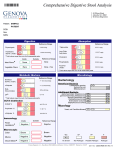
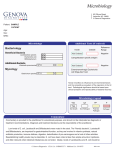
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide - wlhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
Survey
Document related concepts
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
WLHS / AP Bio / Monson Name STUDY GUIDE: Unit 2 - Biochemistry (Ch 5 & 8) UNIT 2 VOCABULARY: Macromolecules, Ch 5 Metabolism & Enzymes, Ch 8: monomer / polymer dehydration synthesis (condensation) polypeptides amino acids metabolism catabolic vs. anabolic pathway hydrolysis carbohydrates mono-/ di- /polysaccharides glycosidic linkages peptide bonds 4 levels of protein structure alpha helix beta pleated sheet kinetic energy / potential energy endergonic / exergonic reactions activation energy catalyst / enzyme starch / glycogen / cellulose / chitin lipids fats / glycerol / fatty acids ester linkages denaturation nucleic acids DNA / RNA nucleotides substrate / active site induced fit cofactors / coenzymes competitive inhibition saturated vs. unsaturated phospholipids steroids / cholesterol phosphodiester bond purines / pyrimidines noncompetitive inhibition cooperativity allosteric regulation / allosteric site feedback inhibition Study / Review Questions: Answer / outline on the back of this page or on a separate piece of paper. 1) Create a chart or outline in which you summarize the information we have learned for each of the four classes of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids). Make sure to include: -the names of the monomers (subunits) -the name of the type of bond or linkage group connecting the monomers -the elements present -the primary function(s) -at least two specific examples of each (and their functions) 2) a) Sketch and label the general structure of an amino acid. b) Summarize / explain the 4 levels of protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. c) Explain how the primary structure of a protein is determined. d) Describe 2 examples of secondary structure. e) Describe 4 types of interactions that contribute to the tertiary structure of a protein. 3) a) List 3 ways in which DNA differs from RNA. b) Sketch and label the general structure of a nucleotide. c) Explain how these monomers (nucleotides) are linked to form nucleic acids. d) How do purines differ from pyrimidines? e) List the full names for the 2 bases that are purines and the 3 bases that are pyrimidines. f) Describe the 3-dimensional structure of DNA. 4) a) Sketch and label the general structure of a fatty acid. b) Distinguish between saturated and unsaturated fats. c) Describe the building blocks, structure and importance of fats, phospholipids and steroids. 5) Explain the difference between the following polysaccharides: starch, cellulose, glycogen, chitin. 6) Describe three differences between hydrolysis and dehydration synthesis (condensation). 7) a) Explain the significance of an enzyme’s active site. b) Summarize at least two environmental factors affecting enzyme function. c) Distinguish between competitive and noncompetitive inhibition. d) Explain how feedback inhibition helps to regulate some metabolic pathways.