BioKnowledgy Quick Quiz on DNA replication, transcription, and
... Explain why DNA must be replicated before mitosis and the role of helicase in DNA replication. ...
... Explain why DNA must be replicated before mitosis and the role of helicase in DNA replication. ...
Molecular Genetics Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice
... Which of the following represents a similarity between RNA and DNA? a. Both are double-stranded. b. the presence of uracil c. the presence of an OH group on the 2' carbon of the sugar d. nucleotides consisting of a phosphate, sugar, and nitrogenous base e. Both are found exclusively in the nucleus. ...
... Which of the following represents a similarity between RNA and DNA? a. Both are double-stranded. b. the presence of uracil c. the presence of an OH group on the 2' carbon of the sugar d. nucleotides consisting of a phosphate, sugar, and nitrogenous base e. Both are found exclusively in the nucleus. ...
Carbon Isomers
... • Double helix – 2 polynucleotide strands connected by hydrogen bonds – Base-pairing rules • A with T • G with C ...
... • Double helix – 2 polynucleotide strands connected by hydrogen bonds – Base-pairing rules • A with T • G with C ...
Protein
... • Two new daughter cells are now separate 2 nuclear membranes form around each set of chromosomes. Nucleolus forms in each of the newly formed cells. ...
... • Two new daughter cells are now separate 2 nuclear membranes form around each set of chromosomes. Nucleolus forms in each of the newly formed cells. ...
Molecular Biology
... How do we know that DNA is the molecule that transfers info? • T.H. Morgan showed that differences in chromosomes determined fly traits ...
... How do we know that DNA is the molecule that transfers info? • T.H. Morgan showed that differences in chromosomes determined fly traits ...
FREE Sample Here
... 15. The nucleotides in a single strand of DNA are held together by which of the following bonds? A) Disulfide B) Phosphodiester C) Hydrogen D) Peptide 16. In DNA replication, the leading strand is the strand that has which conformation? A) 5 to 3 B) 3 to 5 C) Both strands are leading 17. Which o ...
... 15. The nucleotides in a single strand of DNA are held together by which of the following bonds? A) Disulfide B) Phosphodiester C) Hydrogen D) Peptide 16. In DNA replication, the leading strand is the strand that has which conformation? A) 5 to 3 B) 3 to 5 C) Both strands are leading 17. Which o ...
Chapter 8 DNA: the universal molecule of life All living things share
... Many scientists experimented & tried to work out the composition & structure of the ‘heredity’ molecule. Watson & Crick used their information to describe the current model of 2 twisted chains producing the double helix, cross linked with nitrogen bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and Thy ...
... Many scientists experimented & tried to work out the composition & structure of the ‘heredity’ molecule. Watson & Crick used their information to describe the current model of 2 twisted chains producing the double helix, cross linked with nitrogen bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and Thy ...
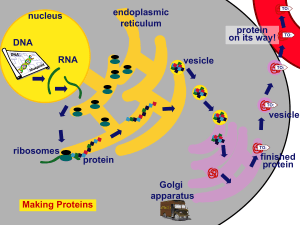
BioH From DNA to proteins
... • Promoter sequence on mRNA - signals “start” for transcribing DNA sequence into RNA sequence • ONE strand only – forming juvenile RNA • Uracil used instead of Thymine • Use Cytosine, Guanine, Adenine (same as DNA) ...
... • Promoter sequence on mRNA - signals “start” for transcribing DNA sequence into RNA sequence • ONE strand only – forming juvenile RNA • Uracil used instead of Thymine • Use Cytosine, Guanine, Adenine (same as DNA) ...
GEN2MHG – MOLECULAR AND HUMAN GENETICS DNA is made
... ▪ phosphodiester bonds form between the 5’ position of one nucleotide and the 3’ end of the next ▪ nitrogenous bases may be; - purines (2 ringed structures) -> adenine and guanine - pyrimidines (1 ringed structure) -> thymine (& uracil) and cytosine ...
... ▪ phosphodiester bonds form between the 5’ position of one nucleotide and the 3’ end of the next ▪ nitrogenous bases may be; - purines (2 ringed structures) -> adenine and guanine - pyrimidines (1 ringed structure) -> thymine (& uracil) and cytosine ...
