DNA Structure and Sequencing - SP14
... the 3' carbon of the sugar of the next nucleotide, thereby forming a 5'-3' phosphodiester bond. Base pairing takes place between a purine and pyrimidine; namely, A pairs with T and G pairs with C. Adenine and thymine are complementary base pairs, and cytosine and guanine are also complementary base ...
... the 3' carbon of the sugar of the next nucleotide, thereby forming a 5'-3' phosphodiester bond. Base pairing takes place between a purine and pyrimidine; namely, A pairs with T and G pairs with C. Adenine and thymine are complementary base pairs, and cytosine and guanine are also complementary base ...
Discovery of DNA
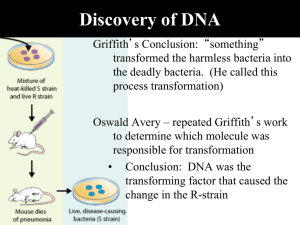
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
1 - marric.us
... 30. What is the function of each of the following organelles? a. Cell membrane (pg 187) d. Ribosomes (pg 193) b. Endoplasmic Reticulum (pg 194) e. Chloroplasts (pg 197) c. Golgi apparatus (pg 195) 31. What are the differences between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell? (pg 185-186) 32. Make a sketch ...
... 30. What is the function of each of the following organelles? a. Cell membrane (pg 187) d. Ribosomes (pg 193) b. Endoplasmic Reticulum (pg 194) e. Chloroplasts (pg 197) c. Golgi apparatus (pg 195) 31. What are the differences between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell? (pg 185-186) 32. Make a sketch ...
Lab/Activity: Prot
... Proteins are made in the cytoplasm by ribosomes. Since DNA cannot leave the nucleus, the information from DNA must be transmitted from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. During transcription, each gene on the DNA is read and codes directly for a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. The mRNA is made by matching ...
... Proteins are made in the cytoplasm by ribosomes. Since DNA cannot leave the nucleus, the information from DNA must be transmitted from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. During transcription, each gene on the DNA is read and codes directly for a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. The mRNA is made by matching ...
Nucleic acid chemistry - Beilstein
... strategies can allow for the desired oligonucleotides modification. This becomes an even more important issue for functionalities, probes or biologically relevant molecules that are incompatible with routine phosphoramidite chemistry. Although nucleic acid chemistry appears to be a mature part of or ...
... strategies can allow for the desired oligonucleotides modification. This becomes an even more important issue for functionalities, probes or biologically relevant molecules that are incompatible with routine phosphoramidite chemistry. Although nucleic acid chemistry appears to be a mature part of or ...
Organic Molecules Worksheet: Review
... “R” groups are very small, others are large, and others form chains and rings. The sequence and shapes of the “R” groups control the shape and function of the protein. 27. How many different amino acids are there? ___________________________________ 28. What part of the amino acid varies from one am ...
... “R” groups are very small, others are large, and others form chains and rings. The sequence and shapes of the “R” groups control the shape and function of the protein. 27. How many different amino acids are there? ___________________________________ 28. What part of the amino acid varies from one am ...
DNA - Moodle
... 4. Living organisms use DNA as their genetic material. Explain how DNA is replicated within the cells of living organisms 8 marks • helix is unwound • two strands are separated • helicase (is the enzyme that unwinds the helix separating the two strands) • by breaking hydrogen bonds between bases • ...
... 4. Living organisms use DNA as their genetic material. Explain how DNA is replicated within the cells of living organisms 8 marks • helix is unwound • two strands are separated • helicase (is the enzyme that unwinds the helix separating the two strands) • by breaking hydrogen bonds between bases • ...
Defined - cloudfront.net
... 1) How are proteins affected if the DNA code is mutated? Example: ATTCGAGG is mutated to ATTCGTGG 2) What is the difference between a point mutation and frame shift mutations? 3) When are mutations passed on to future generations? 4) What are germs cells? 5) What is a mutagen and how do they cause ...
... 1) How are proteins affected if the DNA code is mutated? Example: ATTCGAGG is mutated to ATTCGTGG 2) What is the difference between a point mutation and frame shift mutations? 3) When are mutations passed on to future generations? 4) What are germs cells? 5) What is a mutagen and how do they cause ...
Document
... The genome of any organism contains all the information for making that organism. The information is encoded in various types of genes that are transcribed into 4 types of RNA: mRNA - Messenger RNA: Encodes amino acid sequence of a polypeptide tRNA - Transfer RNA: Brings amino acids to ribosomes du ...
... The genome of any organism contains all the information for making that organism. The information is encoded in various types of genes that are transcribed into 4 types of RNA: mRNA - Messenger RNA: Encodes amino acid sequence of a polypeptide tRNA - Transfer RNA: Brings amino acids to ribosomes du ...
You Asked for it…..
