Lecture 5
... - Polypeptide Chain: series of amino acids linked by peptide bonds (think of box cars linked together) - Protein: one or more polypeptide chains joined and folded in a 3D configuration (folds occur due to electrical charges of amino acids) - Codon: 3 letter nucleotide sequence in messenger RNA that ...
... - Polypeptide Chain: series of amino acids linked by peptide bonds (think of box cars linked together) - Protein: one or more polypeptide chains joined and folded in a 3D configuration (folds occur due to electrical charges of amino acids) - Codon: 3 letter nucleotide sequence in messenger RNA that ...
Transcription and Translation
... REPLICATION (DNA Synthesis) • DNA Helicase partially unwinds the double helix at an area known as the replication fork. • As the two DNA strands separate and the bases are exposed, the enzyme DNA polymerase III moves into position at the point where synthesis will begin. • Primase synthesizes RNA p ...
... REPLICATION (DNA Synthesis) • DNA Helicase partially unwinds the double helix at an area known as the replication fork. • As the two DNA strands separate and the bases are exposed, the enzyme DNA polymerase III moves into position at the point where synthesis will begin. • Primase synthesizes RNA p ...
DNA-RNA Review
... replication Using DNA code to transcription make an RNA = ___________________ Using an RNA message ...
... replication Using DNA code to transcription make an RNA = ___________________ Using an RNA message ...
Compounds of Life
... • The most major class of proteins • Catalysts: speed up the rate of a chemical reaction – Not changed by the reaction – Lower the “start-up” energy required for reactions – Substrates bind to active sites that are extremely specific! ...
... • The most major class of proteins • Catalysts: speed up the rate of a chemical reaction – Not changed by the reaction – Lower the “start-up” energy required for reactions – Substrates bind to active sites that are extremely specific! ...
DNA Replication
... that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material” ~Watson and Crick ...
... that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material” ~Watson and Crick ...
Transcription/Translation foldable
... Fold your paper so the two ends meet in the middle. Label Transcription on one side and Translation on the other. ...
... Fold your paper so the two ends meet in the middle. Label Transcription on one side and Translation on the other. ...
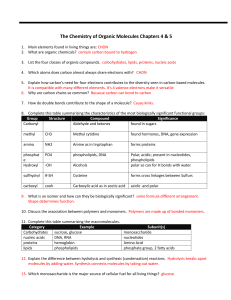
04-05 Biochem review sheet answers ws
... 26. Discuss the effect of prions, both chemically and systematically. causes proteins to fold incorrectly. Causes diseases like Mad Cow. 27. Explain how DNA and RNA work together to build a protein. 28. What is ATP used for? Energy storage 29. Label this diagram showing the structure of a nucleotide ...
... 26. Discuss the effect of prions, both chemically and systematically. causes proteins to fold incorrectly. Causes diseases like Mad Cow. 27. Explain how DNA and RNA work together to build a protein. 28. What is ATP used for? Energy storage 29. Label this diagram showing the structure of a nucleotide ...
Nucleotides Base Pair By Hydrogen bonds
... • Two general types of nitrogenous bases Purines (two rings) Pyrimidines (one ring): Adenine (A) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) Thymine (T) Uracil (U) – only RNA ...
... • Two general types of nitrogenous bases Purines (two rings) Pyrimidines (one ring): Adenine (A) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) Thymine (T) Uracil (U) – only RNA ...
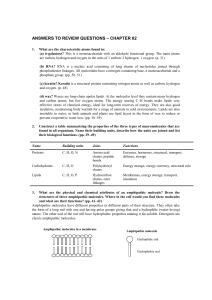
ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS – CHAPTER 02
... are carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in the ratio of 1 carbon: 2 hydrogen: 1 oxygen. (p. 31) (b) RNA? RNA is a nucleic acid consisting of long chains of nucleotides joined through phosphodiester linkages. All nucleotides have a nitrogen-containing base, a monosaccharide and a phosphate group. (pp. 50–51) ...
