and rings. The sequence and shapes of the “R” groups control the shape and function of the protein. ...
CH 9 cont
... Single ringed N Bases = Pyrimidines are C and T 2X ringed N Bases = Purines are A and G Scientists Watson and Crick proposed structure of DNA as a ____________, held together by H Bonds and __________ These complementary bases were A bonded w/ ____ G bonded w/ _______ II. DNA REPLICATION What is it? ...
... Single ringed N Bases = Pyrimidines are C and T 2X ringed N Bases = Purines are A and G Scientists Watson and Crick proposed structure of DNA as a ____________, held together by H Bonds and __________ These complementary bases were A bonded w/ ____ G bonded w/ _______ II. DNA REPLICATION What is it? ...
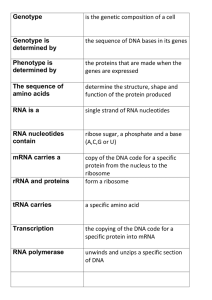
Macromolecule (biomolecule) Review Worksheet
... are very small, others are large, and even others form chains and rings. The sequence and shapes of the “R” groups control the shape and function of the protein. 30. How many different amino acids are there? 31. What part of the amino acid varies from one amino acid to another? 32. What determines t ...
... are very small, others are large, and even others form chains and rings. The sequence and shapes of the “R” groups control the shape and function of the protein. 30. How many different amino acids are there? 31. What part of the amino acid varies from one amino acid to another? 32. What determines t ...
Secondary structures
... Unlike three dimensional structures of proteins, DNA molecules assume simple double helical structures independent on their sequences. There are three kinds of double helices that have been observed in DNA: type A, type B, and type Z, which differ in their geometries. ...
... Unlike three dimensional structures of proteins, DNA molecules assume simple double helical structures independent on their sequences. There are three kinds of double helices that have been observed in DNA: type A, type B, and type Z, which differ in their geometries. ...
HigH-THrougHpuT dna sequencing
... While there are numerous “next generation” sequencing platforms, one of the most frequently used is a “sequencing by synthesis” method. First, the double stranded DNA sample is fragmented and denatured, and the resulting single stranded fragments are attached to the surface of a flow cell. Multiple ...
... While there are numerous “next generation” sequencing platforms, one of the most frequently used is a “sequencing by synthesis” method. First, the double stranded DNA sample is fragmented and denatured, and the resulting single stranded fragments are attached to the surface of a flow cell. Multiple ...
File
... is part of the Ribosomes which work with the other forms of RNA to construct proteins. tRNA carries amino acids which are the smallest building blocks in the process of making proteins. The Ribosomes connect the tRNA to the mRNA so that the code mimics the original DNA. The amino acids that the tRNA ...
... is part of the Ribosomes which work with the other forms of RNA to construct proteins. tRNA carries amino acids which are the smallest building blocks in the process of making proteins. The Ribosomes connect the tRNA to the mRNA so that the code mimics the original DNA. The amino acids that the tRNA ...
DNA, RNA, Protein synthesis, and Mutations
... opposite to the amino acid attachment site is sequence of 3 bases complementary to a specific codon called the ANTICODON ...
... opposite to the amino acid attachment site is sequence of 3 bases complementary to a specific codon called the ANTICODON ...
Transcription
... Converting a gene from the DNA blueprint into a complementary single-stranded RNA sequence ...
... Converting a gene from the DNA blueprint into a complementary single-stranded RNA sequence ...
Electrophoresis literally means “the condition of
... The chemical mixed with water before swishing in the mouth (in order to help break cells away from cheek ...
... The chemical mixed with water before swishing in the mouth (in order to help break cells away from cheek ...
1) Where does glycolysis occur in the cell
... 8) All of the following processes occur within mitochondria except: a) the splitting of glucose b) the formation of citric acid c) the catabolism of citric acid to produce NADH, CO2, AND H+ d) the transfer of electrons form NADH to the electron transport chain e) the reduction of oxygen to form wate ...