... Remember, genes are made of DNA and are in the nucleus Genes (DNA) contain the instruction for making a protein In transcription, DNA is used to make mRNA in the nucleus mRNA then leaves the nucleus and goes to the ribosome In translation, tRNA then brings amino acids in the proper order to make the ...
... Remember, genes are made of DNA and are in the nucleus Genes (DNA) contain the instruction for making a protein In transcription, DNA is used to make mRNA in the nucleus mRNA then leaves the nucleus and goes to the ribosome In translation, tRNA then brings amino acids in the proper order to make the ...
Evidence for Evolution Review
... 12. Generally, the deeper layers of rock contain younger or older fossils 13. The length of time required for half of a radioactive isotope to decay is called its half-life. The half life of C-14 is 5,730 old. If a fossil was found with 1/8 of its original C-14, how old would it be? 14. Could C-14 d ...
... 12. Generally, the deeper layers of rock contain younger or older fossils 13. The length of time required for half of a radioactive isotope to decay is called its half-life. The half life of C-14 is 5,730 old. If a fossil was found with 1/8 of its original C-14, how old would it be? 14. Could C-14 d ...
CH2- pt2 student
... Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) = energy currency of the cells. ◦ Cells need ATP to fuel any work that they do. ATP is an RNA nucleotide containing the nitrogenous base adenine with two additional phosphate groups attached. The bonds between the phosphate groups are called high-energy bonds. ◦ When bon ...
... Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) = energy currency of the cells. ◦ Cells need ATP to fuel any work that they do. ATP is an RNA nucleotide containing the nitrogenous base adenine with two additional phosphate groups attached. The bonds between the phosphate groups are called high-energy bonds. ◦ When bon ...
Protein Synthesis - Los Gatos High School
... Transcription Writing of DNA Message to mRNA • In the nucleus of the cell • Information from DNA is transferred to mRNA. • DNA uncoils and unzips (with the help of more ...
... Transcription Writing of DNA Message to mRNA • In the nucleus of the cell • Information from DNA is transferred to mRNA. • DNA uncoils and unzips (with the help of more ...
Biochemistry Notes
... Most enzymes have an optimal pH of 7. Some enzymes function more effectively in acidic or basic conditions. ...
... Most enzymes have an optimal pH of 7. Some enzymes function more effectively in acidic or basic conditions. ...
DNA - Wiley
... X-ray crystallographic data showed the bond lengths and angles of purine and pyrimidine bases ...
... X-ray crystallographic data showed the bond lengths and angles of purine and pyrimidine bases ...
word - marric.us
... Positions Available in the genetics industry. Hundreds of entry-level openings for tireless workers. No previous experience necessary. Must be able to transcribe code in a nuclear environment. Accuracy and Speed vital for this job in the field of translation. Applicants must demonstrate skills in tr ...
... Positions Available in the genetics industry. Hundreds of entry-level openings for tireless workers. No previous experience necessary. Must be able to transcribe code in a nuclear environment. Accuracy and Speed vital for this job in the field of translation. Applicants must demonstrate skills in tr ...
Protein synthesis
... 12. The second step is called _______________________________ and links _____________________________________ together to form a chain, which folds into a 3D structure to form a ______________________. Be sure to click through Transcription and Translation, too, not just the overview. What three reg ...
... 12. The second step is called _______________________________ and links _____________________________________ together to form a chain, which folds into a 3D structure to form a ______________________. Be sure to click through Transcription and Translation, too, not just the overview. What three reg ...
Macromolecules
... • 3 carbon backbone attached to three fatty acids – Saturated – all three fatty acids chains have maximum number of Hydrogen atoms • Butter – Unsaturated – contain less than the maximum number of hydrogen atoms in one or more of its fatty acid chains • fruits ...
... • 3 carbon backbone attached to three fatty acids – Saturated – all three fatty acids chains have maximum number of Hydrogen atoms • Butter – Unsaturated – contain less than the maximum number of hydrogen atoms in one or more of its fatty acid chains • fruits ...
Extra Credit DNA Study Guide
... 6. Insert the genetic marker and the gene into the plasmid DNA. 54. What is the process illustrated on page 304-305? ...
... 6. Insert the genetic marker and the gene into the plasmid DNA. 54. What is the process illustrated on page 304-305? ...
Title of Assignment:
... 3. A multicellular organism develops from a single zygote, and its phenotype depends on its genotype, which is established at fertilization. 4. Genes are a set of instructions encoded in the DNA sequence of each organism that specify the sequence of amino acids in proteins characteristic of that org ...
... 3. A multicellular organism develops from a single zygote, and its phenotype depends on its genotype, which is established at fertilization. 4. Genes are a set of instructions encoded in the DNA sequence of each organism that specify the sequence of amino acids in proteins characteristic of that org ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.