Bio-Macromolecules Worksheet
... can form single bonds with another atom and also bond to other carbon molecules forming double and triple bonds. This allows carbon based molecules to form single and double rings, chains, and branching chains. Most organic compounds are built primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen but in differe ...
... can form single bonds with another atom and also bond to other carbon molecules forming double and triple bonds. This allows carbon based molecules to form single and double rings, chains, and branching chains. Most organic compounds are built primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen but in differe ...
Name - Lyndhurst School District
... Watson and Crick (1953) Discovered structure of DNA. Rosalind Franklin: Watson and Crick used her photograph to create the double helix but never gave her credit. She died just before they won the Nobel Prize. Each unit of DNA called a nucleotide of DNA consists of 3 parts. Phosphate backb ...
... Watson and Crick (1953) Discovered structure of DNA. Rosalind Franklin: Watson and Crick used her photograph to create the double helix but never gave her credit. She died just before they won the Nobel Prize. Each unit of DNA called a nucleotide of DNA consists of 3 parts. Phosphate backb ...
DNA plasmid minipreps - How it works: Solution I: 50 mM glucose
... - Lysozyme degrades the rigid mucopeptide layer of the cell wall. RNase A or RNase T1 may be added to reduce the amount of RNA copurified with the plasmid DNA. Solution II - NaOH/SDS lyses the spheroplasts and partially denatures nucleases. At a pH of 12.0-12.5, linear plasmid DNA and chromosomal DN ...
... - Lysozyme degrades the rigid mucopeptide layer of the cell wall. RNase A or RNase T1 may be added to reduce the amount of RNA copurified with the plasmid DNA. Solution II - NaOH/SDS lyses the spheroplasts and partially denatures nucleases. At a pH of 12.0-12.5, linear plasmid DNA and chromosomal DN ...
Reading Assignments
... carbohydrate, Lipid, Nucleic Acid, Protein, Covalent bond, Hydrogen bond, monosaccaride, fatty acid, glycerol, amino acid, nucleic acid How can we utilize DNA for identification, enhancement and treatment? DNA, nucleotide, purine, pyrimidine, adenine, cytosine, thymine, guanine, backbone, deoxyribos ...
... carbohydrate, Lipid, Nucleic Acid, Protein, Covalent bond, Hydrogen bond, monosaccaride, fatty acid, glycerol, amino acid, nucleic acid How can we utilize DNA for identification, enhancement and treatment? DNA, nucleotide, purine, pyrimidine, adenine, cytosine, thymine, guanine, backbone, deoxyribos ...
Biology EOC Words for Pages 64-80, Teacher Key Codominance
... DNA bases by removing a piece of DNA. Small deletions may remove one or a few base pairs within a gene, while larger deletions can remove an entire gene or several neighboring genes. The deleted DNA may alter the function of the resulting protein(s). Point Mutation- a single nucleotide changes. Inse ...
... DNA bases by removing a piece of DNA. Small deletions may remove one or a few base pairs within a gene, while larger deletions can remove an entire gene or several neighboring genes. The deleted DNA may alter the function of the resulting protein(s). Point Mutation- a single nucleotide changes. Inse ...
Document
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) is the blueprint for construction of a protein. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is the construction site where the protein is made. Transfer RNA (tRNA) is the truck delivering the proper amino acid to the site at the right time. ...
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) is the blueprint for construction of a protein. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is the construction site where the protein is made. Transfer RNA (tRNA) is the truck delivering the proper amino acid to the site at the right time. ...
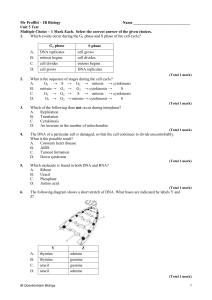
Mr Proffitt – IB Biology Name Unit 3 Test Multiple Choice – 1 Mark
... A sequence of nucleotides on rRNA that corresponds to an amino acid B. A sequence of nucleotides on mRNA that corresponds to an amino acid C. A sequence of nucleotides on tRNA that corresponds to an amino acid D. A sequence of nucleotides on DNA that corresponds to an amino acid (Total 1 mark) ...
... A sequence of nucleotides on rRNA that corresponds to an amino acid B. A sequence of nucleotides on mRNA that corresponds to an amino acid C. A sequence of nucleotides on tRNA that corresponds to an amino acid D. A sequence of nucleotides on DNA that corresponds to an amino acid (Total 1 mark) ...
CH 14 notes - Lincoln Park High School
... Statement of Inquiry: The foundation of living systems can be understood through modeling the related forms and transformations. CH 10: Molecular Biology of the Gene (p.183) Date: DNA Structure (p.186) - knowing structure helps to understand function! Deoxyribonucleic Acid is made of nucleotides ( ...
... Statement of Inquiry: The foundation of living systems can be understood through modeling the related forms and transformations. CH 10: Molecular Biology of the Gene (p.183) Date: DNA Structure (p.186) - knowing structure helps to understand function! Deoxyribonucleic Acid is made of nucleotides ( ...