... are carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in the ratio of 1 carbon: 2 hydrogen: 1 oxygen. (p. 31) (b) RNA? RNA is a nucleic acid consisting of long chains of nucleotides joined through phosphodiester linkages. All nucleotides have a nitrogen-containing base, a monosaccharide and a phosphate group. (pp. 50–51) ...
Name - BIOLOGY
... 9. What enzyme uncoils/unwinds/unzips DNA when it is replicated? DNA Helicase ...
... 9. What enzyme uncoils/unwinds/unzips DNA when it is replicated? DNA Helicase ...
Study Guide - wlhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... Study / Review Questions: Answer / outline on the back of this page or on a separate piece of paper. 1) Create a chart or outline in which you summarize the information we have learned for each of the four classes of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids). Make sure to in ...
... Study / Review Questions: Answer / outline on the back of this page or on a separate piece of paper. 1) Create a chart or outline in which you summarize the information we have learned for each of the four classes of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids). Make sure to in ...
Discovery of DNA structure
... DNA is a polymer its structural unit is the nucleotide composed of nitrogenous base a pentose sugar, a phosphate group ...
... DNA is a polymer its structural unit is the nucleotide composed of nitrogenous base a pentose sugar, a phosphate group ...
DNA Notes - Firelands Local Schools
... SYNTHESIS. – DNA IS A SELF-REPLICATING MOLECULE WHICH GETS PASSED ON FROM ONE GENERATION TO THE NEXT. ...
... SYNTHESIS. – DNA IS A SELF-REPLICATING MOLECULE WHICH GETS PASSED ON FROM ONE GENERATION TO THE NEXT. ...
Protein Synthesis - NCEA Level 2 Biology
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) • This is a clover-leaf shaped molecule. • It has a 3 base anticodon code, (complementary to the codon on mRNA) at one end, and at the other end there is a particular amino acid. • The function of tRNA is to pick up amino acids specific to the anticodon and carry them to the rib ...
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) • This is a clover-leaf shaped molecule. • It has a 3 base anticodon code, (complementary to the codon on mRNA) at one end, and at the other end there is a particular amino acid. • The function of tRNA is to pick up amino acids specific to the anticodon and carry them to the rib ...
FinalExamStudyGuideSemester1
... 3) What are gametes? What type of cellular division makes them? 4) What type of cellular division are sperm and eggs made from? 5) Which organ is responsible for making sperm in men? 6) Which organ is responsible for making and storing eggs in women? 7) What are the possible gametes from the followi ...
... 3) What are gametes? What type of cellular division makes them? 4) What type of cellular division are sperm and eggs made from? 5) Which organ is responsible for making sperm in men? 6) Which organ is responsible for making and storing eggs in women? 7) What are the possible gametes from the followi ...
Compounds of Life Chart
... Used as storage in seeds and eggs Used for transport (like hemoglobin transports oxygen in our blood) ...
... Used as storage in seeds and eggs Used for transport (like hemoglobin transports oxygen in our blood) ...
PROTIEN SYNTHESIS
... The form of RNA that mediates the transfer of genetic information from the cell nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm, where it serves as a template for protein synthesis. It is synthesized from a DNA template during the process of transcription. transfer RNA One of a class of RNA molecules that tra ...
... The form of RNA that mediates the transfer of genetic information from the cell nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm, where it serves as a template for protein synthesis. It is synthesized from a DNA template during the process of transcription. transfer RNA One of a class of RNA molecules that tra ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... a strand of DNA (CGA-TTC-GCT-AAT-ATC) represents a gene that determines a particular trait through a protein. ...
... a strand of DNA (CGA-TTC-GCT-AAT-ATC) represents a gene that determines a particular trait through a protein. ...
Sentence Synthesis Instructions RNA polymerase Instructions, cont
... Modeling Transcription and Translation ...
... Modeling Transcription and Translation ...
BIOLOGY Unit 1 Notes: Characteristics of Life & Biomolecules
... – Cells are the most basic unit of life. – Existing cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
... – Cells are the most basic unit of life. – Existing cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.