... 8) All of the following processes occur within mitochondria except: a) the splitting of glucose b) the formation of citric acid c) the catabolism of citric acid to produce NADH, CO2, AND H+ d) the transfer of electrons form NADH to the electron transport chain e) the reduction of oxygen to form wate ...
You Light Up My Life - Sarasota Military Academy
... and, together with DNA ligase, can repair mistakes in incorrect strand ...
... and, together with DNA ligase, can repair mistakes in incorrect strand ...
TranscriptionTranslation
... tRNA 1. Transferring Agent to bring selected rNTP to rRNA 2. 4 Loops “folded Clover leaf” 3. Amino Acid Binding site 3’ End 4. Anticodon- Determine AA Requested on mRNA 5. Energy Required- Amino Acyl-tRNA Synthetases ...
... tRNA 1. Transferring Agent to bring selected rNTP to rRNA 2. 4 Loops “folded Clover leaf” 3. Amino Acid Binding site 3’ End 4. Anticodon- Determine AA Requested on mRNA 5. Energy Required- Amino Acyl-tRNA Synthetases ...
Some No-Nonsense Facts on
... and determines a particular community. An example is teosinte characteristic in an organism. Teosinte has been selectively bred since Genes undergo mutation when 8000BC. Teosinte has been genetically their DNA sequence changes. modified to produce more kernals of corn on a larger stalk. Teosinte is ...
... and determines a particular community. An example is teosinte characteristic in an organism. Teosinte has been selectively bred since Genes undergo mutation when 8000BC. Teosinte has been genetically their DNA sequence changes. modified to produce more kernals of corn on a larger stalk. Teosinte is ...
Dentistry college - first class Medical biology
... contrast prokaryotic cells store their DNA only in cytoplasm . ...
... contrast prokaryotic cells store their DNA only in cytoplasm . ...
Advanced Genetics Unit 2: DNA Structure and Processes Quiz Bowl
... [nucleotide] 7. Sugar molecule used to build RNA molecules. [ribose] 8. Name any double-ringed base. [A, G] 9. A “friend” told me he saw a nucleotide floating around in a cell’s nucleoplasm which was constructed from a ribose sugar AND a T base. You know he was lying to me. How do you know? [Ribose- ...
... [nucleotide] 7. Sugar molecule used to build RNA molecules. [ribose] 8. Name any double-ringed base. [A, G] 9. A “friend” told me he saw a nucleotide floating around in a cell’s nucleoplasm which was constructed from a ribose sugar AND a T base. You know he was lying to me. How do you know? [Ribose- ...
Me oh Mi!
... What do we call the process where your mother’s egg and father’s sperm combine to exchange DNA? ...
... What do we call the process where your mother’s egg and father’s sperm combine to exchange DNA? ...
Chapter_17_answers
... o each type of tRNA links a specific codon wth its corresponding amino acid o anticodon: sequence of tRNA complementary to mRNA codon o made in the nucleus during transcription o strand of 80 nucleotides folded into cloverleaf-like shape o 45 different tRNA’s the base-pairing rules relax a bit on ...
... o each type of tRNA links a specific codon wth its corresponding amino acid o anticodon: sequence of tRNA complementary to mRNA codon o made in the nucleus during transcription o strand of 80 nucleotides folded into cloverleaf-like shape o 45 different tRNA’s the base-pairing rules relax a bit on ...
sharpmass™ 50
... SHARPMASS™50 Ready-to-load DNA Ladder consists of 17 DNA fragments ranging from 50 bp to 1.5 kb. It is designed to show virtually uniform spacing over a wide fragment range. The ladder allows sizing and concentration estimate of DNA fragments on agarose gels generated by PCR or restriction digest. T ...
... SHARPMASS™50 Ready-to-load DNA Ladder consists of 17 DNA fragments ranging from 50 bp to 1.5 kb. It is designed to show virtually uniform spacing over a wide fragment range. The ladder allows sizing and concentration estimate of DNA fragments on agarose gels generated by PCR or restriction digest. T ...
2.7 quiz - Peoria Public Schools
... Explain why DNA must be replicated before mitosis and the role of helicase in DNA replication. ...
... Explain why DNA must be replicated before mitosis and the role of helicase in DNA replication. ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.