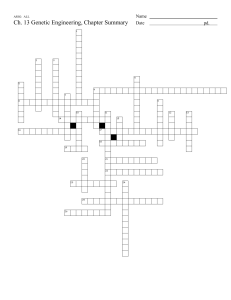
Ch. 13 Genetic Engineering, Chapter Summary Date
... 6. a techniques scientist used to make many copies of a certain gene. 8. produced by combining DNA from different species or different sources. 14. a technique that breed specific animals and plants with desired traits. This technique takes advantage of naturally occurring genetic variation in a gro ...
... 6. a techniques scientist used to make many copies of a certain gene. 8. produced by combining DNA from different species or different sources. 14. a technique that breed specific animals and plants with desired traits. This technique takes advantage of naturally occurring genetic variation in a gro ...
11.2 Reading Guide - Lewis Center for Educational Research
... be used to form ______________ when a strand of mRNA is translated at a ribosome. Since this chart outlines how ______________ on mRNA can be “translated” into a(an) ______________ sequence for every living organism, the genetic code is said to be ______________ and is evidence either for a common _ ...
... be used to form ______________ when a strand of mRNA is translated at a ribosome. Since this chart outlines how ______________ on mRNA can be “translated” into a(an) ______________ sequence for every living organism, the genetic code is said to be ______________ and is evidence either for a common _ ...
No Slide Title
... deoxyribose / ribose sugar Purine : Adenine / Guanine Pyrimidine : Cytosine / Thymine / Uracil ...
... deoxyribose / ribose sugar Purine : Adenine / Guanine Pyrimidine : Cytosine / Thymine / Uracil ...
Introduction to Molecular Genetics
... DNA Replication DNA opens at an Ori ( origin of replication) Combination of many enzymes coordinate the replicative process Template strand used to make the copy DNA polymerases read the template and match the complementary base ...
... DNA Replication DNA opens at an Ori ( origin of replication) Combination of many enzymes coordinate the replicative process Template strand used to make the copy DNA polymerases read the template and match the complementary base ...
Aim # 29: NYS Lab Relationships and
... Use low power on the microscope to examine cross sections of the stems. Look for a scattered arrangement of bundles or a circular arrangement of bundles. d. Paper Chromatography to Separate Plant Pigments Using clean, separate pipettes for each sample, transfer two drops of each plant extract to ...
... Use low power on the microscope to examine cross sections of the stems. Look for a scattered arrangement of bundles or a circular arrangement of bundles. d. Paper Chromatography to Separate Plant Pigments Using clean, separate pipettes for each sample, transfer two drops of each plant extract to ...
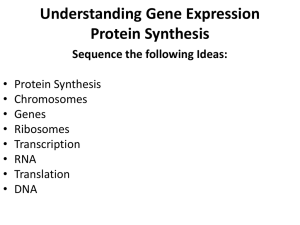
Protein Synthesis Quick Questions
... separates the 2 strands • RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template for assembling an mRNA complementary strand • This creates a strand of mRNA which can carry the genetic code out of the nucleus to complete the second step of protein synthesis. ...
... separates the 2 strands • RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template for assembling an mRNA complementary strand • This creates a strand of mRNA which can carry the genetic code out of the nucleus to complete the second step of protein synthesis. ...
Name: Protein Synthesis PRICE DNA DNA contains ______
... • rRNA is a single strand 100 to 3000 nucleotides long • Globular in ________ • Made inside the ________ of a cell • Associates with ___________ to form ribosomes • Site of _________ Synthesis The Genetic Code • A codon designates an ________ acid • An amino acid may have more than ____ codon • Ther ...
... • rRNA is a single strand 100 to 3000 nucleotides long • Globular in ________ • Made inside the ________ of a cell • Associates with ___________ to form ribosomes • Site of _________ Synthesis The Genetic Code • A codon designates an ________ acid • An amino acid may have more than ____ codon • Ther ...
Genetics Quiz Study Guide
... Amino Acid. An organic molecule made of C, H, O, and N that serves as a building block for proteins and other molecules in living organisms. Chromosome. An organized structure of DNA and protein found in the nucleus of a cell. Chromosomes store genetic information for the cell. Co-dominant. Conditio ...
... Amino Acid. An organic molecule made of C, H, O, and N that serves as a building block for proteins and other molecules in living organisms. Chromosome. An organized structure of DNA and protein found in the nucleus of a cell. Chromosomes store genetic information for the cell. Co-dominant. Conditio ...
Sequences vs Viruses: Producer vs Product, Cause and
... By the 19th century, biochemists had isolated deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) from cell nuclei. It was realized only later that nucleotides were of two types – DNA containing deoxyribose and RNA containing ribose. In 1910, Thomas Hunt Morgan showed that genes resided on chromo ...
... By the 19th century, biochemists had isolated deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) from cell nuclei. It was realized only later that nucleotides were of two types – DNA containing deoxyribose and RNA containing ribose. In 1910, Thomas Hunt Morgan showed that genes resided on chromo ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.