Protein synthesis
... The sequence of the nucleotides determines a meaningful (vocabulary) code of instructions. A sequence of nucleotides in DNA are copied into a matching chain of nucleotides for messenger RNA (mRNA). a. DNA nucleotides [(A) Adenine, (G) Guanine, (C) Cytosine, (T) Thymine] b. RNA nucleotides [(A) Adeni ...
... The sequence of the nucleotides determines a meaningful (vocabulary) code of instructions. A sequence of nucleotides in DNA are copied into a matching chain of nucleotides for messenger RNA (mRNA). a. DNA nucleotides [(A) Adenine, (G) Guanine, (C) Cytosine, (T) Thymine] b. RNA nucleotides [(A) Adeni ...
HANDOUT: CH 17 pt 1 Study
... CHAPTER 17 STUDY QUESTIONS, part 1: From Gene to Protein (p. 325-344) 1) Summarize the one gene – one polypeptide hypothesis. ...
... CHAPTER 17 STUDY QUESTIONS, part 1: From Gene to Protein (p. 325-344) 1) Summarize the one gene – one polypeptide hypothesis. ...
transfer RNA
... represent “genes”. Genes are regions on chromosomes that code for specific proteins. While many parts of that code are important parts of the “recipe”, some parts are simply “filler”, and are unnecessary, so far as we understand. These unnecessary sections are called introns, and they are sequences ...
... represent “genes”. Genes are regions on chromosomes that code for specific proteins. While many parts of that code are important parts of the “recipe”, some parts are simply “filler”, and are unnecessary, so far as we understand. These unnecessary sections are called introns, and they are sequences ...
The Origins Of Life
... molecules Composed of one phosphate, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogenous base These monomers are used to build nucleic acids The acids can be used for various functions in life such as storage, transfer of vital information, and even enzymes ...
... molecules Composed of one phosphate, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogenous base These monomers are used to build nucleic acids The acids can be used for various functions in life such as storage, transfer of vital information, and even enzymes ...
ch4 reading guide
... 9. More than one type of tRNA can correspond to the same __________________ __________________________________________________________________ 10. The genetic code is degenerate because_______________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 11. A ribosome i ...
... 9. More than one type of tRNA can correspond to the same __________________ __________________________________________________________________ 10. The genetic code is degenerate because_______________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 11. A ribosome i ...
8-3 Notes with Power point
... 4. Another enzyme, called _______________________________, adds new _____________________ to the RNA Primer. It always reads ________to _________________ and synthesizes the new strand from _________ to _____________ This occurs in the direction following ________________________ opening up the “rep ...
... 4. Another enzyme, called _______________________________, adds new _____________________ to the RNA Primer. It always reads ________to _________________ and synthesizes the new strand from _________ to _____________ This occurs in the direction following ________________________ opening up the “rep ...
BioInformatics at FSU - whose job is it and why it needs
... Genes (less than 5% of all), providing the coding information. Instructions for protein synthesis, regulatory functions.. Redundancy translates to robustness!! Synonymous codons Dual strands Diploid In translation the information now encoded in RNA is deciphered (translated) into instructions for ma ...
... Genes (less than 5% of all), providing the coding information. Instructions for protein synthesis, regulatory functions.. Redundancy translates to robustness!! Synonymous codons Dual strands Diploid In translation the information now encoded in RNA is deciphered (translated) into instructions for ma ...
Protein Synthesis
... The mRNA is single stranded. The mRNA uses U instead of T. (A,U,G,C) The DNA zips back together. ...
... The mRNA is single stranded. The mRNA uses U instead of T. (A,U,G,C) The DNA zips back together. ...
Final review questions: ch 13-15 How does RNA differ from DNA
... Chapter 15 18. Polyploidy may instantly produce new types of organisms that are larger and stronger than their diploid relatives in animals. A plants. B bacteria. C fungi D ...
... Chapter 15 18. Polyploidy may instantly produce new types of organisms that are larger and stronger than their diploid relatives in animals. A plants. B bacteria. C fungi D ...
Review sheet – Chapter 10
... Understand that DNA replication occurs on both strands, with the old (parental strand) serving as a template for the new (daughter) strand being laid down (synthesized), resulting in 2 complete DNA molecules, each consisting of a double helix of a parental and daughter strand ...
... Understand that DNA replication occurs on both strands, with the old (parental strand) serving as a template for the new (daughter) strand being laid down (synthesized), resulting in 2 complete DNA molecules, each consisting of a double helix of a parental and daughter strand ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.